

Client-side scripting. By viewing the file that contains the script, users may be able to see its source code. Many web authors learn how to write client-side scripts partly by examining the source code for other authors' scripts. Due to security restrictions, client-side scripts may not be allowed to access the user's computer beyond the web browser application. Techniques like ActiveX controls can be used to sidestep this restriction.
Client-side scripting is not inherently unsafe. Users, though, are encouraged to always keep their web browsers up-to-date to avoid exposing their computer and data to new vulnerabilities. Ajax (programming) Ajax is not a single technology, but a group of technologies.
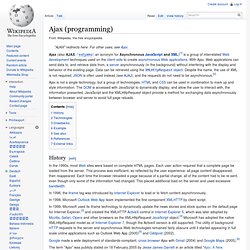
HTML and CSS can be used in combination to mark up and style information. The DOM is accessed with JavaScript to dynamically display, and allow the user to interact with, the information presented. JavaScript and the XMLHttpRequest object provide a method for exchanging data asynchronously between browser and server to avoid full page reloads. In 1996, the iframe tag was introduced by Internet Explorer to load or to fetch content asynchronously.
In 1998, Microsoft Outlook Web App team implemented the first component XMLHTTP by client script. Google made a wide deployment of standards-compliant, cross browser Ajax with Gmail (2004) and Google Maps (2005).[6] The term "Ajax" was publicly stated on 18 February 2005 by Jesse James Garrett in an article titled "Ajax: A New Approach to Web Applications", based on techniques used on Google pages.[1] get-ajax-data.js: JavaScript. JavaScript is classified as a prototype-based scripting language with dynamic typing and first-class functions.
This mix of features makes it a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented,[6] imperative, and functional[1][7] programming styles. JavaScript has been standardized in the ECMAScript language specification. History[edit] Beginnings at Netscape[edit] JavaScript was originally developed by Brendan Eich, while working for Netscape Communications Corporation. Although it was developed under the name Mocha, the language was officially called LiveScript when it first shipped in beta releases of Netscape Navigator 2.0 in September 1995, but it was renamed JavaScript[10] when it was deployed in the Netscape browser version 2.0B3.[11] The change of name from LiveScript to JavaScript roughly coincided with Netscape adding support for Java technology in its Netscape Navigator web browser.
jQuery. jQuery is a cross-platform JavaScript library designed to simplify the client-side scripting of HTML.[2] It was released in January 2006 at BarCamp NYC by John Resig.

It is currently developed by a team of developers led by Dave Methvin. Used by over 80% of the 10,000 most visited websites,[3] jQuery is the most popular JavaScript library in use today.[4][5] The set of jQuery core features—DOM element selections, traversal and manipulation—enabled by its selector engine (named "Sizzle" from v1.3), created a new "programming style", fusing algorithms and DOM-data-structures; and influenced the architecture of other JavaScript frameworks like YUI v3 and Dojo.
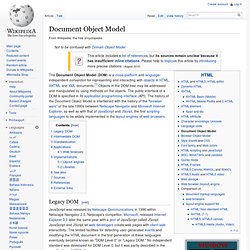
Microsoft and Nokia bundle jQuery on their platforms.[7] Microsoft includes it with Visual Studio[8] for use within Microsoft's ASP.NET AJAX framework and ASP.NET MVC Framework while Nokia has integrated it into the Web Run-Time widget development platform.[9] jQuery has also been used in MediaWiki since version 1.16.[10] Document Object Model. Hierarchy of objects in an example HTML DOM—Document Object Model Legacy DOM[edit] Intermediate DOM[edit] In 1997, Netscape and Microsoft released version 4.0 of Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer respectively, adding support for Dynamic HTML (DHTML), functionality enabling changes to a loaded HTML document.
DHTML required extensions to the rudimentary document object that was available in the Legacy DOM implementations. Although the Legacy DOM implementations were largely compatible since JScript was based on JavaScript, the DHTML DOM extensions were developed in parallel by each browser maker and remained incompatible. Standardization[edit] The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), founded in 1994 to promote open standards for the World Wide Web, brought Netscape Communications and Microsoft together with other companies to develop a standard for browser scripting languages, called "ECMAScript.
" After the release of ECMAScript, W3C began work on a standardized DOM. Font Awesome, the iconic font designed for use with Twitter Bootstrap. Getting. Gallery of free HTML snippets for Twitter Bootstrap. Carousel Extended.