

Questions to think about! From the Spec: BTEC NEW Unit 4 Ass 1 TMC 1.2. Playlist for this assignment. How the Collaboration Between HR and Finance Can Improve Business. HR and finance's ability to work together and understand each other's role can be critical to your organization.
In many organizations, human resources and finance are two distinct business areas. Finance helps allocate resources to support an organization's goals, maintaining a balance between costs and revenue. HR hires, recruits and motivates people to advance those same goals.
YouTube's Copyright System Isn't Broken. The World's Is. Monkey selfie copyright dispute. Selfies by Celebes crested macaques One of the monkey selfies at issue in the dispute The monkey selfie copyright dispute is a series of disputes about the copyright status of selfies taken by Celebes crested macaques using equipment belonging to the British nature photographer David Slater.
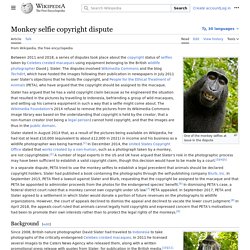
The disputes involve Wikimedia Commons and the blog Techdirt, which have hosted the images following their publication in newspapers in July 2011 over Slater's objections that he holds the copyright, and People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA), who have argued that the macaque should be assigned the copyright. Slater has argued that he has a valid copyright claim, as he engineered the situation that resulted in the pictures by travelling to Indonesia, befriending a group of wild macaques, and setting up his camera equipment in such a way that a "selfie" picture might come about. Background[edit] The other disputed image, a full-body "selfie" Copyright issues[edit] Expert opinions[edit] About CC Licenses. Creative Commons licenses give everyone from individual creators to large institutions a standardized way to grant the public permission to use their creative work under copyright law.
From the reuser’s perspective, the presence of a Creative Commons license on a copyrighted work answers the question, “What can I do with this work?” There are six different license types, listed from most to least permissive here: CC BY: This license allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, so long as attribution is given to the creator.
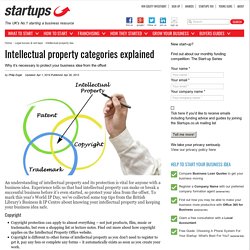
The license allows for commercial use. CC BY includes the following elements: BY. Intellectual Property Office. Intellectual property and your work. Having the right type of intellectual property protection helps you to stop people stealing or copying: the names of your products or brands your inventions the design or look of your products things you write, make or produce Copyright, patents, designs and trade marks are all types of intellectual property protection.
You get some types of protection automatically, others you have to apply for. Intellectual property is something unique that you physically create. An idea alone is not intellectual property. Owning intellectual property You own intellectual property if you: Intellectual property categories explained - Startups.co.uk: Starting a business advice and business ideas. By Philip Eagle Updated: Apr 1, 2014 Published: Apr 26, 2013.
Wipo pub 450. Design right. ‘Design right’ automatically protects your design for 10 years after it was first sold or 15 years after it was created - whichever is earliest.
You can use it to stop someone copying your design. Register a design. Intellectual property: Copyright, trademarks and patents. Intellectual property (or IP) refers to creative work which can be treated as an asset or physical property.
Intellectual property rights fall principally into four main areas; copyright, trademarks, design rights and patents. Copyright Copyright applies to work that is recorded in some way; rights exist in items such as literary, artistic, musical and dramatic work as well as films, sound recordings and typographical arrangements. It gives the author specific rights in relation to the work, prohibits unauthorised actions, and allows the author to take legal action against instances of infringement or plagiarism. Please see our pages: Copyright law, the Berne Convention, or UK copyright law for more details of the protection. Trademarks. What is Intellectual Property? Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce.
IP is protected in law by, for example, patents, copyright and trademarks, which enable people to earn recognition or financial benefit from what they invent or create. Intellectual Property 101 – Gutwein IP Microsite. Trademarks – Protecting Identifiers Trademarks protect words, names, symbols or designs used to identify your goods or services.

