

Australian Timelines.
Celts. Diachronic distribution of Celtic peoples: core Hallstatt territory, by the 6th century BC maximal Celtic expansion, by 275 BC Lusitanian area of Iberia where Celtic presence is uncertain The Celts (/ˈkɛlts/, occasionally /ˈsɛlts/, see pronunciation of Celtic) or Kelts were an ethnolinguistic group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Medieval Europe who spoke Celtic languages and had a similar culture,[1] although the relationship between the ethnic, linguistic and cultural elements remains uncertain and controversial.
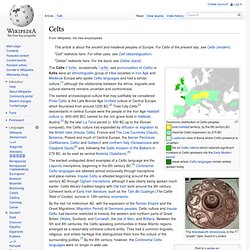
The earliest undisputed direct examples of a Celtic language are the Lepontic inscriptions, beginning in the 6th century BC.[6] Continental Celtic languages are attested almost exclusively through inscriptions and place-names. Names and terminology Continental Celts are the Celtic-speaking people of mainland Europe and Insular Celts are the Celtic-speaking peoples of the British and Irish islands and their descendants. Origins Overview of the Hallstatt and La Tène cultures: List of timelines. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of timelines currently on Wikipedia.
§Types[edit] §General timelines[edit] §History[edit] §Arts[edit] §Biographical timelines[edit] §Crime[edit] §Events[edit] §Disasters[edit] §Economics[edit] §Entertainment[edit] §Environmental issues[edit] §Fiction[edit] §Geographical timelines[edit] Timeline of country and capital changes §Ancient civilizations[edit] §Extant civilizations[edit] §Supranational entities and regions, peoples[edit] §Sovereign states[edit] §Subnational regions and cities, narrow timelines[edit] History of the world. World population[1] from 10,000 BCE to 2,000 CE.
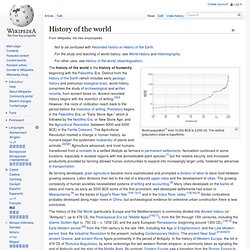
The vertical (population) scale is logarithmic. History. Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it.[1] History (from Greek ἱστορία, historia, meaning "inquiry, knowledge acquired by investigation")[2] is the study of the past, particularly how it relates to humans.[3][4] It is an umbrella term that relates to past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of information about these events.

Scholars who write about history are called historians. Events occurring prior to written record are considered prehistory. History can also refer to the academic discipline which uses a narrative to examine and analyse a sequence of past events, and objectively determine the patterns of cause and effect that determine them.[5][6] Historians sometimes debate the nature of history and its usefulness by discussing the study of the discipline as an end in itself and as a way of providing "perspective" on the problems of the present.[5][7][8][9] Etymology Description Historiography. Timeline. Prehistory For events dating from the formation of the planet to the rise of modern humans see: Timeline of natural historyFor events dating from the first appearance of Homo sapiens to before the invention of writing see: Timeline of human prehistory These timelines of world history detail recorded events since the creation of writing roughly 5000 years ago (which marks the beginning of history) to the present day.
For events from c. 3500 BC to c. 500 AD see: Timeline of ancient historyFor events from c. 500 to 1499, see: Timeline of the Middle AgesFor events from 1500 to 1900, see: Timeline of early modern historyFor events since 1901, see: Timeline of modern history Future.