

Dandring33. Dandring33. Cannabis: All You Need to Know. Google. Absentee ballot. An absentee ballot is a vote cast by someone who is unable or unwilling to attend the official polling station.
Numerous methods have been devised to facilitate this. Increasing the ease of access to absentee ballots is seen by many as one way to improve voter turnout, though some countries require that a valid reason, such as infirmity or travel, be given before a voter can participate in an absentee ballot. Methods[edit] Postal voting[edit] In a postal vote, the ballot papers are posted out to the voter – usually only on request – who must then fill them out and return them, often with some form of certification by a witness and their signature to prove their identity.
Proxy voting[edit] To cast a proxy vote, the user appoints someone as their proxy, by authorizing them to cast or secure their vote in their stead. Internet voting[edit] Corporations and organizations routinely use Internet voting to elect officers and Board members and for other proxy elections.[1] Coattail effect. The coattail effect is the tendency for a popular political party leader to attract votes for other candidates of the same party in an election.
For example, in the United States, the party of a victorious presidential candidate will often win many seats in Congress as well; these congressmen are voted into office “on the coattails” of the president. This theory is prevalent at all levels of government. A popular statewide candidate for governor or senator can attract support for down ballot races of their party as well. This is prevalent in the United Kingdom especially in a general election. People have a tendency to vote on the basis of a political party instead of the MP for their area. This also refers to the phenomenon that members of the U.S. The "coattail effect" has also been used to derogatorily describe the effect of Group Representation Constituencies (GRCs) in Singapore, where candidates for Parliament run on a party slate of 3 to 6 candidates.
Elections. Chapter 7 The Electoral Process Flashcards - Flashcard Exchange. United States presidential election in Florida, 2000. The 2000 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 7, 2000 as part of the greater 2000 United States presidential election.
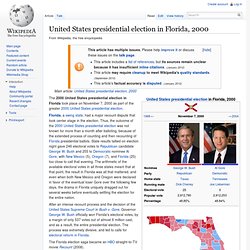
After an intense recount process and the decision of the United States Supreme Court in Bush v. Gore, Governor George W. Bush officially won Florida's electoral votes, by a margin of only 537 votes out of almost 6 million cast, and as a result, the entire presidential election. The process was extremely divisive, and led to calls for electoral reform in Florida. Campaign[edit] Initially Florida had been considered a reliable red state. Also there was heavy backlash amongst the Cuban-American population against democrats during the Elian Gonzalez dispute, which Janet Reno the attorney general under Bill Clinton ordered Elian to be returned to Cuba. In late October, one poll found that Gore was leading Bush and third parties with 44-42-4 among registered voters and 46-42-4 among likely voters.[4] Recount[edit]
About the Federal election commission. In 1975, Congress created the Federal Election Commission (FEC) to administer and enforce the Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) - the statute that governs the financing of federal elections.
The duties of the FEC, which is an independent regulatory agency, are to disclose campaign finance information, to enforce the provisions of the law such as the limits and prohibitions on contributions, and to oversee the public funding of Presidential elections. The Commission is made up of six members, who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. Each member serves a six-year term, and two seats are subject to appointment every two years. By law, no more than three Commissioners can be members of the same political party, and at least four votes are required for any official Commission action. This structure was created to encourage nonpartisan decisions.
Files marked [PDF] require Adobe Reader from Adobe. Ch 7 Vocabulary: Electoral Process flashcards. Find the Meanings and Definitions of Words at Dictionary.com.
Testing Chapter 7 Study Guide.