

Who's Who in the Arena? Circus Maximus, Rome. The Circus Maximus was the largest stadium in ancient Rome.
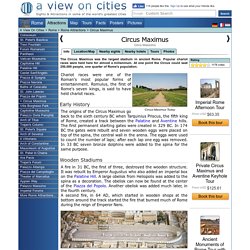
Popular chariot races were held here for almost a millennium. At one point the Circus could seat 250,000 people, one quarter of Rome's population. Circus Maximus Today Chariot races were one of the Roman's most popular forms of entertainment. Romulus, the first of Rome's seven kings, is said to have held chariot races. Early History The origins of the Circus Maximus go back to the sixth century BC when Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome, created a track between the Palatine and Aventine hills. Wooden Stadiums A fire in 31 BC, the first of three, destroyed the wooden structure.
Scale model of the Circus Maximus in Ancient Rome The Marble Stadium After yet another fire the Circus was rebuilt by Trajan in 103 AD. Popular Events The Circus Maximus was occasionally used for events such as processions or gladiator combats, but on most days only chariot races with quadrigaes, pulled by four horses, were held here.
Roman photos. Rotten Romans Video Clip. Ancient Rome for Kids: The City of Pompeii. History >> Ancient Rome The city of Pompeii was a major resort city during the times of Ancient Rome.
However, in 79 AD, disaster struck the city when it was buried under 20 feet of ash and debris from the eruption of the nearby volcano, Mount Vesuvius. History Pompeii was originally settled around the 7th century BC by the Oscan peoples. The port city was in a prime location for trade as well as farming. Interactive Map of the Roman Empire and Celtic Lands. Interactive Map of the Roman Empire and Celtic Lands - K.S. 2 Timeline of the Roman Empire and Lands of the Celtic People 475BC The people of Rome and their allies (the Latin League) overthrew their Etruscan rulers.
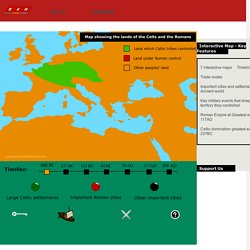
After the Gallic attack on Rome the city was gradually rebuilt to become one of the largest in Italy. BY 338 BC the Romans ruled the Latin League with absolute power. From 300-280BC the Romans mastered their local enemies: the Etruscans, Samnites and the Gauls of North of Italy (Po Valley). The Greek cities in the south of Italy concerned at the power of Rome sent their champion Pyrrhus against her. 279BC The Gauls advanced into Macedonia, Greece and Thrace. 264-241BC The Romans went to war with Carthage and built a strong navy. 236BC The Celts began to loose their lands to other people. In 219BC Celtic tribes lost land in Spain to the Carthaginians. We do not know to whether large movements of Celtic people or close trade brought Celtic culture to Britain. Romans.
Idp3.lgfl.org. Roman Timeline. Can I find the Roman names of places in Britain? How and why did people become gladiators? by cyada2000 cyada2000 on Prezi. Austin's Butterfly: Building Excellence in Student Work - Models, Critique, and Descriptive Feedback. Who were the Romans? What is an archaeologist?
Roman Timelines. West Thornton's roman website - Home.