

Www.proofpoint.com/downloads/Proofpoint-Gartner-Magic-Quadrant-for-Secure-Email-Gateways-2010.pdf. Mobile Armor: Your Data. Secure. Anywhere. Anytime. Check Point Positioned in Leaders' Quadrant for Mobile Data Protection. Www.symantec.com/content/en/us/about/media/industryanalysts/Gartner_MQ_mobiledataprotection_Sept10.pdf. Www.paloaltonetworks.com/literature/whitepapers/Gartner-Magic-Quadrant2010.pdf. Computer Security: Protecting ...
Www.forum-intrusion.com/Buyers_Guide.pdf. Barracuda Networks - Worldwide leader in email and Web security. Acceptable use policy. In some cases a fair usage policy applied to a service allowing nominally unlimited use for a fixed fee simply sets a cap on what may be used, intended to allow normal usage but prevent what is considered excessive.
For example, users of an "unlimited" broadband Internet service may be subject to suspension, termination, or bandwidth limiting for usage which is "continually excessive, unfair, affects other users' enjoyment of the broadband service, or is not consistent with the usage typically expected on a particular access package".[6] The policy is enforced directly, without legal proceedings. Terminology[edit] AUP documents are similar to and often serve the same function as the Terms of Service document (e.g., as used by Google Gmail and Yahoo!)
, although not always. In the case of IBM.com for instance, the Terms of Use are about the way in which IBM presents the site, how they interact with visitors of the site and little to no instruction as to how to use the site. Single sign-on. Single sign-on (SSO) is a property of access control of multiple related, but independent software systems.
With this property a user logs in once and gains access to all systems without being prompted to log in again at each of them. Conversely, single sign-off is the property whereby a single action of signing out terminates access to multiple software systems. As different applications and resources support different authentication mechanisms, single sign-on must internally translate and store credentials for the different mechanisms, from the credential used for initial authentication. Benefits[edit] Benefits of using single sign-on include: Reducing password fatigue from different user name and password combinationsReducing time spent re-entering passwords for the same identityReducing IT costs due to lower number of IT help desk calls about passwordsIncreases security of third party accounts because long and complicated passwords can be set without needing to remember them.
ArcSight. ArcSight was a company founded in 2000 that provides big data security analytics and intelligence software for security information and event management (SIEM).[1] It became a subsidiary of Hewlett-Packard in 2010.
HP ArcSight, headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, USA, with sales offices in other countries. History[edit] ArcSight was incorporated in May 2000. Silicon Valley Internet Capital, a small investment firm founded by Robert Shaw,[2] was the initial lead investor. Alex Daly was the founding CEO, who was previously CEO of Cygnus Solutions, acquired by Red Hat. In July 2001, Alex Daly, the founding CEO, ceased working for ArcSight due to health issues, but kept his 10.30% stake in the company as major shareholder. [4] Robert Shaw stepped up to take the position of CEO. Accelops. AccelOps is a company that sells a software virtual appliance for security information and event management (SIEM) and performance, availability, and change monitoring of Data Center Infrastructure from network devices, environmental equipment such as UPS, servers, storage, hypervisors, and applications.
Description[edit] Details[edit] Security information management. Security information management (SIM) is an industry term in related to information security referring to the collection of data (typically log files) into a central repository for trend analysis.[1] SIM products generally comprise of software agents running on the computer systems that are to be monitored, which then send the log information to a centralized server acting as a "security console".
The console typically displays reports, charts, and graphs of that information, often in real time. Some software agents can incorporate local filters, to reduce and manipulate the data that they send to the server, although typically from a forensic point of view you would collect all audit and accounting logs to ensure you can recreate a security incident. The security console is monitored by a human being, who reviews the consolidated information, and takes action in response to any alerts issued.[2][3] Notable solutions in the SIM/SEM marketplace[5][6][7][edit] Juniper Networks. History[edit] In 1995 Pradeep Sindhu, a principal scientist at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center, returned from vacation with the idea to start a company to supply high-performance routers to support the quickly emerging Internet.
