

How to get rid of jet lag. Six "Health Tips" That Are Actually TERRIBLE Advice. As with all fields of scientific research, biomedical science is an emergent truth built out of a tapestry of studies, not just one.
Often, however, each health-based study is presented by the media as if it’s an indelible fact. Rarely are faults or limits of the study, along with vital additional context, included. Have You Had Your Tonsils Removed? We Have Really Bad News For You. For decades, millions of children across the world’s developed nations have undergone surgery to remove their tonsils and adenoids.
These lymphatic tissue structures, which serve to trigger a first-line immune response to pathogens entering the respiratory tract, frequently become chronically inflamed in the first years of life. Since the medical community has long believed that their absence does not significantly impact adult health, many doctors opt to relieve children of the persistent throat pain and ear infections that accompany such inflammation by cutting out the source. Have You Had Your Tonsils Removed? We Have Really Bad News For You. Lyme : des moyens existent pour se protéger des tiques. Nattō. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Le nattō (納豆?) Est un aliment japonais traditionnel à base de haricots de soja fermentés, consommé le plus souvent comme accompagnement du riz nature dans la cuisine japonaise, notamment au petit déjeuner. Lyme, Seven Other Tick-Borne Diseases Detected with New Serochip. 11 Fitness Myths That Are Doing More Harm Than Good. Shutterstock Whether you want to tone up, slim down, or boost your mood, you've likely taken a stab at tweaking your fitness routine.
We could solve drug resistance by getting microbes to fight each other. Scientists are in a battle to develop treatments faster than viruses develop barriers against them, but new research suggests putting pathogens at war with each other could be an effective way of countering existing drug resistance, as well as preventing it in the future.
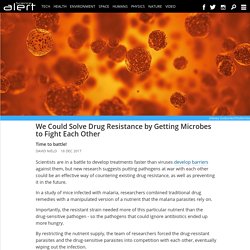
In a study of mice infected with malaria, researchers combined traditional drug remedies with a manipulated version of a nutrient that the malaria parasites rely on. Importantly, the resistant strain needed more of this particular nutrient than the drug-sensitive pathogen - so the pathogens that could ignore antibiotics ended up more hungry.
By restricting the nutrient supply, the team of researchers forced the drug-resistant parasites and the drug-sensitive parasites into competition with each other, eventually wiping out the infection. Une arme absolue contre tous les virus aurait été découverte. Des chercheurs de l'École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne ont développé des nanoparticules d’or qui ont la propriété d'attirer les virus à elles pour les détruire.
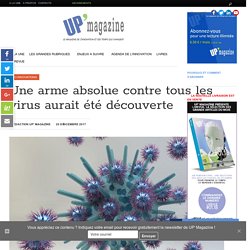
Complètement nouvelle, cette approche pourrait, à l’instar des antibiotiques à large spectre, détruire plusieurs types de virus comme le HIV, la dengue, l’herpès ou Ebola qui tuent des millions de personnes dans le monde. Le HIV, la dengue, le papillomavirus, l'herpès ou Ebola. La liste des virus est longue et ils tuent des millions de personnes chaque année, dont une majorité d'enfants dans des pays en voie de développement. Si des médicaments permettent d'en traiter certains, il n'existe aucun traitement qui pourrait être utilisé contre plusieurs virus, comparable aux antibiotiques à large spectre contre les bactéries.
ÉTAT DE SANTÉ - Maladie de Lyme, mieux dépister et mieux traiter. Artificial spleen cleans up blood. Harvard’s Wyss Institute.
7 Myths About How To Stay In Shape. Get fit.
Stay fit. Easy goals to set, but they're hard to achieve. At least part of the reason for that is that the science on fitness and dieting has changed over time. People who read about fitness in the '70s heard different information than those who read about fitness in the '90s. And the scientific consensus in the '90s was based on less complete information than researchers have today. But those old ideas stick around, and sometimes bad new ideas — only supported by one or two studies — get repeated in the media as fact. Here's the truth about some widely-believed myths about how to be healthy.
