

Wakamaru. Wakamaru greeting the viewer.
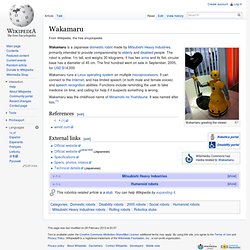
Wakamaru is a Japanese domestic robot made by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, primarily intended to provide companionship to elderly and disabled people. The robot is yellow, 1m tall, and weighs 30 kilograms. It has two arms and its flat, circular base has a diameter of 45 cm. The first hundred went on sale in September, 2005, for USD $14,000. Wakamaru runs a Linux operating system on multiple microprocessors. Wakamaru was the childhood name of Minamoto no Yoshitsune. References[edit] wired.com External links[edit] Robot. The branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots,[2] as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing is robotics.
These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behavior, and/or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. These robots have also created a newer branch of robotics: Soft robotics. Robots have replaced humans[4] in the assistance of performing those repetitive and dangerous tasks which humans prefer not to do, or are unable to do due to size limitations, or even those such as in outer space or at the bottom of the sea where humans could not survive the extreme environments. There are concerns about the increasing use of robots and their role in society. Summary History Early beginnings. Robotics. Robotics is the branch of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots,[1] as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing.
These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behavior, and/or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. The concept of creating machines that can operate autonomously dates back to classical times, but research into the functionality and potential uses of robots did not grow substantially until the 20th century.[2] Throughout history, robotics has been often seen to mimic human behavior, and often manage tasks in a similar fashion. Etymology[edit] History of robotics[edit] Robotic aspects[edit] Components[edit] Power source[edit] Humanoid robot. Purpose[edit] Humanoid robots are used as a research tool in several scientific areas.
Researchers need to understand the human body structure and behavior (biomechanics) to build and study humanoid robots. On the other side, the attempt to the simulation of the human body leads to a better understanding of it. Human cognition is a field of study which is focused on how humans learn from sensory information in order to acquire perceptual and motor skills. This knowledge is used to develop computational models of human behavior and it has been improving over time. It has been suggested that very advanced robotics will facilitate the enhancement of ordinary humans.
Although the initial aim of humanoid research was to build better orthosis and prosthesis for human beings, knowledge has been transferred between both disciplines. They are becoming increasingly popular for providing entertainment too. Sensors[edit] A sensor is a device that measures some attribute of the world. Actuators[edit]