

Ocean Biome Facts. Marine Biomes. The marine regions are divided between coral reefs, estuaries, and oceans. Oceans represent the largest and most diverse of the ecosystems; salt water evaporates and turns to rain which falls on the land regions, while most of the oxygen in our atmosphere is generated by algae. Algae is also responsible for the absorption of large amounts of carbon dioxide from our atmosphere. The ocean connect to the land via what is called the inter-tidal zone. Because of rising and falling tides, coastal areas are constantly changing, with various animals and marine plants living at the bottom, and on the seashore. Rocky coastal areas are host to fewer species due to the fact that only the highest of tides will reach the top of the cliffs. In the warm shallow waters which line the continents and surrounding islands lie barriers called coral reefs. Climate and Weather - Marine Biome.
Biomes of the World. Oceans cover 71 percent of the earth’s surface and contain 99 percent of the habitable space on the planet.

The sea is not a uniform water world but a collection of highly variable habitats that change with distance from land, distance from the Equator, and depth below the surface. The biome concept is difficult to apply to this vast region of the planet and perhaps not appropriate at all. On land, the biomes are defined on the basis of dominant vegetation, while the plant life of the oceans consists mainly of algae, most of which are microscopic and provide no structural element to the environment. Marine biologists and oceanographers have attempted to formulate various schemes for delineating biomes in the world’s oceans, but to date no consensus has been reached. One of the most common and indeed conventional ways of categorizing marine environments is to identify three main types: coastal, continental shelf, and deep sea, a classification that is used here.
The Five Oceans 1. 2. 3. Marine 3. Science for Kids: Marine or Ocean Biome. There are two major aquatic or water biomes, the marine biome and the freshwater biome.
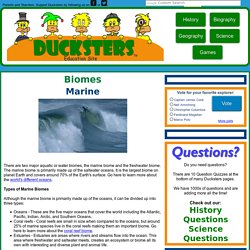
The marine biome is primarily made up of the saltwater oceans. It is the largest biome on planet Earth and covers around 70% of the Earth's surface. Go here to learn more about the world's different oceans. The marine biome. Online exhibits : The world's biomes The marine biome Marine regions cover about three-fourths of the Earth's surface and include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries.

Marine algae supply much of the world's oxygen supply and take in a huge amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide. The evaporation of the seawater provides rainwater for the land. Oceans The largest of all the ecosystems, oceans are very large bodies of water that dominate the Earth's surface. The intertidal zone is where the ocean meets the land — sometimes it is submerged and at other times exposed, as waves and tides come in and out. The pelagic zone includes those waters further from the land, basically the open ocean. The benthic zone is the area below the pelagic zone, but does not include the very deepest parts of the ocean (see abyssal zone below).
The deep ocean is the abyssal zone. Coral reefs Coral reefs are widely distributed in warm shallow waters. KDE Santa Barbara. Location | Weather | Plants | Animals | People | Links LOCATION: The marine biome is the biggest biome in the world!

It covers about 70% of the earth. It includes five main oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern, as well as many smaller Gulfs and Bays. Marine regions are usually very salty! There is about one cup of salt per gallon of water in the ocean. The ocean is divided up into three vertical zones. WEATHER: The marine biome has a big influence on our terrestrial climate! The constant motion of the ocean results in currents and waves that may either be warm or cold depending on the weather and temperature of that area. PLANTS: Over 1 million species of plants and animals have been discovered in the oceans, and scientists say there may be as many as 9 million species we haven't found yet. Through photosynthesis, marine plants and algae provide much of the worlds oxygen supply and take in huge amounts of carbon dioxide.