If you brought a space alien to the average American supermarket and let them wander around, they'd probably tell you "fat" was a kind of human poison, on par with arsenic and mercury. As with any nutrient, it's possible to overeat fat. "No pain, no gain" is a popular idea in the workout world, forming the foundation of several popular programs. See Which Health Supplements Aren't Backed By Science. There are a lot of fad diets and articles out there that tell you which commonplace and obscure supplements you should be adding to your diet.
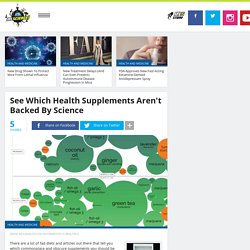
But how do you discern the genuine from the bullsh*t? This graph by David McCandless from Information is Beautiful ranks hundreds of health supplements based on the amount of scientific research backing their big claims. 3 Quick Ways to Relieve Neck Pain for Heavy Computer UsersVideo. Virtual Events, Webinars and Videos. Electrolytes are ions that carry an electrical charge and travels in and out of cells.

The most common types of electrolytes in your body are sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, and magnesium. Electrolytes trigger an event called action potential. Action potentials are the signals your brain transmits through neurons to parts of your body to contract the muscle. The principal ions involved in action potentials are sodium and potassium. As these two ions travel in and out of cells, the cells’ charge switch back and forth from negative to positive. La fabrique de micro-organes humains. NUMÉRIQUE. Article extrait du n°828 de Sciences et Avenir. Aberkane - Un Français a trouvé la solution pour la pénurie de sang dans le monde. This pill may be a cure for radiation poisoning.
After the US dropped atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki at the end of World War Two, more than 100,000 people died — many from exposure to radiation. At high doses, radiation blasts through tissues, ruptures DNA strands and alters the rhythms of cell division. Disrupted cells cause nausea, diarrhea and fever, then dizziness, weakness and hair loss. Over time they may turn cancerous. Russian Man Will Become Subject Of First Human Head Transplant Ever Performed. New Bandage Sucks Bacteria Out Of A Wound. Bandages are an important barrier between the wound and the world. They prevent bacteria entering the body and causing infection. However, what about bacteria that have already found their way into a scratch?
Introducing the bandage that's a total rip-off. It "sucks out" bacteria from a cut, allowing them to be removed along with the bandage. The technology, in development at the Swinburne University of Technology in Australia, hasn't been tested on human skin yet, only on tissue-engineered skin models.
The bacterial species investigated included Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, both of which are known to cause chronic wound infection. Syndrome métabolique – Risque cardiométabolique. Our Star Trek-Style Skin-Healing Technology Could Be The End Of Chronic Wounds. The ability to quickly heal wounds is among the most appealing of all technologies imagined by science fiction. Perhaps most famously, doctors in Star Trek are able to patch up cuts and burns by instantly regenerating their patients' skin using a kind of medical ray gun.
The injured crew of the Enterprise can return to action almost immediately instead of spending months recovering. Such technology might seem like pure fantasy (as well as a useful plot device) but it might now be closer to reality than you think. La médecine sans médecin ? Dans cet essai, paru début 2015 aux éditions Gallimard, Guy Vallancien, chirurgien urologue et membre de l’Académie nationale de médecine, décrit l’émergence de ce qu’il propose d’appeler la « média médecine ». L’innovation technologique et l’irruption du numérique bouleversent les pratiques médicales et le système de soins dans sa globalité. Porteuses de progrès considérables pour le patient, ces mutations doivent être anticipées pour envisager une transformation profonde de notre système de santé. New Method Could Reveal Your Entire Viral Infection History With A Single Drop Of Blood. By analyzing just a single drop of blood, scientists could reveal every virus you’ve ever been infected with.
