

Free CCNA Workbook. Configuring the Free CCNA Workbook GNS3 Topology. Download and import the Free CCNA Workbook dot com GNS3 Lab topology for use with the Free CCNA Workbook dot com website.

Real World Application This lab will teach you how to import the Free CCNA Workbook Lab topology into GNS3. This is required if you have not built a physical lab to use with this website. Real world application does not apply to this lab however in this lab you will learn how to configure the Free CCNA Workbook GNS3 topology which is used on 95% of all labs found in the Free CCNA Workbook. Lab Prerequisites Have GNS3 installed and the GNS3 environment variables configured which include the working directory, execution path, IOS Image directory and temp paths. Lab Objectives Lab Instruction Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. Step 4. After making sure that the router has booted up into user mode; if prompted you can type “n” to skip the Initial Configuration Dialog and wait till you receive the prompt Router>
CCNA Labs: 642-813. Link Aggregation Control Protocol Configuration: Suppose you have just added a new switch (SwitchB) to the existing network as shown in the topology.
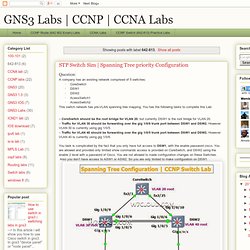
RouterA is currently configured correctly for providing the routing function for devices on SwitchA and SwitchB. You need to be modified SwitchA to support the addition of SwitchB. You have been tasked with competing the needed configuring of SwitchA and SwitchB. SwitchA and SwitchB use Cisco as the enable password. Configuration Requirements for SwitchA The VTP and STP configuration modes on SwitchA is correct and should not be modified. Configuration Requirements for SwitchB. A Guide to the Intense School GNS3 Labs. A Guide to the Intense School GNS3 Labs GNS3 is an open-source software that allows the user to simulate large and complex networks by emulating physical devices, routers and switches from multiple vendors.
It has a GUI (graphical user interface) that eases the usage and runs on x86 hardware and on multiple operating systems, including Linux, Windows and Mac OS. Based on the type of devices you want to use, different tools will be needed on your computer along with GNS3. In most cases, GNS3 is used to simulate networks with Cisco devices. To do so, you will need Dynamips, the Cisco IOS emulator. GNS3 is used by engineers that are pursuing different Cisco certifications. Right now, Intense School offers a wide variety of GNS3 labs that covers different topics, mostly covering topics from the CCNA Routing and Switching exams.
Adding hosts to your Topologies. There are four possible ways to add a computer to your topology.
If you just need to check for connectivity using ping or traceroute, the best way is to use the Virtual PC Simulator. The second way is to use a Qemu or VirtualBox guest (Qemu and VirtualBox support are integrated into GNS3). Third way is adding another router but configure it to act like a PC. Finally, you may use your real PC as described in the Connecting GNS3 to real networks tutorial. Using the Virtual PC Simulator (and the Symbol Library) The Virtual PC Simulator is a program that runs within Windows orLinux. Extract the archive to your PC, and then in Windows run vpcs.exe If you are running Linux, following these additional steps: right-click the vpcs (not vpcs.exe) and choose Properties.
Now just click the VPCS icon on your desktop as it is best to open the Virtual PC Simulator before starting GNS3. For help, just type ? Building More Complex Topologies. Although a single router is useful to get familiar with commands, it would be nice to build more complex topologies.
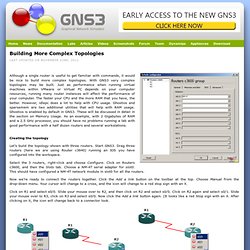
With GNS3 very complex topologies may be built. Just as performance when running virtual machines within VMware or Virtual PC depends on your computer resources, running many router instances will affect the performance of your computer. Creating the Simplest Topology. We describe how to build a more complex topology later, but for now, let’s just learn how to place one router on the desktop, start it, and console into it.
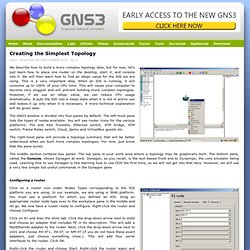
We will then learn how to find an idlepc value for the IOS we are using. This is a very important step. When an IOS is running, it will consume up to 100% of your CPU time. This will cause your computer to become very sluggish and will prevent building more complex topologies. However, if we use an idlepc value, we can reduce CPU usage dramatically. The GNS3 window is divided into four panes by default. The right-most pane will provide a topology summary that will be better understood when we built more complex topologies. Quick Start Guide for Windows Users.
This page will take you through the steps to get started with GNS3 in a Windows environment.
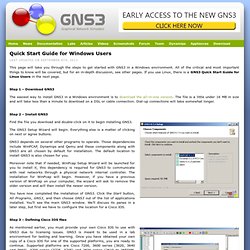
All of the critical and most important things to know will be covered, but for an in-depth discussion, see other pages. Introduction to GNS3. GNS3 is a Graphical Network Simulator that allows emulation of complex networks.

You may be familiar with VMWare, VirtualBox or Virtual PC that are used to emulate various operating systems in a virtual environment. These programs allow you to run operating systems such as Windows XP Professional or Ubuntu Linux in a virtual environment on your computer. GNS3 allows the same type of emulation using Cisco Internetwork Operating Systems. It allows you to run a Cisco IOS in a virtual environment on your computer. Dynamips is the core program that allows IOS emulation. GNS3 also supports other emulation programs, namely Qemu, Pemu and VirtualBox. GNS3 allows the emulation of Cisco IOSs on your Windows, Linux and Mac OS X based computer.