

JSONP. JSONP or "JSON with padding" is a communication technique used in JavaScript programs running in web browsers to request data from a server in a different domain, something prohibited by typical web browsers because of the same-origin policy.
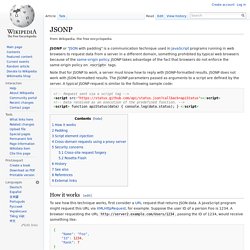
JSONP takes advantage of the fact that browsers do not enforce the same-origin policy on <script> tags. Note that for JSONP to work, a server must know how to reply with JSONP-formatted results. JSONP does not work with JSON-formatted results. The JSONP parameters passed as arguments to a script are defined by the server. A typical JSONP request is similar to the following sample code: Shared nothing architecture.
A shared nothing architecture (SN) is a distributed computing architecture in which each node is independent and self-sufficient, and there is no single point of contention across the system.
More specifically, none of the nodes share memory or disk storage. Apache Software Foundation Cassandra Reviews and Ratings - NoSQL Databases. C10k problem. Hadoop Download. Future of big data using Apache Hadoop.
My applications. REST API Rate Limiting in v1.1. Per User or Per Application Rate limiting in version 1.1 of the API is primarily considered on a per-user basis — or more accurately described, per access token in your control.
If a method allows for 15 requests per rate limit window, then it allows you to make 15 requests per window per leveraged access token. This is similar to the way API v1 had per-user/per-access token limits when leveraging OAuth. When using application-only authentication, rate limits are determined globally for the entire application. If a method allows for 15 requests per rate limit window, then it allows you to make 15 requests per window — on behalf of your application. 15 Minute Windows Rate limits in version 1.1 of the API are divided into 15 minute intervals, which is a change from the 60 minute blocks in version 1.0. Search Search will be rate limited at 180 queries per 15 minute window for the time being, but we may adjust that over time. HTTP Headers and Response Codes GET and POST Request Limits. REST API v1.1 Limits per window by resource.
OAuth. Updated on Mon, 2013-03-11 12:22 Send secure authorized requests to the Twitter API Twitter uses OAuth to provide authorized access to its API.

Features Secure - Users are not required to share their passwords with 3rd party applications, increasing account security. Standard - A wealth of client libraries and example code are compatible with Twitter's OAuth implementation. API v1.1's Authentication Model There are two forms of authentication in the new model, both still leveraging OAuth 1.0A.
Community – Supported Platforms. Cassandra is completely free to download, use and share.
DataStax Community is a free packaged distribution of Apache Cassandra™ made available by DataStax. There’s no faster, easier way to get started with the latest development release of Apache Cassandra than to download, install, and use DataStax Community. If you’re new to Cassandra, take advantage of the resources available for taking advantage of the NoSQL platform. This is What a Tweet Looks Like. Think a tweet is just 140 characters of text?
Think again. To developers building tools on top of the Twitter platform, they know tweets contain far more information than just whatever brief, passing thought you felt the urge to share with your friends via the microblogging network. Community. Apache Mahout: Scalable machine learning and data mining.
Kaggle: making data science a sport. NoSQL. MySQL vs. NoSQL and NewSQL: 2011-2015. Long Format Report Information Management 22 May, 2012 ~ Executive Summary MySQL was once the default database for new Web applications.
Now it faces a competitive challenge from alternative database technologies and support providers. The MySQL ecosystem is arguably more healthy and vibrant than ever, with a strong vendor committed to the core product, and many alternative and complementary products and services on offer to maintain the competitive pressure on Oracle. This report examines the current state of the MySQL ecosystem, assessing Oracle's ownership of the open source database, and exploring in greater detail the competitive dynamic between NoSQL, NewSQL and MySQL. Not a Subscriber? For more details about this report please fill out the form below, or contact our sales staff: By email at sales@the451group.com, or by phone at (212) 505-3030 in the US. 451 Research is an independent technology industry analyst company focused on the business of enterprise IT innovation.
General Parallel File System. IBM General Parallel File System (GPFS) The Fast, Simple, Scalable and Complete Storage Solution for Today’s Data Intensive Enterprise IBM’s General Parallel File System (GPFS) is a proven, scalable, high-performance data and file management solution that’s being used extensively across multiple industries worldwide.
GPFS provides simplified data management and integrated information lifecycle tools capable of managing petabytes of data and billions of files, in order to arrest the growing cost of managing ever growing amounts of data. The Challenge Today’s never ending data growth is challenging traditional storage and data management solutions. The Solution. General Parallel File System. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Le General Parallel File System (GPFS) est un système de fichiers conçu pour adresser de façon unique des volumes de données dépassant le pétaoctet et répartis sur un nombre de supports physiques pouvant dépasser le millier. Conçu par IBM qui le rend public en 1998, GPFS est disponible pour des clusters d'ordinateurs fonctionnant sous AIX, Linux et Windows Server 2003. Il a été testé en 2006 sur des débits de 102 gigaoctets par seconde. Il a aussi permis, en juillet 2011, de battre un record : recenser 10 milliards de fichiers sur un système de stockage en 43 minutes.
Big Data.