This new method, developed by researchers from Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI), is called ‘Virscan’ and it could revolutionize existing diagnostics. Traditional blood tests, known as ELISA assays, are only able detect one pathogen at a time and scientists have yet to develop ELISA assays against all viruses. In comparison, Virscan can simultaneously test for more than a thousand different strains of viruses that have previously or currently infected a person. “What makes this so unique is the scale: right now, a physician needs to guess what virus might be at play and individually test for it. With VirScan, we can look for virtually all viruses, even rare ones, with a single test,” says corresponding author Stephen Elledge, in a statement. Child Revived Almost 2 Hours After "Drowning" - But How?
Last Wednesday evening, a 22-month-old child tripped and fell into an icy tributary of Buffalo Creek, outside Mifflinburg, Pennsylvania. The boy was quickly swept downstream for about a quarter of a mile before being washed up on a grassy knoll, which was where a neighbor later found him. The infant had no pulse and was not breathing at the time of discovery and may have been in the 1oC (34oF) water for as long as 30 minutes.
According to PennLive, emergency services were immediately called and as soon as they arrived they began to perform CPR on him, which continued uninterrupted as they made their way to Evangelical Community Hospital before boarding a helicopter destined for Geisinger. Human Head Transplants Could Become A Reality By 2017. Head transplants, or body transplants depending on how you look at them, are not just a thing of quirky horror movies. The first documented procedure was carried out back in the ‘50s when surgeon and transplant pioneer Vladimir Demikhov grafted the head and forelimbs of a puppy onto the body of a different dog.
Disturbingly, he followed this with his more famous work, which involved the creation of two-headed dogs. Iodine - Drug information, side effects, and reviews. Dépister le Sida et la syphilis en 15 minutes à l'aide d'un smartphone - Sciencesetavenir.fr. Institut Langevin - Ondes et Images : Echographie Ultrarapide. Quantified self. The Scientific Power of Meditation. How do vaccines work? - Kelwalin Dhanasarnsombut. Ben Goldacre: What doctors don't know about the drugs they prescribe. A Copper Bedrail Could Cut Back On Infections For Hospital Patients : Goats and Soda. Geraldine Hamilton: Body parts on a chip. Tal Golesworthy: How I repaired my own heart. Watch A Neurosurgeon Perform A Subdural Hematoma Operation. George Whitesides: A lab the size of a postage stamp. Blood Test Could Predict Alzheimer’s 10 Years Before Symptoms Appear. Joe Landolina: This gel can make you stop bleeding instantly.
Exponential Medicine: Data Deluge to Disrupt Healthcare This Decade. Regenerative Medicine Has Huge Potential But It Does Not Come Cheap. XMED: Latest XPRIZE Winner Unleashes the Health Data in Your Blood. Cheap Blood Pressure Drug Cures Diabetes In Mice, Human Trials Announced. Peter Attia: Is the obesity crisis hiding a bigger problem? Which New Technology Will Win the Race to Repair and Replace Our Organs?
Régénérer un os suite à une fracture sévère grâce à un implant riche en protéines actives. Man With Severed Spinal Cord Walks Again After Cell Transplant. Nouvelle technique permettra Robot à pratiquer la chirurgie du cerveau par renvoi. Artificial Spleen ‘Cleans’ Blood of Pathogens. Lego-Like Blocks Connect to Form Microfluidic Mini-Laboratories. Spinal Cord Stimulation Allows Completely Paralyzed Rats To Walk Again. Scientists Develop Blood-Cleansing Artificial Spleen. How Horseshoe Crab Blood Saves Millions Of Lives. Scientists Create Functioning Whole Organ From Cells.
Implantable Scaffold Regenerates Lost Bone. CHU Rennes : Les doigts du chirurgien pilotent un robot qui opère. Info. Check Out This Video of a Complete Heart Transplant! Redonner la vue aux aveugles : des chercheurs ont trouvé un moyen de faire repousser la cornée. Suspended Animation Human Trials About to Begin. Medics Given The Go Ahead For A Trial Of Suspended Animation.