

The cognitive benefits of play: Effects on the learning brain. © 2008 - 2014, Gwen Dewar, Ph.D., all rights reserved Science supports many of our intuitions about the benefits of play. Playful behavior appears to have positive effects on the brain and on a child’s ability to learn. In fact, play may function as an important, if not crucial, mode for learning. Want specifics? Here are some examples. Animal experiments: Play improves memory and stimulates the growth of the cerebral cortex In 1964, Marion Diamond and her colleagues published an exciting paper about brain growth in rats.
When researchers examined the rats’ brains, they discovered that the “enriched” rats had thicker cerebral cortices than did the “impoverished” rats (Diamond et al 1964). Subsequent research confirmed the results—rats raised stimulating environments had bigger brains. Deconstructing Role Play – Provide the Resources, Step Back and Watch Children’s Learning Flourish. Hospital, vet’s surgery, post office, travel agent – themed role play areas are often seen as a must for an early years setting. They are often meticulously prepared to be aesthetically pleasing, covered in laminated words and pictures with the aim of enticing children in. But this is where I encountered a problem: in these areas, children are expected to come together to play out adult scenarios that are consistent with these themes. Yet how many children have visited a travel agent to book a holiday recently, or operated on a pet dog in a vet’s surgery?
For the majority of children, themed areas such as those described above are simply too alien for high-quality cooperative play to develop – which is why I found the children in my class would revert back to playing ‘mums and dads’ by mid-morning, rather than booking a holiday to Costa Rica, as the poster on the wall in the travel agent suggested! I decided action had to be taken; it was time to improve my role play corner. The benefits. Symbolic play and language development. 1. Introduction 1.1. Scientists Say Child's Play Helps Build A Better Brain : NPR Ed : NPR. The cognitive benefits of play: Effects on the learning brain. Play to Learn. Play to Learn: Discussion.
Why Movement is Essential in Early Childhood. Primary school shake-up to focus on ‘play-led’ learning. Children at primary schools would not study traditional subjects until as late as 10 years of age, under proposals being considered by policymakers. Instead, there would be a much greater emphasis on creative play during the early years of primary school, and broader areas of learning in later years. The reforms are based loosely on some of the features of top-performing education systems in countries such as Finland, as well as new research on how children learn. The proposals, drafted by the National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA), represent some of the biggest proposed changes to teaching and learning at primary level in more than two decades.
Low-cost play ideas & materials. Importance of play for babies & children. Australian Government Department of Education and Training (2009). Belonging, being and becoming: The early years learning framework for Australia. Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 19 June 2019 from Cole-Hamilton, I. (2011). David whitebread importance of play report. Taking Playtime Seriously. So part of encouraging play is pulling back on how much programmed goal-directed learning we expect from very young children, to leave them time for the fun of exploration, curiosity and, well, fun. But another important part may be creating environments that foster children’s play and parents’ participation and attention.
Dr. Hirsh-Pasek, who is a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, cited its Learning Landscapes Initiative, which aims to set up learning opportunities in public places where people will encounter them. Importance of play for babies & children. How young children learn English through play. As we release Learning Time with Timmy – our first app for early-years learners of English – Danitza Villarroel, a teacher on our Learning Time with Shaun and Timmy course in Chile, explains the importance of learning through play, and offers a few tips for teachers new to this age group. Teaching English to pre-school children can be daunting for teachers new to this age group. Young children have shorter attention spans than older children and adults, and they're still learning their mother tongue.
But teaching these learners can be enormously rewarding once you've taken a few basic principles on board. ZERO TO THREE. ZERO TO THREE. Heuristic play. Heuristic play is rooted in young children’s natural curiosity.
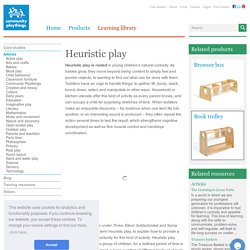
As babies grow, they move beyond being content to simply feel and ponder objects, to wanting to find out what can be done with them. Toddlers have an urge to handle things: to gather, fill, dump, stack, knock down, select and manipulate in other ways. Household or kitchen utensils offer this kind of activity as every parent knows, and can occupy a child for surprising stretches of time. When toddlers make an enjoyable discovery – for instance when one item fits into another, or an interesting sound is produced – they often repeat the action several times to test the result, which strengthens cognitive development as well as fine muscle control and hand/eye coordination. BOOK. You speak with an accent. I don’t. Accents are things that only other people have.
They are, by extension, things that you don’t want to have. Accents are, in short, shortcomings. This is why, if someone tells you that “you speak with no accent”, you can be sure of two things: that you have received words of praise indeed; and that you speak with the same accent as that person. So the person is actually not only praising her own accent, she is also giving evidence that she has no idea she’s got one. We seldom hear people say “We speak with an accent” or “I speak with an accent” – unless we’re talking about our uses of foreign languages. So let’s check out your accent. This is (choose the nearest answer – I was going to say “the best answer”, but I suddenly remembered that “best” has prescriptive connotations): a tomahto a potahto a tomayto a potayto I could tweak this test a little, like this: 1.1 a tomahto 1.2 ay tomahto 1.3 ay toemahto 1.4 a tomahtoe. Deb Roy: The birth of a word. Listen to Your Mother.
Young children face a remarkable challenge in learning to use the language of their culture. Toddlers vary widely, however, in the rate at which they learn new words.1 A team of Harvard Graduate School of Education researchers set out to ask whether and how children's language environment can impact vocabulary development. In their study of mother-child pairs from low-income families, they found that mothers who used many different words (not just many words) had toddlers with faster growth in vocabulary use. During the toddler and preschool years, most children learn to use hundreds of words, combining them into sentences and engaging in conversation with others.
From previous research, we know that variation in vocabulary growth relates to child characteristics like gender, and also to parental factors. What did they find? Why does my toddler love repetition? Paediatric speech and language therapist It may test your patience when your toddler demands 'Row, row, row your boat' for the 10th time.
But there's a good reason for her insistence. Toddlers love repetition because it helps them to learn, and because it's familiar and comforting. From around the age of two, you will notice your toddler repeating the same words and phrases constantly. By the time she's three, she will also demand her favourite stories and nursery rhymes over and over again. How can I help my child to start talking? (Video) Health visitor Sara Patience describes how you can help develop your child's language skills by talking and playing with her.
Show transcript. Multilingual Preschoolers. It’s amazing how young children learn to converse with others. They have to not only internalize grammar and vocabulary, but also develop an understanding of culture: how to take turns in a conversation, who to talk to, and how to narrate a story. For dual language learners (DLLs) — children under the age of 5 with a home language other than English — that process can be complex.