

Breathtaking impact craters. Meteor Crater, sometimes referred to as Barringer Crater, after Daniel Barringer, the geologist who was first to propose the crater was formed by the impact of meteorite, is located 43 miles east of Flagstaff, Arizona.
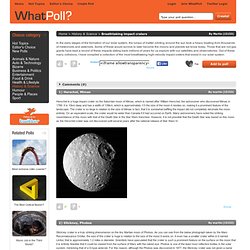
Although small compared to other impact craters in the solar system with a diameter of around 1.1km, it is a truly breathtaking site to cast your eyes upon. How to Find a Meteorite. Earth is under constant bombardment by space rocks.
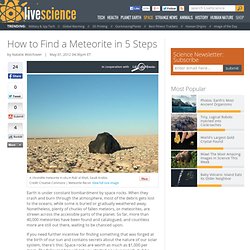
When they crash and burn through the atmosphere, most of the debris gets lost to the oceans, while some is buried or gradually weathered away. Nonetheless, plenty of chunks of fallen meteors, or meteorites, are strewn across the accessible parts of the planet. So far, more than 40,000 meteorites have been found and catalogued, and countless more are still out there, waiting to be chanced upon. If you need further incentive for finding something that was forged at the birth of our sun and contains secrets about the nature of our solar system, there's this: Space rocks are worth as much as $1,000 per gram. The following tips will get you started on your search, but be warned: This extraterrestrial treasure hunt requires hard work and dedication.
Step 1. Before you plan a meteorite hunt, make sure that if you find one, you'll be allowed to keep it. Step 2. In a world full of rocks, narrowing your search is key. Step 3. Step 4. Step 5. What the sky would look like if Earth had rings like Saturn. How a slight tap could literally knock down The Empire State Building. Putting your hand in the Large Hadron Collider. Canada Missing Gravity. For more than 40 years, scientists have tried to figure out what's causing large parts of Canada, particularly the Hudson Bay region, to be "missing" gravity.
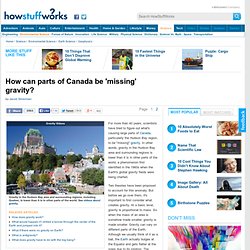
In other words, gravity in the Hudson Bay area and surrounding regions is lower than it is in other parts of the world, a phenomenon first identified in the 1960s when the Earth's global gravity fields were being charted. Two theories have been proposed to account for this anomaly. But before we go over them, it's important to first consider what creates gravity. At a basic level, gravity is proportional to mass. So when the mass of an area is somehow made smaller, gravity is made smaller.
One theory centers on a process known as convection occurring in the Earth's mantle. A new theory to account for the Hudson Bay area's missing gravity concerns the Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered much of present-day Canada and the northern United States. So which theory is correct? Double-Slit Experiment. The video below shows scientific proof that there is something NOT quite logical or scientific about this universe.

The mere act of observation can completely change the outcome of an event! Before I get too ahead of myself, you need to watch the video below to understand: (Forgive the corny cartoon character explaining the concept — at least he knows his stuff) Recap: When a camera observed the electrons, they acted as particles. However, when the no equipment was used to observe the electrons, they acted as waves and particles simultaneously. So what’s the reason for this? Want even further proof? Then in 2002, a group of researchers set up the experiment in a way that the electron could not possibly receive information about the existence of an observing instrument.
The Results: The photons acted like particles 93% of the time that they were observed. Past, Present and Future. 05-02-17_wifi_why_for_us-freq-allocations-chart_big.jpg (JPEG Image, 2550x1632 pixels) - Scaled (39%) Focused Sunlight. 10 Strange Things About The Universe. Space The universe can be a very strange place.
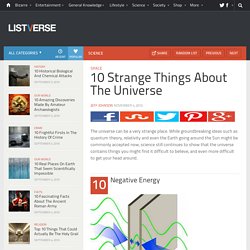
While groundbreaking ideas such as quantum theory, relativity and even the Earth going around the Sun might be commonly accepted now, science still continues to show that the universe contains things you might find it difficult to believe, and even more difficult to get your head around. Theoretically, the lowest temperature that can be achieved is absolute zero, exactly ? 273.15°C, where the motion of all particles stops completely. However, you can never actually cool something to this temperature because, in quantum mechanics, every particle has a minimum energy, called “zero-point energy,” which you cannot get below. One of the properties of a negative-energy vacuum is that light actually travels faster in it than it does in a normal vacuum, something that may one day allow people to travel faster than the speed of light in a kind of negative-energy vacuum bubble.
Relativity of Simultaneity Antimatter Retrocausality.
Cosmology. Material Science. .bodycard 2214.