

Protoceratops dinosaurs' facial features including frills formed part of sexual displays. The horns, frills and crests of dinosaurs have helped cement their reputation as heavily armed, and armoured, beasts in the public imagination.
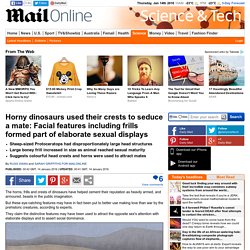
But these eye-catching features may have in fact been put to better use making love than war by the prehistoric creatures, according to experts. They claim the distinctive features may have been used to attract the opposite sex's attention with elaborate displays and to assert social dominance. Fossil Definition and Information.
Fossils are precious gifts from the geologic past: signs and remains of ancient living things preserved in the Earth's crust.
The word has a Latin origin, from fossilis meaning "dug up," and that remains the key attribute of what we label as fossils. Most people, when they think of fossils, picture skeletons of animals or leaves and wood from plants, all turned to stone. But geologists have a more complicated view, so let's dig into the subject. The Different Kinds of Fossils Fossils can include ancient remains, the actual bodies of ancient life.
Body fossils, or mineralized organisms—dinosaur bones and petrified wood and everything else like them—are the best known kind of fossil. The tracks, nests, burrows and feces of ancient living things are another category called trace fossils or ichnofossils. Finally there are chemical fossils or chemofossils, remains that consist of mere organic compounds or proteins found in a body of rock. What Becomes Fossils? History of the Earth - EvoWiki. From EvoWiki Painting of a late Jurassic Scene on one of the large island in the Lower Saxony basin in northern Germany.
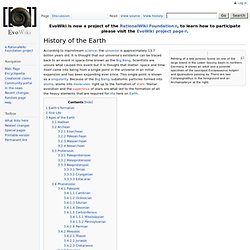
It shows an adult and a juvenile specimen of the sauropod Europasaurus holgeri and Iguanodons passing by. There are two Compsognathus in the foreground and an Archaeopteryx at the right. According to mainstream science, the universe is approximately 13.7 billion years old. It is thought that our universe's existence can be traced back to an event in space-time known as the Big Bang. Artist's conception of a protoplanetary disk Artist's impression from 2005 of the asteroid belt and a hypothetical outer planet (now known to really exist as HD 69830 d) Our Earth formed quite some time after the universe did, scientists believe, based on current evidence, that it formed around 4.57 billion years ago. Foundational Concepts : Introduction to Dating Methods.
Timeline of evolutionary history of life. Timeline of natural history. History of the Earth. The history of the Earth concerns the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.[1][2] Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's past.
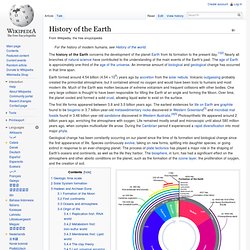
The age of Earth is approximately one-third of the age of the universe. An immense amount of biological and geological change has occurred in that time span. The first life forms appeared between 3.8 and 3.5 billion years ago. The earliest evidences for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland[3] and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia.[4][5] Photosynthetic life appeared around 2 billion years ago, enriching the atmosphere with oxygen. Life remained mostly small and microscopic until about 580 million years ago, when complex multicellular life arose. Geologic time scale[edit] Geologic time scale. The geologic time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological measurement that relates stratigraphy to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred throughout Earth's history.
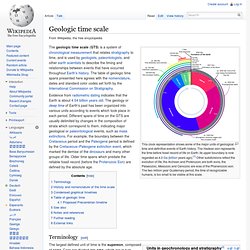
The table of geologic time spans presented here agrees with the nomenclature, dates and standard color codes set forth by the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Evidence from radiometric dating indicates that the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The geology or deep time of Earth's past has been organized into various units according to events which took place in each period. Different spans of time on the GTS are usually delimited by changes in the composition of strata which correspond to them, indicating major geological or paleontological events, such as mass extinctions. Terminology[edit]
AMNH, NY: Permanent Exhibitions. The Biodiversity and Environmental Halls offer a vivid and inspiring vision of the spectacular beauty and abundance of life on Earth.
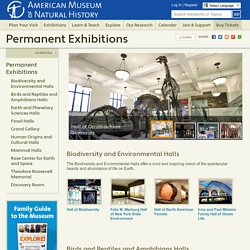
The Museum’s Birds Halls portray the wide variety of avian life on the planet, and the Hall of Reptiles and Amphibians reviews the anatomy, behavior, and various adaptations of these vertebrates. The Earth and Planetary Sciences halls showcase remarkable specimens, including meteorites, minerals, and rare gems, that offer clues about the origins of our solar system and the dynamic processes of our planet. One of the premier attractions in New York City is the Museum's series of fossil halls, including its two famed dinosaur halls in the David H. Koch Dinosaur Wing, as well as the Lila Acheson Wallace Wing of Mammals and Their Extinct Relatives. Sediment Samples from Japanese Lake Extend Carbon Dating Timeline.
Tighter carbon dates for the remains of Neanderthals could help explain why they became extinct.
Image: J. Reader/SPL. Climate records from a Japanese lake will improve the accuracy of dating techniques, which will probably help shed light on some mysteries such as the extinction of the Neanderthals as well as paradoxes that have arisen due to dating. Bad News: DNA Has Limited Half-Life. Michael Harper for redOrbit.com — Your Universe Online Despite its status as a best selling novel and blockbuster hit, it turns out Jurassic Park was based on a fundamentally flawed premise–bad news for dinoDNA researchers.
After drilling through some old bird bones, palaeogeneticists in Copenhagen and Australia have discovered DNA can hardly survive 1,000 years, let alone make it through the millions of years that separate us from our reptilian overlords. Led by Morten Allentoft at the University of Copenhagen and Michael Bunce at Murdoch University in Perth, Australia, a group of palaeogeneticists studied many bones from a Moa bird fossil to understand just how feasible it is to clone a Raptor these days.
“We’ve been permanently plagued by this Jurassic Park myth that’s been kicking around since the early nineties,” Bunce told the Sydney Morning Herald, reports the Telegraph. Celebrate National Fossil Day On October 17. October 14, 2012 April Flowers for redOrbit.com – Your Universe Online October 17, 2012 is National Fossil Day, sponsored by the National Park Service (NPS) and the American Geological Institute (AGI).
BBC Nature - Wildlife Finder - Fossils. The Robotic Dinosaurs That Could Change Paleontology Forever. Could Tyrannosaurus rex run down its prey or did the eight-ton “tyrant lizard” shuffle its feet on the ground like an elephant?
How did large dinosaurs lay eggs? Could they kneel down or did they simply drop off their offspring from 2 1/2 stories in the air and hope they survived? Darwin's lost fossils: Treasures that helped shape theory of evolution found by chance in dusty cabinet. By Tamara Cohen Updated: 08:26 GMT, 17 January 2012 For 160 years they lay forgotten in a dusty cabinet, lost to science because they had been hastily filed away. Welcome to Understanding Geologic Time. Fossil resources, guides and information by Discovering Fossils. Contact details Follow us on: news ● discuss ● share Join us on a fossil hunt Left: A birthday party with a twist - fossil hunting at Peacehaven. Right: A family hold their prized ammonite at Beachy Head.
Fossil Sites.