

Hyperion (mythology) Hyperion's son Helios was referred to in early mythological writings as Helios Hyperion (Ἥλιος Ὑπερίων, "Sun High-one").
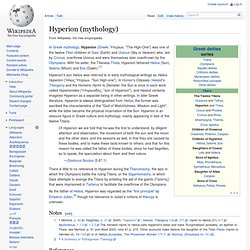
In Homer's Odyssey, Hesiod's Theogony and the Homeric Hymn to Demeter, the Sun is once in each work called Hyperionides (Ὑπεριωνίδης, "son of Hyperion"), and Hesiod certainly imagines Hyperion as a separate being in other writings. Helios. Names[edit] Greek mythology[edit] Helios in his chariot, early 4th century BC, Athena's temple, Ilion The best known story involving Helios is that of his son Phaëton, who attempted to drive his father's chariot but lost control and set the earth on fire.
Helios was sometimes characterized with the epithet Helios Panoptes ("the all-seeing"). Electryone. It is speculated by some that she was possibly a goddess of the morning, or of man's waking sense, which causes him to wake up in the morning; the Doric form of her name is akin to the Greek word for "rooster" (Alectrona, the feminine genitive of Αλεκτορ, Alektor, the Greek word for "rooster"), while the Greek form Electryone is akin to the word for "amber" (Ἠλέκτρα, Elektra), as in the amber color of sunrise (as opposed to sunset, implied by Helios being her father); naturally, either of which would be an appropriate name for a solar goddess.
A marble tablet from the 3rd century BC found in Ialyssus contains an inscription about the regulations for visitors to the temple of Alectrona.[2] Notes[edit] References[edit] Apollo. Apollo (Attic, Ionic, and Homeric Greek: Ἀπόλλων, Apollōn (GEN Ἀπόλλωνος); Doric: Ἀπέλλων, Apellōn; Arcadocypriot: Ἀπείλων, Apeilōn; Aeolic: Ἄπλουν, Aploun; Latin: Apollō) is one of the most important and complex of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology.
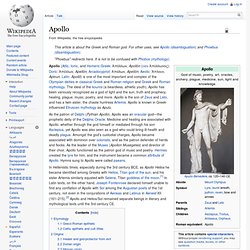
The ideal of the kouros (a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun, truth and prophecy, healing, plague, music, poetry, and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Etymology Tetradrachm from the Illyro-Paeonian region, representing Apollo The etymology of Apollo is uncertain. Several instances of popular etymology are attested from ancient authors. A Luwian etymology suggested for Apaliunas makes Apollo "The One of Entrapment", perhaps in the sense of "Hunter".[11] Greco-Roman epithets. Eos. Etymology[edit] Greek literature [edit] From The Iliad: Now when Dawn in robe of saffron was hastening from the streams of Oceanus, to bring light to mortals and immortals, Thetis reached the ships with the armor that the god had given her.
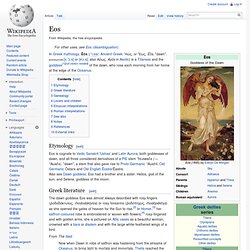
—Iliad xix.1 Quintus Smyrnaeus pictured her exulting in her heart over the radiant horses (Lampus and Phaëton) that drew her chariot, amidst the bright-haired Horae, the feminine Hours, climbing the arc of heaven and scattering sparks of fire.[5] She is most often associated with her Homeric epithet "rosy-fingered" (rhododactylos), but Homer also calls her Eos Erigeneia: That brightest of stars appeared, Eosphoros, that most often heralds the light of early-rising Dawn (Eos Erigeneia). Hesiod wrote: And after these Erigeneia ["Early-born"] bore the star Eosphoros ("Dawn-bringer"), and the gleaming stars with which heaven is crowned. Genealogy[edit] Lovers and children[edit] Etruscan interpretations[edit] Roman interpretations[edit] See also[edit] Dawn goddess. Greek mythology. Greek mythology is explicitly embodied in a large collection of narratives, and implicitly in Greek representational arts, such as vase-paintings and votive gifts.
Greek myth attempts to explain the origins of the world, and details the lives and adventures of a wide variety of gods, goddesses, heroes, heroines, and mythological creatures. These accounts initially were disseminated in an oral-poetic tradition; today the Greek myths are known primarily from Greek literature. Archaeological findings provide a principal source of detail about Greek mythology, with gods and heroes featured prominently in the decoration of many artifacts. Geometric designs on pottery of the eighth century BC depict scenes from the Trojan cycle as well as the adventures of Heracles.
Sources Literary sources The poetry of the Hellenistic and Roman ages was primarily composed as a literary rather than cultic exercise. Archaeological sources Survey of mythic history.