

LED Plant Growth Light - Viewing Comments 1-40. How to convert lumens to watts (W) Grow light. Dual spectrum compact fluorescent grow light.
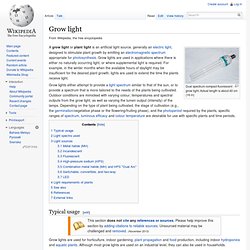
Actual length is about 40 cm (16 in) A grow light or plant light is an artificial light source, generally an electric light, designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting an electromagnetic spectrum appropriate for photosynthesis. Grow lights are used in applications where there is either no naturally occurring light, or where supplemental light is required. For example, in the winter months when the available hours of daylight may be insufficient for the desired plant growth, lights are used to extend the time the plants receive light. Light Calculator. High-refractive-index polymer.
A high-refractive-index polymer (HRIP) is a polymer that has a refractive index greater than 1.50.[1] Such materials are required for anti-reflective coating and photonic devices such as light emitting diodes (LEDs) and image sensors.[1][2] The refractive index of a polymer is based on several factors which include polarizability, chain flexibility, molecular geometry and the polymer backbone orientation.[3][4] As of 2004, the highest refractive index for a polymer was 1.76.[5] Substituents with high molar fractions or high-n nanoparticles in a polymer matrix have been introduced to increase the refractive index in polymers.[6] Properties[edit] Refractive index[edit] A typical polymer has a refractive index of 1.30–1.70, but a higher refractive index is often required for specific applications.
Optical properties[edit] Optical dispersion is an important property of an HRIP. Color temperature. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black body radiator that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source. Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, horticulture, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is only meaningful for light sources that do in fact correspond somewhat closely to the radiation of some black body, i.e. those on a line from reddish/orange via yellow and more or less white to blueish white; it does not make sense to speak of the color temperature of e.g. a green or a purple light.
Color temperature is conventionally stated in the unit of absolute temperature, the kelvin, having the unit symbol K. Categorizing different lighting[edit] The black-body radiance (Bλ) vs. wavelength (λ) curves for the visible spectrum. Electric Clothing. LED. Photoperiodism. Photoperiodism is the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of day or night.
It occurs in plants and animals. Photoperiodism can also be defined as the developmental responses of plants to the relative lengths of the light and dark periods. Here it should be emphasized that photoperiodic effects relate directly to the timing of both the light and dark periods. In plants[edit] Many flowering plants (angiosperms) use a photoreceptor protein, such as phytochrome or cryptochrome,[1] to sense seasonal changes in night length, or photoperiod, which they take as signals to flower. In 1920, W. Modern biologists believe[citation needed] that it is the coincidence of the active forms of phytochrome or cryptochrome, created by light during the daytime, with the rhythms of the circadian clock that allows plants to measure the length of the night.
Long-day plants[edit] Long-day plants flower when the day length exceeds their critical photoperiod. Some long-day obligate plants are: D.E. Photosynthetically active radiation. Photosynthetically active radiation, often abbreviated PAR, designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis.
This spectral region corresponds more or less with the range of light visible to the human eye. Photons at shorter wavelengths tend to be so energetic that they can be damaging to cells and tissues, but are mostly filtered out by the ozone layer in the stratosphere. Photons at longer wavelengths do not carry enough energy to allow photosynthesis to take place. Other living organisms, such as green bacteria, purple bacteria and Heliobacteria, can exploit solar light in slightly extended spectral regions, such as the near-infrared. These bacteria live in environments such as the bottom of stagnant ponds, sediment and ocean depths.