

Kaliningrad. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
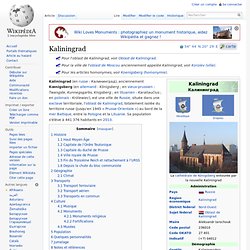
Kaliningrad (en russe : Калининград), anciennement Kœnigsberg (en allemand : Königsberg ; en vieux-prussien : Twangste, Kunnegsgarbs, Knigsberg ; en lituanien : Karaliaučius ; en polonais : Królewiec), est une ville de Russie, située dans une exclave territoriale, l'oblast de Kaliningrad, totalement isolée du territoire russe (jusqu'en 1945 « Prusse-Orientale ») au bord de la mer Baltique, entre la Pologne et la Lituanie.
Sa population s'élève à 441 376 habitants en 2013. Histoire[modifier | modifier le code] Sea of Azov. Names[edit] The name likely derives from the settlement of and area around Azov, whose name comes from the Kipchak Turkish asak or azaq ("lowlands").[6] A Russian folk etymology, however, instead derives it from an eponymous Cuman prince named "Azum" or "Asuf", said to have been killed defending his town in 1067.[7] A formerly common spelling of the name in English was the Sea of Azoff,[8] which is closer to the Russian pronunciation.
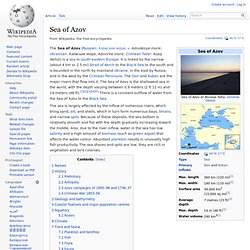
The medieval Russians knew it as the Sea of Surozh after the adjacent city now known as Sudak.[1][17] It was known in Ottoman Turkish as the Balük-Denis ("Fish Sea") from its high productivity.[8] History[edit] Prehistory[edit] Caspian Sea. The Caspian Sea (Azerbaijani: Xəzər dənizi, Kazakh: Каспий теңізі, Persian: دریای خزر Daryā-i Xazar, دریای مازندران Daryā-i Māzandarān, Russian: Каспийское море, Turkmen: Hazar deňizi) is the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea.[2][3] The sea has a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,200 sq mi) (not including Garabogazköl Aylagy) and a volume of 78,200 km3 (18,800 cu mi).[4] It is in an endorheic basin (it has no outflows) and is bounded to the northwest by Russia, to the west by Azerbaijan, to the south by Iran, to the southeast by Turkmenistan, and to the northeast by Kazakhstan.
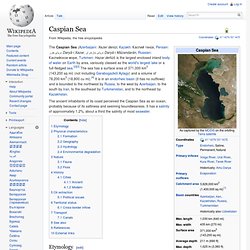
The ancient inhabitants of its coast perceived the Caspian Sea as an ocean, probably because of its saltiness and seeming boundlessness. It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third the salinity of most seawater. Black Sea. The Black Sea is a sea in Southeastern Europe.
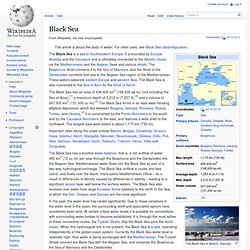
It is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean Seas and various straits. The Bosphorus Strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the Strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean Sea region of the Mediterranean. These waters separate eastern Europe and western Asia. Volga River. "Idel" redirects here.
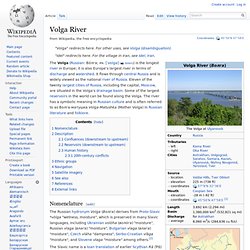
For the village in Iran, see Idel, Iran. The Volga (Russian: Во́лга; IPA: [ˈvolɡə] ( Nomenclature[edit] White Sea. This article is about the inlet of the Barents Sea.
