

Savanna Explorer - Northern Australia - All Regions - Landscapes & Climate - Landscapes. Landscapes can be complex to describe.

This is because they can be described at different scales using different variables to describe them. You can describe a landscape by looking at its geography or topography such as the hills, rivers and gullies. You may also look for signs and stories about how these places have been impacted upon by humans. This can be talked about as the cultural landscape. The landscape of the tropical savannas can be described in many ways. The tropical savannas region has many diverse landscapes. Evolution Australian savannas have been evolving for many millions of years. Because of a long history of evolution, savannas are highly complex and diverse ecosystems. The savannas also have many different animal species, both vertebrate and invertebrate. Fire has influenced the nature of the savannas over the course of their evolution. Landforms Most of the savanna region is less than 500 m above sea-level, with local relief generally less than 100 m.
Savanna Biomes. A savanna is a rolling grassland scattered with shrubs and isolated trees, which can be found between a tropical rainforest and desert biome.

Not enough rain falls on a savanna to support forests. Savannas are also known as tropical grasslands. They are found in a wide band on either side of the equator on the edges of tropical rainforests. Encyclopedia.com articles about savanna. Savanna. From New World Encyclopedia A savanna or savannah is a tropical or subtropical woodland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close, above a continuous tall grass understory.
The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses. There are three basic subcategories of savanna-wet, dry, and thornbush—depending on the length of the dry season, which can vary from three to five months, five to seven months, or even longer. Alternative subdivisions include woodland savanna, tree savanna, shrub savanna, and grass savanna.
Some classification systems also recognize a grassland savanna from which trees are absent. Regardless of subcategory, all savannas can be defined as tropical or subtropical vegetation types with a continuous grass cover occasionally interrupted by trees and shrubs. Definitions and distributions Savanna ecoregions Tree clearing. Tropical Savanna Biome: Video Resource. Savannas are the tropical version of the temperate grasslands.

Most savannas are caused by climatic patterns where there is a strong dry season for a large part of the year. Few trees survive in these regions, but most savannas do have some form of trees that scatter the landscape. If you look at the map below you'll realize that a large part of Africa, nearly half its landmass, is covered in some sort of savanna. Large tracks of savanna are also found in South America, India and Australia.
Climate: Tropical Savannas. Introduction: Tropical savannas or grasslands are associated with the tropical wet and dry climate type (Koeppen’s Aw), but they are not generally considered to be a climatic climax.
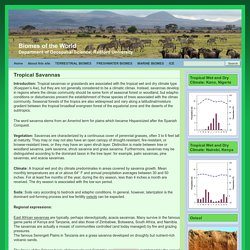
Instead, savannas develop in regions where the climax community should be some form of seasonal forest or woodland, but edaphic conditions or disturbances prevent the establishment of those species of trees associated with the climax community. Seasonal forests of the tropics are also widespread and vary along a latitudinal/moisture gradient between the tropical broadleaf evergreen forest of the equatorial zone and the deserts of the subtropics. The word savanna stems from an Amerind term for plains which became Hispanicized after the Spanish Conquest. Vegetation: Savannas are characterized by a continuous cover of perennial grasses, often 3 to 6 feet tall at maturity. Climate: A tropical wet and dry climate predominates in areas covered by savanna growth. Regional expressions: Edaphic Subclimaxes: