

Gestalt psychology. Gestalt psychology or gestaltism (German: Gestalt – "shape or form") is a theory of mind of the Berlin School.
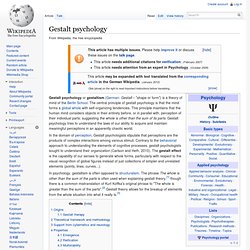
The central principle of gestalt psychology is that the mind forms a global whole with self-organizing tendencies. This principle maintains that the human mind considers objects in their entirety before, or in parallel with, perception of their individual parts; suggesting the whole is other than the sum of its parts. Gestalt psychology tries to understand the laws of our ability to acquire and maintain meaningful perceptions in an apparently chaotic world. In the domain of perception, Gestalt psychologists stipulate that perceptions are the products of complex interactions among various stimuli. Contrary to the behaviorist approach to understanding the elements of cognitive processes, gestalt psychologists sought to understand their organization (Carlson and Heth, 2010). Origins[edit] Gestalt therapy[edit] Theoretical framework and methodology[edit] Properties[edit] Reification. GESTALT Psychology. "Gestalt theory began toward the close of the 19th century in Austriaand south Germany as a protest against associationist and structural schools' piecemeal analysis of experience into atomistic elements.

" Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Khler and Kurt Koffka collaborated to found Gestalt. (Britannica) Early studies dealt with illusion, for example, the Kanizsa triangle, which we used as the background for many of our pages. As you look at the Kanisza triangle, a boundary can be seen where the perceived white triangle meets the white background; a boundary between white and white! "The Gestalt psychologists (Koffka, 1935; Khler, 1940) believed that a number of innate tendencies influence the way we see.
While many contemporary psychologists maintain that even these tendencies are the result of experience and learning, all agree that they are strong and virtually universal tendencies. " Look at the image (Gombrich 104)of "The < > must get done," What is the second word, covered by the ink blot? The Gestalt Principles. The Gestalt Principles Gestalt is a psychology term which means "unified whole".

It refers to theories of visual perception developed by German psychologists in the 1920s. These theories attempt to describe how people tend to organize visual elements into groups or unified wholes when certain principles are applied. These principles are: Similarity Similarity occurs when objects look similar to one another. The example above (containing 11 distinct objects) appears as as single unit because all of the shapes have similarity. Unity occurs because the triangular shapes at the bottom of the eagle symbol look similar to the shapes that form the sunburst.
When similarity occurs, an object can be emphasised if it is dissimilar to the others. The figure on the far right becomes a focal point because it is dissimilar to the other shapes. Continuation Continuation occurs when the eye is compelled to move through one object and continue to another object. Closure Examples Proximity Figure and Ground. Fun With Gestalt images « Pennsylvania Echoes - Pale Moon. A Gestalt Chalice When You look at the Image above which do you see first?
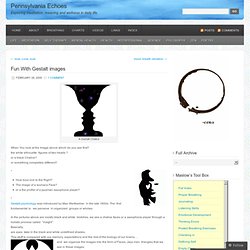
The white silhouette figures of two heads ? Or a black Chalice? Or something completely different? How bout one to the Right? *Gestalt psychology was introduced by Max Wertheimer in the late 1800s. In the pictures above are mostly black and white blotches. we see a chalice faces or a saxophone player through a holistic process called “insight”. And we organize the images into the form of Faces, Jazz men triangles that we see in these images. If you see a Triangle in the left image, you will note that the three lines of triangle are not even in the picture. A very simple way to explain this holistic process of forming the “gestalts” in these images are: This simple graph of how we perceive… becomes more complicated if as we try define “expectation”, “Biology”, and “memory” and learned behaviors separately in this graph, also if we represent conscious and subconscious with circles.
Like this: Like Loading...