Created to protect the public from deception as to the origin or quality of goods and services, trademarks can help you defend against counterfeit activity while building value around your brand. Intellectual Property 101: What It Is and Why I Should Protect It. Startups and early stage companies have many things to focus on and worry about, and the protection of intellectual property (IP) is likely not on the top of the list, if it’s on the list at all.

Why? Because a business startup is focused on sales and revenue, cash flow and profits, and quite frankly sometimes just surviving the initial launch and startup of their new business. The marketplace is more competitive than ever, with consumers having so many choices among all the emerging technologies and businesses and the points of differentiation becoming more subtle. Why Should Startups Care About Intellectual Property? Sales…marketing…revenue…getting more customers…growing my company – these are all at the top of the mind of startups and early stage companies and rightfully so, because without revenue, there will be no company. However, often times "intellectual property" is among the last things that an early stage company thinks about…and it shouldn't be.
What is Intellectual Property? Intellectual property, or "IP", is often misunderstood and confused – to some, everything seems to be protected by a patent, when it may actually be a trademark that applies to the situation or vice versa. The four primary categories of IP – trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and patents – are often mistaken for one another. Intellectual Property 101: Patents and Trademarks. Ideas are a difficult thing to protect because they are so easily imitated or copied. We don't yet live in the world of Star Trek where you can just have a replicator instantly make you an exact duplicate of physical things like a cup of coffee or some exotic alien delicacy, but we can easily duplicate the ideas of others, such as copying a piece of written material, using a similar brand name, or creating a product in imitation of someone else's product.
Products take time to develop and bring to market. Once a product has been developed, it can be imitated in a fraction of the time. It would be easy for other companies to create competitive products or services within a very short period of time. For example, consider the recent "employee discount" advertising campaigns from the major auto manufacturers. On the other hand, consider the innovative Segway transportation device. Intellectual Property 101: What Your Business Needs To Know About Trademark Law. Co-author Teri Karobonik contributed to this post* When you think of a “trademark” you may think of a logo (Apple’s apple logo) or a product or service name (Forbes).
You may even assume that trademarks are only a concern for internationally famous brands like fashion companies (Prada) and fast food (Pizza Hut). In reality, trademark protection extends further than logos and can cover everything from sounds (the 20th Century Fox Fanfare before the opening movie credits), to colors (the “green” on a John Deere tractor), to the design of a taco shop. Although many of the common examples you hear about are large corporate brands, understanding trademark protection is just as important for startups, independent creators, and small business. Contract - Express & Implied Terms (GCSE) However, sometimes a term which has not been mentioned by either party will nonetheless be ‘included’ in the contract, often because the contract doesn’t make commercial sense without that term.
Terms like this are called implied terms, and there are two main types: Terms implied by statute: the Sale of Goods Act 1979. The key provisions are: Section 12: the person selling the goods has to have the legal right to sell them. Employment contract terms. What is the difference between implied and express terms? Force Majeure. Contract and Tender Process. 5 Common Types of Business Contracts. 4 Common Types of Construction Contracts. A construction contract provides a legal binding agreement, for both the owner and the builder, that the executed job will receive the specific amount of compensation or how the compensation will be distributed. There are several types of construction contracts used in the industry, but there are certain types of construction contracts preferred by construction professionals. Types of Commercial Contracts Law and Legal Definition.
Indemnity - Definition, Examples & Agreements in Business Law. The word indemnity means security or protection against a financial liability. It typically occurs in the form of a contractual agreement made between parties in which one party agrees to pay for losses or damages suffered by the other party. In corporate law, an indemnity agreement serves to hold Board Directors and company executives free from personal liability if the company becomes sued or suffers damages. What is indemnity? definition and meaning - BusinessDictionary.com. Warranty Vs. Guarantee. Warranty. What is a warranty? definition and meaning - BusinessDictionary.com. What is a Warranty and Indemnity? - Definition from Divestopedia. The difference between a warranty and an indemnity – CNP Law.