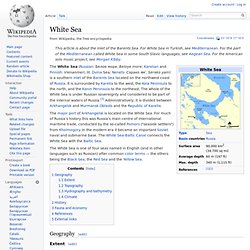
For White Sea in Turkish, see Mediterranean. For the part of the Mediterranean called White Sea in some South Slavic languages, see Aegean Sea. For the American solo music project, see Morgan Kibby. Mer Noire. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
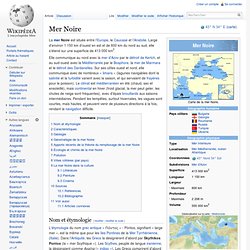
La mer Noire et la mer Méditerranée. Saint-Pétersbourg. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
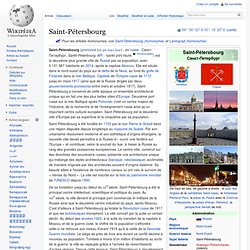
Saint-Pétersbourg a été fondée en 1703 par le tsar Pierre le Grand dans une région disputée depuis longtemps au royaume de Suède. Par son urbanisme résolument moderne et son esthétique d'origine étrangère, la nouvelle ville devait permettre à la Russie d’« ouvrir une fenêtre sur l'Europe » et contribuer, selon le souhait du tsar, à hisser la Russie au rang des grandes puissances européennes. Le centre-ville, construit sur des directives des souverains russes, présente une architecture unique qui mélange des styles architecturaux (baroque, néoclassique) acclimatés de manière originale par des architectes souvent d'origine italienne. Sa beauté alliée à l'existence de nombreux canaux lui ont valu le surnom de « Venise du Nord ».
La ville est inscrite sur la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO depuis 1990. Géographie[modifier | modifier le code] Kaliningrad. Mer Baltique. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
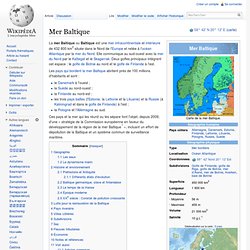
La mer Baltique ou Baltique est une mer intracontinentale et intérieure de 432 800 km2 située dans le Nord de l'Europe et reliée à l'océan Atlantique par la mer du Nord. Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer du Nord par le Kattegat et le Skagerrak. Deux golfes principaux intègrent cet espace : le golfe de Botnie au nord et le golfe de Finlande à l'est. Les pays qui bordent la mer Baltique abritent près de 100 millions d'habitants et sont : Eurasia Canal. Lake Manych-Gudilo is midway on the course of the proposed Eurasia Canal The Eurasia Canal (Russian: Канал "Евразия", Kanal "Evraziya") is a proposed 700-kilometre (430 mi) long canal connecting the Caspian Sea to the lower Black Sea along the Kuma-Manych Depression, which is often considered the border between Europe and Asia.
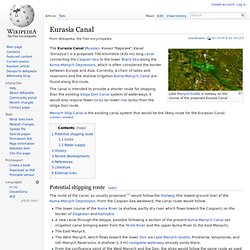
Currently, a chain of lakes and reservoirs and the shallow irrigation Kuma-Manych Canal are found along this route. The canal is intended to provide a shorter route for shipping than the existing Volga-Don Canal system of waterways; it would also require fewer locks (or lower-rise locks) than the Volga-Don route. Transport in Russia. The export of transport services is an important component of Russia’s GDP. The government anticipates that between 2007 and 2030, the measures included in its 2008 transport strategy will increase the export of transport services to a total value of $80 billion, a sevenfold increase on its 2008 value. Foreign cargo weight transported is expected to increase from 28 million tonnes to 100 million tonnes over the same period. Rail transport[edit] Russia has the world's second-largest railway network, second only to that of the United States,[1] with a total track length of 87,157 kilometres (54,157 mi) as of 2011.
Of this, 86,200 kilometres (53,600 mi) uses a broad rail gauge of 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in), while a narrow gauge of 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) is used on a 957-km (595-mile) stretch of railway on Sakhalin Island. List of canals in Russia. Problems donating? | Other ways to give | Frequently asked questions | By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy. The Wikimedia Foundation is a nonprofit, tax-exempt organization.By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy and to sharing your information with the Wikimedia Foundation and its service providers in the U.S. and elsewhere.
The Wikimedia Foundation is a nonprofit, tax-exempt organization.By donating, you are agreeing to our donor privacy policy and to sharing your information with the Wikimedia Foundation and its service providers in the U.S. and elsewhere. *Recurring payments will be debited by the Wikimedia Foundation until you notify us to stop. We'll send you an email receipt for each payment, which will include a link to easy cancellation instructions. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of navigable canals that are at least partially located in Russia. File:White Sea Canal map.png. White Sea Canal map - White Sea–Baltic Canal. Volga–Baltic Waterway.