

What's It Like Where You Live? Garst Wildlife Photos. Grasslands are found on every continent, although they are named because of their dominant vegetation of grasses, bushes and scattered trees are also part of grassland habitats.

There are a variety of other names for the grassland, which can be distinguished by continent in which they are found. In North America grasslands are also termed "plains" or "prairies;" whereas in Asia they are called "steppes;" South America called "pampas," "llanos," or cerrados;" in Africa called "savannas" or "velds;" and in Australia termed "rangelands. " Most grasslands receive heavy rains, but then experience long periods with little to no rain. Grasslands, unlike many other biomes are very successful because the root structure of grasses is able to attach strongly to the soil, even during long periods of drought. They are also wind pollinated rather than being dependent upon insects as many plants need.
Blue Planet Biomes - World Biomes. What is a Biome?
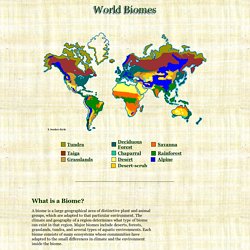
A biome is a large geographical area of distinctive plant and animal groups, which are adapted to that particular environment. The climate and geography of a region determines what type of biome can exist in that region. Major biomes include deserts, forests, grasslands, tundra, and several types of aquatic environments. Each biome consists of many ecosystems whose communities have adapted to the small differences in climate and the environment inside the biome. All living things are closely related to their environment. The earth includes a huge variety of living things, from complex plants and animals to very simple, one-celled organisms. Facts on a Grassland Ecosystem. Grassland. Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae), however sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) families can also be found.
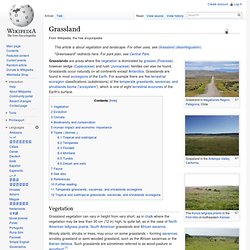
Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica. Grassland & Prairies. Grassland 3. Grassland : Mission: Biomes. Grassland Biome Information. Grassland Climate. Grasslands. Modern agriculture does make some nods to these problems.
Crop rotation, where one crop is grown in a field one year and another crop the next, does much to combat the worst problems of pest buildup and soil nutrient exhaustion in fields. In many cases, corn is rotated with soybeans; the latter are legumes which harbor Rhizobium, an endosymbiotic bacterium which converts atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use to make proteins. In this way, planting soybeans (or alfalfa) may increase the nitrogen content of the soil and reduce the need for nitrogen-based fertilizers. In any event, agricultural systems displace natural communities; given the world's need for food to feed the human population (and we're now raising corn to convert into ethanol to fuel our cars!)
This is not due to change anytime soon. As an aside, it should be pointed out that not all of our agriculture is for food. Grasslands. The Prairie The soil in prairies is excellent for growing crops and much of the grassland in North America has been turned into farms and ranches.

The combination of high summer temperatures, strong winds and little rain makes prairies vulnerable to fire. Fire keeps trees from growing on the prairie, but grasses and other prairie plants can survive fire and even thrive! There are three types of prairies: tall grass, mixed grass and short grass. Tall Grass Prairies Tall grass prairies get the most rain, about 30 inches a year. Grasslands Biome. Grassland biomes are large, rolling terrains of grasses, flowers and herbs.

Latitude, soil and local climates for the most part determine what kinds of plants grow in a particular grassland. A grassland is a region where the average annual precipitation is great enough to support grasses, and in some areas a few trees. The precipitation is so eratic that drought and fire prevent large forests from growing. Grasses can survive fires because they grow from the bottom instead of the top. Their stems can grow again after being burned off. When the settlers of the United States moved westward, they found that the grasslands, or prairies as they called them, were more than just dry, flat areas. KDE Santa Barbara. Location | Weather | Plants | Animals | People | Links LOCATION: The name for this biome, temperate grasslands, is a great description for what it is like here.

KDE Santa Barbara. Landforms of the Grasslands Biome. When one thinks of the savanna, they tend to think of Africa as home to the typical savanna landscape.
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands - Academic Kids. The grassland biome. Online exhibits : The world's biomes The grassland biome Grasslands are characterized as lands dominated by grasses rather than large shrubs or trees.

In the Miocene and Pliocene Epochs, which spanned a period of about 25 million years, mountains rose in western North America and created a continental climate favorable to grasslands. Ancient forests declined and grasslands became widespread. Following the Pleistocene Ice Ages, grasslands expanded in range as hotter and drier climates prevailed worldwide. Savanna Savanna is grassland with scattered individual trees.
The soil of the savanna is porous, with rapid drainage of water. Savanna has both a dry and a rainy season. The Grassland Biome. Grasslands are characterized as lands dominated by grasses rather than large shrubs or trees.

In the Miocene and Pliocene Epochs, which spanned a period of about 25 million years, mountains rose in western North America and created a continental climate favorable to grasslands. Ancient forests declined and grasslands became widespread. Following the Pleistocene Ice Ages, grasslands expanded in range as hotter and drier climates prevailed worldwide.