

Bisphosphonate. Basic structure of a bisphosphonate on top.
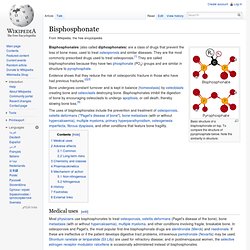
To compare the structure of pyrophosphate below. Note the similarity in structure. Bisphosphonates (also called diphosphonates) are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone mass, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis.[1] They are called bisphosphonates because they have two phosphonate (PO 3) groups and are similar in structure to pyrophosphate. Evidence shows that they reduce the risk of osteoporotic fracture in those who have had previous fractures.[2][3] Bone undergoes constant turnover and is kept in balance (homeostasis) by osteoblasts creating bone and osteoclasts destroying bone.
Medical uses[edit] Most physicians use bisphosphonates to treat osteoporosis, osteitis deformans (Paget's disease of the bone), bone metastasis (with or without hypercalcaemia), multiple myeloma, and other conditions involving fragile, breakable bone. Adverse effects[edit] Rotten Egg Gas May Be Key to Human Longevity. A gaseous compound called hydrogen sulfide may play a wide-ranging role in staving off aging, according to a team of scientists from University of South China, Hunan.
Hydrogen sulfide may have an effect on the age-related gene Klotho to promote longevity. Klotho can improve longevity by inhibiting IIS signaling, inducing FOXO (forkhead box proteins) derepression, and decreasing angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress (Zhang Y et al) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a colorless, poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. A few breaths of air containing high levels of this gas can cause death. Lower, longer-term exposure can cause eye irritation, headache, and fatigue. Human body produces small amounts of hydrogen sulfide and uses it as a signaling molecule. “Hydrogen sulfide is produced within the human body, and has a variety of important physiological effects. CAN DEPRENYL (SELEGILINE) EXTEND HUMAN LIFESPAN? By Ben Best (First section written mostly in the mid-1990s.)

Several years ago L-deprenyl (selegiline) was the darling drug of life-extensionists. Some negative Parkinson's Disease studies then caused Deprenyl to fall into disrepute among both life-extensionists and conventional gerontologists. But recent studies merit a re-evaluation of deprenyl by life extensionists. And there are good reasons why the negative Parkinson's Disease studies which have discouraged gerontologists should be considered irrelevant for lifespan increase. In 1988 Dr. The reasons for this discrepancy may be because the Canadians had used Fischer-344 rats which have a life expectancy of 28 months. In 1992 the Japanese researcher K.Kitani doubled the dose of deprenyl used by the previous researchers to 0.5mg/kg in a lifespan study on Fischer-344 rats beginning at 18 months and 24 months.
Aging slowed in mice with supplement mix - Health. It might be possible to cure aging, say scientists who've found that lab mice get smarter and more agile as they age when fed a mix of nutritional supplements.
The diet and supplement plan isn't a conventional "cure. " But the animal results at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., illustrate how investigators aim to slow down the aging process to avoid the physical and mental declines that often come as more candles are added to the birthday cake. At Prof. David Rollo's biology laboratory, mice that ate bagel bits soaked in a cocktail of supplements such as B vitamins, vitamin D, ginseng and garlic lived longer than those not taking the special mice chow. "If you put them on a supplement, they actually learn better as they age," Rollo said. Scientists Halt Aging in Mice by Tweaking Activity in Almond-Sized Brain Region : Science/Tech. (Photo : Regis Duvigna/Reuters) Scientists have discovered for the first time that the body's aging switch may be located in the brain region that controls growth, reproduction and metabolism.
The latest study, published online in the journal Nature, revealed that the brain's hypothalamus, an almond-sized brain region located just above the brain stem deep in the brain, may be the body's "fountain of aging". Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University believe their discovery could lead to new treatments for extending lifespan and combating age-related diseases "Scientists have long wondered whether aging occurs independently in the body's various tissues or if it could be actively regulated by an organ in the body," senior author Dr. Dongsheng Cai, a professor of molecular pharmacology at Einstein, said in a news release. The hypothalamus is known to play essential roles in growth, development, reproduction and metabolism.
Featured Video : Dr. Rhodiola Extract Extends Lifespan in Drosophila, Scientists Find. The herbal extract of a yellow-flowered perennial plant known as Golden Root has been shown in a study reported in the journal PLoS ONE to extend the lifespan of fruit flies by 24 percent.
Rhodiola rosea has been used for centuries by Scandinavians and Russians to reduce stress. This image shows Rhodiola in the Berlin Botanical Garden Scientists at the University of California Irvine have discovered that Golden Root (Rhodiola rosea) works in a manner completely unrelated to dietary restriction and affects different molecular pathways. “This is significant, because dietary restriction is considered the most robust method of improving lifespan in laboratory animals. And scientists have been scrambling to identify compounds that can mimic its effects,” explained study senior author Dr Mahtab Jafari.