

Anubis. Anubis (/əˈnuːbəs/ or /əˈnjuːbəs/;[2] Ancient Greek: Ἄνουβις) is the Greek name[3] for a jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife in ancient Egyptian religion.
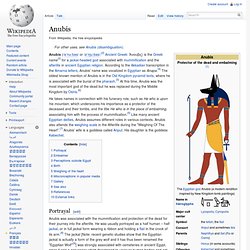
Hathor. Hathor (/ˈhæθɔr/ or /ˈhæθər/;[2] Egyptian: ḥwt-ḥr and from Greek: Άθωρ, "mansion of Horus")[1] is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of joy, feminine love, and motherhood.[3] She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt.
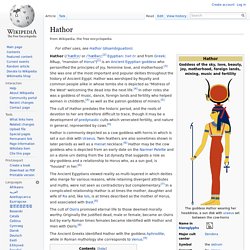
Hathor was worshiped by Royalty and common people alike in whose tombs she is depicted as "Mistress of the West" welcoming the dead into the next life.[4] In other roles she was a goddess of music, dance, foreign lands and fertility who helped women in childbirth,[4] as well as the patron goddess of miners.[5] The cult of Hathor predates the historic period, and the roots of devotion to her are therefore difficult to trace, though it may be a development of predynastic cults which venerated fertility, and nature in general, represented by cows.[6] Hathor is commonly depicted as a cow goddess with horns in which is set a sun disk with Uraeus. Early depictions[edit] Temples[edit] Horus. Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times.
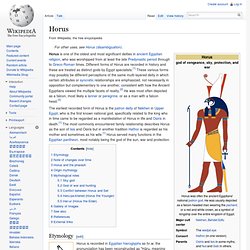
Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egypt specialists.[1] These various forms may possibly be different perceptions of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality.[2] He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner or peregrine, or as a man with a falcon head.[3] Etymology[edit] Horus was also known as Nekheny, meaning "falcon". Some have proposed that Nekheny may have been another falcon-god, worshipped at Nekhen (city of the hawk), with which Horus was identified from early on.
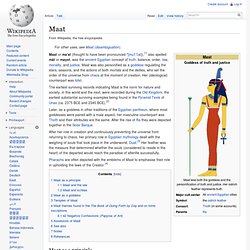
Note of changes over time[edit] Maat. The earliest surviving records indicating Maat is the norm for nature and society, in this world and the next, were recorded during the Old Kingdom, the earliest substantial surviving examples being found in the Pyramid Texts of Unas (ca. 2375 BCE and 2345 BCE).[2] Later, as a goddess in other traditions of the Egyptian pantheon, where most goddesses were paired with a male aspect, her masculine counterpart was Thoth and their attributes are the same.
Osiris. Osiris (/oʊˈsaɪərɨs/; also Usiris), is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead.
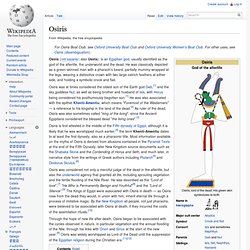
He was classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. Osiris is first attested in the middle of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, although it is likely that he was worshipped much earlier;[4] the term Khenti-Amentiu dates to at least the first dynasty, also as a pharaonic title. Thoth. Ra. Ra /rɑː/[1] or Re /reɪ/ (Egyptian: 𓂋ꜥ, rˤ) is the ancient Egyptian solar deity.
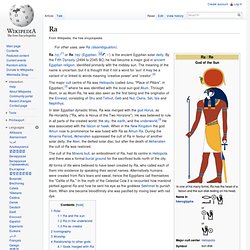
By the Fifth Dynasty (2494 to 2345 BC) he had become a major god in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the midday sun. The meaning of the name is uncertain, but it is thought that if not a word for 'sun' it may be a variant of or linked to words meaning 'creative power' and 'creator'.[2] In later Egyptian dynastic times, Ra was merged with the god Horus, as Re-Horakhty ("Ra, who is Horus of the Two Horizons"). He was believed to rule in all parts of the created world: the sky, the earth, and the underworld.[3] He was associated with the falcon or hawk. When in the New Kingdom the god Amun rose to prominence he was fused with Ra as Amun-Ra. All forms of life were believed to have been created by Ra, who called each of them into existence by speaking their secret names. Khepri.
Khepri (also spelled Khepera, Kheper, Khepra, Chepri) is a god in ancient Egyptian religion.
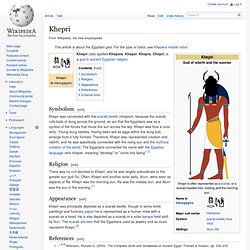
Symbolism[edit] Khepri was connected with the scarab beetle (kheprer), because the scarab rolls balls of dung across the ground, an act that the Egyptians saw as a symbol of the forces that move the sun across the sky. Khepri was thus a solar deity. Young dung beetles, having been laid as eggs within the dung ball, emerge from it fully formed. Atum. Atum (/ɑ-tum/), sometimes rendered as Atem or Tem, is an important deity in Egyptian mythology.
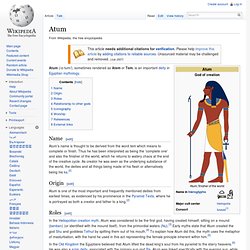
Name[edit] Atum's name is thought to be derived from the word tem which means to complete or finish.