

Overpopulation, overconsumption – in pictures. What is BIOMASS? Within this definition, biomass for energy can include a wide range of materials.
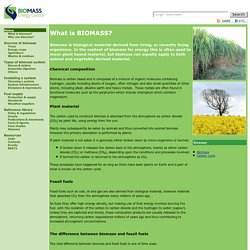
The realities of the economics mean that high value material for which there is an alternative market, such as good quality, large timber, are very unlikely to become available for energy applications. However there are huge resources of residues, co-products and waste that exist in the UK which could potentially become available, in quantity, at relatively low cost, or even negative cost where there is currently a requirement to pay for disposal. There are five basic categories of material: Virgin wood, from forestry, arboricultural activities or from wood processing Energy crops: high yield crops grown specifically for energy applications Agricultural residues: residues from agriculture harvesting or processing Food waste, from food and drink manufacture, preparation and processing, and post-consumer waste Industrial waste and co-products from manufacturing and industrial processes.
Population Change. 09 ecology notes part 1. Earth Floor: Biomes. There are many different kinds of plants and animals on the Earth, but only certain kinds are naturally found at any particular place.

(We are not counting zoos here!) For example, cacti are found in the desert, polar bears are found in the Arctic, and elephants are found in central Africa and India. So, why don't people living in south Texas have to be on the lookout for snow leopards, or why don't kids in Minnesota have to worry about finding giant boa constrictors in their back yards? It is because these animals are not adapted to live in the average weather conditions found in Texas or Minnesota. These average weather conditions, such as the range of temperature and rainfall that typically occur in a particular location like Minnesota, are called the climate of that location.
Plants and animals don't live in isolation, but they live together with other plants and animals in an interdependent group called an ecological community. Next. Book Trailer : Short Version. Teacher.scholastic.com/products/scholasticprofessional/authors/pdfs/duke_sample_pages.pdf. Mark and recapture. Jackdaw with a numbered aluminum ring on its left tarsus Marked Chittenango ovate amber snail.
Mark and recapture is a method commonly used in ecology to estimate an animal population's size. A portion of the population is captured, marked, and released. Later, another portion is captured and the number of marked individuals within the sample is counted. Since the number of marked individuals within the second sample should be proportional to the number of marked individuals in the whole population, an estimate of the total population size can be obtained by dividing the number of marked individuals by the proportion of marked individuals in the second sample.
Another major application for these methods is in epidemiology,[2] where they are used to estimate the completeness of ascertainment of disease registers. Field work related to mark-recapture[edit] Typically a researcher visits a study area and uses traps to capture a group of individuals alive. Notation[edit] Let Derivation[edit] ). Recycled crafts. 10 Fascinating Facts About Grasshoppers. Grasshoppers are both beloved characters in children's stories and despised pests that plague farmers and ranchers.
Their songs contribute to the soundtrack of summer. Although grasshoppers are one of the insects we encounter nearly every day, most people know very little about them. Learn more about these fascinating creatures, starting with these 10 facts about grasshoppers. 1. Grasshoppers and locusts are the same thing.Mention grasshoppers, and many people recall pleasant childhood memories of trying to catch them in meadows or backyards. Say the word locusts, however, and most people think of historic plagues of pests, raining down on farm fields and eating every plant in sight. 2. 3. They can detect differences in intensity and rhythm, but not pitch. 4. 5. 6. Keystone species (ecology) Wolves Impact Everything! 9f44fdee15143bbb809e516cecc658e9-original. Ecology. Quick Ecology for Dummies. Ecology is the science of how everything is connected and intertwined with each other.
The stars, universe, energy, climate, trees and flowers, bacteria, genetics, you and I. Ecology is the cytoplasm of life containing all the different sciences, a holistic perspective to our existence. It seems like an impossible task for anyone to learn and understand all the intricacies of it, but everyone can learn and understand the basic concepts. Main concepts The field of ecology can comprise everything existing, and understanding my limitations this once, I have chosen to narrow down this article to some of the important cycles and interactions in nature. Photosynthesis The green plants are the producers on earth, and the rest of us are consumers. The sugar produced (C6H12O6) is stored energy from the sun, and later when it is released, we can feel it as the heat around a camp fire, or the received energy from a chocolate bar during a hike. Energy Flow Nutrient and Mineral Cycles Carbon Cycle.
10 suggestions to strengthen Ecology.