

SHR (operating system) The current unstable and testing release is for Openmoko's Neo 1973 and FreeRunner, both having an ARM architecture.
At the moment SHR Core is being ported to Nexus S, GTA04 and Nokia N900 devices. The following software packages are shipped and pre-installed by default: Bada. Bada (stylized as bada; Korean: 바다) was an operating system for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers.
It was developed by Samsung Electronics. Its name is derived from "바다 (bada)", meaning "ocean" or "sea" in Korean. OpenZaurus. OpenZaurus is a defunct embedded operating system for the Sharp Zaurus personal mobile tool PDA.
History[edit] The OpenZaurus project was revamped completely, becoming Debian-based built from source, from the ground up. Due to the change in direction, OpenZaurus became quite similar to other embedded Debian-based distributions, such as Familiar for the iPAQ. Openmoko Linux. For the project that includes both hardware and software development, see Openmoko.
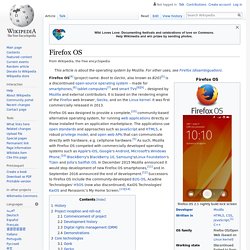
Openmoko Linux is an operating system for smartphones developed by the Openmoko project. It is based on the Ångström distribution, comprising various pieces of free software.[1] The main targets of Openmoko Linux were the Openmoko Neo 1973 and the Neo FreeRunner. Furthermore there were efforts to port the system to other mobile phones.[2] Firefox OS. History[edit] Firefox OS was publicly demonstrated in February 2012, on Android-compatible smartphones.[15][16] By December 16, 2014, fourteen operators in 28 countries throughout the world offered Firefox OS phones.[17] In January 2016 Mozilla announced that Firefox OS would power Panasonic's UHD TVs (as previously announced Firefox OS "would pivot to connected devices").[21] In September 2016 Mozilla announced that work on Firefox OS had ceased, and that all B2G-related code would be removed from mozilla-central.[22] Project inception and roll-out[edit] Commencement of project[edit]
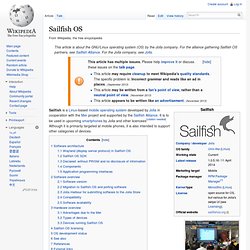
Sailfish OS. Software architecture[edit] The architecture is: Hardware.
Tizen. The Tizen Association was formed to guide the industry role of Tizen, including requirements gathering, identifying and facilitating service models, and overall industry marketing and education.[5] Members of the Tizen Association represent every major sector of the mobility industry and every region of the world.
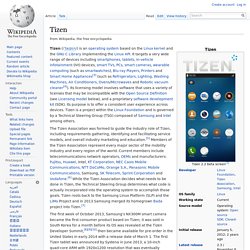
Current members include telecommunications network operators, OEMs and manufacturers: Fujitsu, Huawei, Intel, KT Corporation, NEC Casio Mobile Communications, NTT DoCoMo, Orange S.A., Panasonic Mobile Communications, Samsung, SK Telecom, Sprint Corporation and Vodafone.[6] While the Tizen Association decides what needs to be done in Tizen, the Technical Steering Group determines what code is actually incorporated into the operating system to accomplish those goals. Tizen roots back to the Samsung Linux Platform (SLP) and the LiMo Project and in 2013 Samsung merged its homegrown Bada project into Tizen.[7] System architecture[edit] Overview[edit] Open environment[edit]
MeeGo. MeeGo was a Linux-based free mobile operating system project resulting from the fusion of Intel's Moblin and Nokia's Maemo operating systems.[1] Primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market, MeeGo was designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet computers, mobile computing and communications devices, in-vehicle infotainment devices, SmartTV / ConnectedTV, IPTV-boxes, smart phones, and other embedded systems.[2] MeeGo is currently hosted by the Linux Foundation.[3] History[edit] MeeGo was first announced at Mobile World Congress in February 2010 by Intel and Nokia in a joint press conference.
Moblin. Moblin, short for 'mobile Linux', was an open source operating system and application stack for Mobile Internet Devices (MIDs), netbooks, nettops and embedded devices.[1] It first merged with the Maemo effort and then both were integrated with the MeeGo project.
Nokia stopped all MeeGo development after switching to Windows Phone. Intel discontinued work on MeeGo using Tizen instead. After the MeeGo project was scrapped, a group of people left Nokia and formed their own company, Jolla OY. Maemo. Maemo is a software platform developed by Nokia and then handed over to Hildon Foundation for smartphones and Internet tablets.[2] It is based on the Debian GNU/Linux distribution.
The platform comprises the Maemo operating system and the Maemo SDK. The user interface in Maemo 4 is similar to many hand-held interfaces, and features a "home" screen, which acts as a central point from which all applications and settings are accessed. WebOS. WebOS also known as LG webOS, Open webOS or HP webOS, is a Linux kernel-based operating system for smart TVs,[1] and formerly a mobile operating system.[2] Initially developed by Palm, which was acquired by Hewlett-Packard, the operating system was later sold to LG Electronics.
Through all iterations of the operating system (Palm, HP and now LG) the official name has been consistently stylized as webOS (lowercase 'w').[3][note 1] Palm launched WebOS in January 2009, then called Palm WebOS. Various versions of WebOS have been featured on several devices, including Pre, Pixi, and Veer phones and the HP TouchPad tablet. The latest version, 3.0.5, was released on January 12, 2012. Replicant (operating system) An example of phone information in Replicant, including a brief hardware description The software that was in charge of handling the communication with the modem (which is called Radio Interface Layer – RIL) was then replaced by free code, thus making the telephony part usable.
A library handling the GPS was then adapted from free code that was originally written for another phone and permitted the HTC Dream to have GPS working with Replicant.[13] Android (operating system) Free and open-source operating system for mobile devices, developed by Google Initially developed by Android Inc., which Google bought in 2005, Android was unveiled in 2007, with the first commercial Android device launched in September 2008. The current stable version is Android 10, released on September 3, 2019. The core Android source code is known as Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is primarily licensed under the Apache License. This has allowed variants of Android to be developed on a range of other electronics, such as game consoles, digital cameras, PCs and others, each with a specialized user interface.
Some well known derivatives include Android TV for televisions and Wear OS for wearables, both developed by Google. Mobile Linux Distributions. Linux Distributions. Unix & Linux.