Sindhu started the company in February 1996 with $200,000 in seed money from powerful venture capital firm Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, the deal led by Vinod Khosla. Check Point. Check Point headquarters, Tel Aviv, Israel Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. is an international provider of software and combined hardware and software products for IT security, including network security, endpoint security, data security and security management.
Magic Quadrant for SSL VPNs. Virtual private network. VPN connectivity overview A virtual private network connection across the Internet is similar to a wide area network (WAN) link between sites.
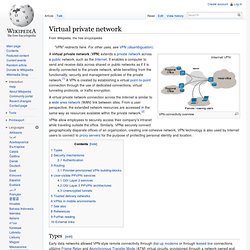
From a user perspective, the extended network resources are accessed in the same way as resources available within the private network.[2] VPNs allow employees to securely access their company's intranet while traveling outside the office. Similarly, VPNs securely connect geographically disparate offices of an organization, creating one cohesive network. VPN technology is also used by Internet users to connect to proxy servers for the purpose of protecting personal identity and location. Types[edit] Firewall (computing) An illustration of where a firewall would be located in a network.
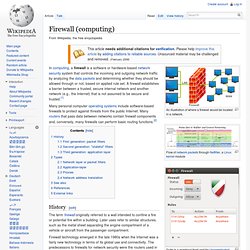
In computing, a firewall is a software or hardware-based network security system that controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic by analyzing the data packets and determining whether they should be allowed through or not, based on applied rule set. A firewall establishes a barrier between a trusted, secure internal network and another network (e.g., the Internet) that is not assumed to be secure and trusted.[1] Firewall technology emerged in the late 1980s when the Internet was a fairly new technology in terms of its global use and connectivity. The predecessors to firewalls for network security were the routers used in the late 1980s:[3] The first paper published on firewall technology was in 1988, when engineers from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) developed filter systems known as packet filter firewalls. Packet filters act by inspecting the "packets" which are transferred between computers on the Internet.
Safend Achieves RSA Secured(R) Partner Program Certification to Provide Enhanced Endpoint Data Leakage Prevention. RSA, The Security Division of EMC: Security Solutions for Business Acceleration. Partners. Unisys is proud to have built relationships with leaders in Commerce, Communications, CRM, ERP, Finance, Supply Chain, Enterprise Content Management, Health Care, Systems and Software, Infrastructure Hardware and Software, Storage, and Security.
About Unisys. Security Index Reveals Most Americans Support Internet “Kill Switch” As National Security Remains Top Overall Concern. BLUE BELL, Pa. – October 27, 2010 –Sixty-one percent of Americans said the President should have the ability to shut down portions of the Internet in the event of a coordinated malicious cyber attack, according to research conducted in August by Unisys Corporation (NYSE: UIS). The Unisys survey also found that while Americans are taking proactive steps to protect themselves against cyber crime and identity theft, only slightly more than a third of Internet users in the U.S. regularly use and update passwords on their mobile devices – creating a potentially huge security hole for organizations as more consumer devices invade the workplace. The findings, part of the latest bi-annual Unisys Security Index, illustrate that recent events such as the Stuxnet computer worm attack and the attempted Times Square car bombing may have heightened the American public’s awareness of and concern over global and domestic cybersecurity threats.
Mobile Devices: A Hole in American Defenses? Overall U.S. Strategic Partners - ArcSight Corporate Partners - ArcSight. Company Overview - ArcSight. Investor Relations - Financial news. Case Studies and Customer Solutions. IDC Report: Most Insider Leaks Happen By Accident - data leak prevention/Security - DarkReading. Unintentional leaks may cause more damage than internal fraud, research study says Accidental security leaks happen more frequently and cause more damage than malicious insiders, according to a study published earlier today by an industry research firm. According to a report (PDF) issued by research firm IDC and sponsored by RSA, 52 percent of respondents characterized their insider threat incidents as predominantly accidental, while only 19 percent believed the threats were deliberate.
Twenty-six percent believed their insider issues were an equal combination of accidental and malicious threats, while 3 percent were unsure. "One of the things that jumped out at us from the study was how many insider incidents are unintentional," says Chris Young, senior vice president of RSA products. "These are individual actors who often are just trying to do their jobs and don't understand that what they are doing is dangerous. "