

Self-Determination Theory (Deci and Ryan) Theories of Motivation. Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism: Comparing Critical Features From an Instructional Design Perspective. E-Learning Theory (Mayer, Sweller, Moreno) Online Collaborative Learning Theory (Harasim) 4.4 Online collaborative learning. 4.4.1 What is online collaborative learning? The concurrence of both constructivist approaches to learning and the development of the Internet has led to the development of a particular form of constructivist teaching, originally called computer-mediated communication (CMC), or networked learning, but which has been developed into what Harasim (2012) now calls online collaborative learning theory (OCL).
She describes OCL as follows (p. 90): OCL theory provides a model of learning in which students are encouraged and supported to work together to create knowledge: to invent, to explore ways to innovate, and, by so doing, to seek the conceptual knowledge needed to solve problems rather than recite what they think is the right answer. From the very early days of online learning, some instructors have focused heavily on the communication affordances of the Internet (see for instance, Hiltz and Turoff, 1978). 4.4.2 Core design principles of OCL 4.4.3 Community of Inquiry 4.4.8 Summary 1. 2. 3.
EffectiveUseofLearningObjectives. Activities for Metacognition. Metacognition, or thinking about one’s thinking, is key to facilitating lasting learning experiences and developing lifelong learners.
Linda Darling-Hammond and her colleagues (2003) identify two types of metacognition: reflection, or “thinking about what we know,” and self-regulation, or “managing how we go about learning. " Metacognitive activities can guide students as they: Identify what they already know Articulate what they learned Communicate their knowledge, skills, and abilities to a specific audience, such as a hiring committee Set goals and monitor their progress Evaluate and revise their own work Identify and implement effective learning strategies Transfer learning from one context to another Activities that promote metacognition should: Facilitate equal participation Ensure students do most of the talking Take place before, during, and after an experience Happen in different group configurations (individuals, pairs, small group, large group)
30 Ways to Inspire Divergent Thinking. When we stop talking about creativity and innovation in abstract terms and start thinking about how they originate, we get divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking is more than thinking outside the box; it’s thinking without the box, and imposing structure later. The goal of divergent thinking is to generate many different ideas about a topic in a short period of time. It involves breaking a topic down into its various component parts in order to gain insight about the various aspects of the topic. Divergent thinking typically occurs in a spontaneous, free-flowing manner, such that the ideas are generated in a random, unorganized fashion. Unexpected connections are often drawn. The CPS Process - Creative Education Foundation.
If you search the Internet for “Creative Problem Solving,” you’ll find evidence of many variations, all of which may be traced back to the work that was started by Alex Osborn in the 1940s, developed with Sid Parnes in the 1950s, and nurtured at SUNY Buffalo State and the Creative Education Foundation.
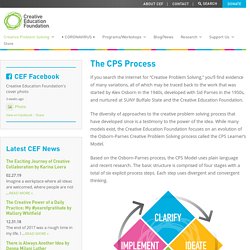
The diversity of approaches to the creative problem solving process that have developed since is a testimony to the power of the idea. While many models exist, the Creative Education Foundation focuses on an evolution of the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving process called the CPS Learner’s Model. Based on the Osborn-Parnes process, the CPS Model uses plain language and recent research. The basic structure is comprised of four stages with a total of six explicit process steps. Each step uses divergent and convergent thinking. Learner’s Model based on work of G.J. 30 Things You Can Do To Promote Creativity. The concept of teaching creativity has been around for quite some time. Academics such as E. Paul Torrance, dedicated an entire lifetime to the advancement of creativity in education. Torrance faced much opposition in his day about the nature of creativity. Creativity was considered to be an immeasurable, natural ability. Torrance called for explicit teaching of creativity.
In recent times, there has been a shift towards the increased acceptance of valuing creativity for all learners. Much of the blame for a lack of creativity, and therefore innovation, can be traced to our traditional educational systems. It relies on teaching to the correct answer. - Critical Thinking Model 1. To Analyze Thinking We Must Identify and Question its Elemental Structures Standard: Clarityunderstandable, the meaning can be grasped Could you elaborate further?

Could you give me an example? Could you illustrate what you mean? Standard: Accuracyfree from errors or distortions, true How could we check on that? Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains: The Cognitive Domain. Bloom's Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning).
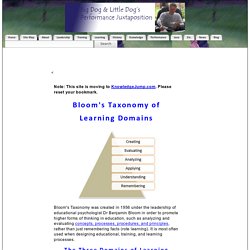
It is most often used when designing educational, training, and learning processes. The Three Domains of Learning The committee identified three domains of educational activities or learning (Bloom, et al. 1956): Cognitive: mental skills (knowledge) Affective: growth in feelings or emotional areas (attitude or self) Psychomotor: manual or physical skills (skills) Since the work was produced by higher education, the words tend to be a little bigger than we normally use. Teaching and Learning Resources. Center for Teaching Innovation. What 7 Factors Should Educators Consider When Choosing Digital Tools for Underserved Students? Seven.

That’s the magic number. Why? In the report published last week by the Stanford Center for Opportunity Policy in Education, Professor Linda Darling-Hammond and I summarized research findings about the conditions and practices that support positive outcomes of technology use and digital learning experiences for underserved, under-resourced, and underprepared students. We reviewed countless articles, reports, and white papers, and have pulled together a series of relevant and detailed examples for those interested in what the promising practices really looks like when used effectively.
The report introduces these seven practices in two categories: technology and context. Seven Items to Consider When Choosing Tools or Activities Related to technology specifically, the education research indicates that underserved students benefit from: Opportunities to learn that include one-to-one access to devices.High-speed Internet access. EdCog 2017 - Andrew Butler. Cult of Pedagogy. How To Make the Most of a Video Introduction for an Online Course.
LMS | Tutorial Page 2 of 2 How To Make the Most of a Video Introduction for an Online Course This builds upon findings from previous studies — one of which had half the students told ahead of time that a guest lecturer had a "warm" personality and the other half being told that the guest lecturer had a rather "cold" personality (Widmeyer & Loy, 1988).
The subjects were exposed to the exact same lecture and those who had been led to believe the lecturer had a "warm" personality viewed him as a more effective teacher than those students who were led to believe he had a "cold" personality. Russo & Campbell (2004) found that students liked seeing a photo of the instructor and hearing the instructor's voice.