

Ancient Egyptian Families - Facts for Kids. Ancient Egyptians placed high value on their family life.
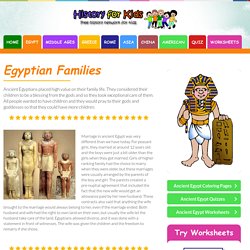
They considered their children to be a blessing from the gods and so they took exceptional care of them. All people wanted to have children and they would pray to their gods and goddesses so that they could have more children. Marriage in ancient Egypt was very different than we have today. What Type of Government Does Egypt Have? What Type of Government Does Egypt Have?
Egypt is a Northern Africa country bordering four other countries including the Gaza Strip, Israel, Libya, and Sudan. Egypt manages the Sinai Peninsula, the only land connecting Africa and the other parts of the Eastern Hemisphere. The Suez Canal which is a portion of the sea linking the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean is also controlled by Egypt. The country is formally known as the Arab Republic of Egypt and locally known as the Jumhuriyat Misr al-Arabiyah or just Misr. The country attained independence on February 28, 1922, from Britain as a protectorate. Egypt - Government and society. Egypt has operated under several constitutions, both as a monarchy and, after 1952, as a republic.
The first and most liberal of these was the 1923 constitution, which was promulgated just after Britain declared Egypt’s independence. That document laid the political and cultural groundwork for modern Egypt, declaring it an independent sovereign Islamic state with Arabic as its language. The vote was extended to all adult males. This constitution provided for a bicameral parliament, an independent judiciary, and a strong executive in the form of the king. In 1930 this constitution was replaced by another one, which gave even more powers to the king and his ministers. Eastern Africa Population 2019 (Demographics, Maps, Graphs) Bantu people (Central, East, Southern Africa) Several events in the history of Africa have shaped the current Africa: Sahara desertification, African Islamisation, slavery, colonisation, or Bantu expansion from Northern Cameroon.
The Bantu expansion originated around 2,000 before the common era. The word Bantu means «people» or «human». The term Bantu does not refer specifically to an ethnic group or a particular language, but to a set of more than 400 ethnic groups that speak Bantu languages (more than 650 Bantu languages, Nigerian-Congolese languages) that live between Cameroon and Somalia; in Central Africa, East Africa and Southern Africa. The main countries with singnificat Bantu groups are: Eastern Africa. The earliest written accounts of the East African coast occur in the Periplus Maris Erythraei—apparently written by a Greek merchant living in Egypt in the second half of the 1st century ce—and in Ptolemy’s Guide to Geography, the East African section of which, in its extant form, probably represents a compilation of geographic knowledge available at Byzantium about 400.
The Periplus describes in some detail the shore of what was to become northern Somalia. Ships sailed from there to western India to bring back cotton cloth, grain, oil, sugar, and ghee, while others moved down the Red Sea to the East African coast bringing cloaks, tunics, copper, and tin. Aromatic gums, tortoiseshell, ivory, and slaves were traded in return. Definition, Characteristics, & Facts. Bantu languages, a group of some 500 languages belonging to the Bantoid subgroup of the Benue-Congo branch of the Niger-Congo language family.
The Bantu languages are spoken in a very large area, including most of Africa from southern Cameroon eastward to Kenya and southward to the southernmost tip of the continent. Twelve Bantu languages are spoken by more than five million people, including Rundi, Rwanda, Shona, Xhosa, and Zulu. Swahili, which is spoken by five million people as a mother tongue and some 30 million as a second language, is a Bantu lingua franca important in both commerce and literature. Read More on This Topic Southern Africa: The spread of Bantu languages. French Polynesia Population 2019 (Demographics, Maps, Graphs) French Polynesia is an overseas collectivity or country of the French Republic that is comprised of many groups of Polynesian islands.
The most well-known of these islands is Tahiti in the Society Islands group, with is also the most populous. In 2019, the population of French Polynesia is estimated at 279,287, which ranks 185th in the world. French Polynesia is divided into five island groups: the Austral Islands, the Marquesas Islands, the Gambier Islands, the Tuamotu Archipelago, and the Society Islands archipelago, which is made up of the Leeward Islands and the Windward Islands. 67 of the nation's 118 atolls and islands are inhabited. The most populous island is Tahiti, which is part of the Society Islands. Weather Forecast for Tahiti. Tahiti is a tropical holiday destination popular for its warm sunny weather, beautiful beaches and stunning natural environment.
The Tahiti climate is considered marine tropical, meaning it is hot and humid yet tempered by the ocean. Receiving an average of 2,500-2,900 hours of sunshine annually, Tahiti enjoys just enough rainfall to maintain its lush vegetation and colourful flowers.Tahiti weather offers mild to warm temperatures year round, with daytime temperatures ranging from 24°C to 30°C. Lagoon water temperatures offer some relief, generally varying between 23°C to 26°C. Tahiti’s warm sunny days are tempered by northeast and southeast trade winds which also create two distinct seasons – the dry season and the rainy season.
Hawaii Population 2019 (Demographics, Maps, Graphs) Based on the most recent estimates released by the US Census, we estimate the 2020 population of Hawaii at 1.41 million.
At the 2010 census the population of Hawaii was declared at a total of 1,360,301. Estimates of the population are produced in the years between censuses - and in 2015, this number had risen to 1,431,603. This represents a 5.2% increase from the 1.36 million recorded during the 2010 Census. Religion in Hawaii - Living in Hawaii - Moving to Oahu, Maui, Kauai, Big Island. Over more than six years in Hawaii I didn’t meet many people that were overtly, devoutly religious.

It seems like the people in the islands, in general, are extremely happy to be living in paradise on earth and they’re not looking for whatever paradise might be found in religion. That said, there are churches all over the islands – and some Buddhist temples as well. Weather in Hawaii. Weather in The Hawaiian Islands is very consistent, with only minor changes in temperature throughout the year. There are really only two seasons in Hawaii: summer (kau) from May to October and winter (hooilo) from November to April.
The average daytime summer temperature at sea level is 85° F (29.4° C), while the average daytime winter temperature is 78° (25.6° C). Geography of Hawaii - World Atlas. The lush, green islands of Hawaii are the visible tops of a chain of submerged volcanic mountains that stretch 3,100 miles from Hawaii, all the way to the Aleutian Trench in the North Pacific Ocean. Excluding the largest islands (shown on the map), most are atolls; inactive stumps of volcanic rock, encircled by coral reefs. Ironically in this tropical paradise the summits of the (sporadically active ) volcanoes of Mauna Loa and Muana Kea on the Big Island, are frequently snow-capped. Kilauea, the youngest volcano in Volcanoes National Park, still erupts occasionally, spewing lava and creating new land.
Hawaiian Landforms (pictures) Other volcanoes of note includes Maui's. Geography of Hawaii - World Atlas. Polynesian Mythology - Myth Encyclopedia - god, legend, war, world, creation, life, hero, people, children. Polynesia is a vast region of the Pacific Ocean consisting of many hundreds of widely separated, culturally and politically diverse island groups. Ranging from Midway and Hawaii in the north to New Zealand in the south, the triangular area called Polynesia also includes Tahiti, Samoa, Tonga, Tuamotu, the Cook Islands, and the Pitcairn Islands.
Although the mythology of Polynesia took different forms on various islands, many of the basic stories, themes, and deities were surprisingly similar throughout the region. Foundations of Religion and Myth. Scholars believe that humans first migrated to Polynesia from Southeast Asia about 2,000 years ago. These people carried with them their mythological traditions about events, deities, and heroes.