

Single SideBand Modulation. Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) modulation was the basis for all long distance telephone communications up until the last decade.
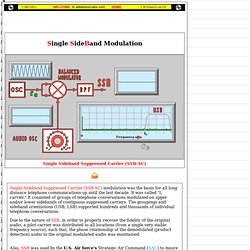
It was called "L carrier. " It consisted of groups of telephone conversations modulated on upper and/or lower sidebands of contiguous suppressed carriers. The groupings and sideband orientations (USB, LSB) supported hundreds and thousands of individual telephone conversations. Due to the nature of-SSB, in order to properly recover the fidelity of the original audio, a pilot carrier was distributed to all locations (from a single very stable frequency source), such that, the phase relationship of the demodulated (product detection) audio to the original modulated audio was maintained. Also, SSB was used by the U.S. The main reason-SSB-is superior to-AM,-and most other forms of modulation, is due to the following: SSB-ver-AM(1) Since the carrier is not transmitted, there is a reduction by 50% of the transmitted power (-3dBm).
Single Side-Band AM. Introduction to Naval Weapons Engineering Objectives State the following regarding single side-band (SSB) systems: Effect on efficiency and bandwidth Required modification to equipment Conventional AM This is how a typical AM system transmitter works: The information signal is mixed with the carrier signal and produces the full AM signal to be transmitted.

The receiver: Then must process out the carrier by demodulation to reproduce the information signal. Problems with Conventional AM Conventional AM transmission has several problems: Bandwidth is wasted by having two identical side-bands on either side of the carrier The efficiency is limited to 33% to prevent distortion in the receiver when demodulating. Single Side-Band The concept of single side-band (SSB) is very simple: if you don't need two side-bands, get rid of one!
Here's what the SSB transmitter looks like: Note that the band pass filter has removed the lower side-band (LSB) and the carrier from the spectrum. What is SSB? SSB What is Single Side Band - Introduction to Single Side Band Operating For The New Ham Radio Operator! Single-sideband modulation. Illustration of the spectrum of AM and SSB signals.
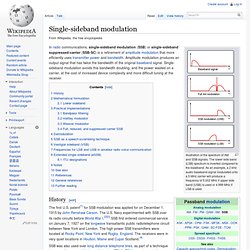
The lower side band (LSB) spectrum is inverted compared to the baseband. As an example, a 2 kHz audio baseband signal modulated onto a 5 MHz carrier will produce a frequency of 5.002 MHz if upper side band (USB) is used or 4.998 MHz if LSB is used. History[edit] The first U.S. patent[1] for SSB modulation was applied for on December 1, 1915 by John Renshaw Carson. The U.S. SSB was also used over long distance telephone lines, as part of a technique known as frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). Amateur radio operators began serious experimentation with SSB after World War II. Mathematical formulation[edit] Single-sideband has the mathematical form of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) in the special case where one of the baseband waveforms is derived from the other, instead of being independent messages: where is the message, is its Hilbert transform, and is the radio carrier frequency.
Coherent demodulation of to recover . And axis. When .