

Heliophysics. Heliophysics We live in the extended atmosphere of an active star.
While sunlight enables and sustains life, the Sun's variability produces streams of high energy particles and radiation that can harm life or alter its evolution. Under the protective shield of a magnetic field and atmosphere, the Earth is an island in the Universe where life has developed and flourished. Home Page. Clearing the 'cosmic fog' of the early universe: Massive stars may be responsible.
The space between the galaxies wasn't always transparent.
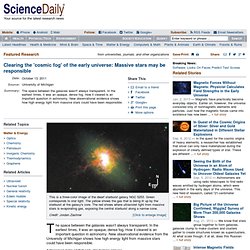
In the earliest times, it was an opaque, dense fog. How it cleared is an important question in astronomy. New observational evidence from the University of Michigan shows how high energy light from massive stars could have been responsible. Astronomy: Planets in our galaxy may be vastly more numerous than believed - latimes.com. The Milky Way galaxy may be filled with millions upon millions of Jupiter-sized planets that have escaped their solar systems and are wandering freely in space, researchers said Wednesday in a finding that seems certain to make astronomers rethink their ideas about planetary formation.
Scientists had previously thought that about 20% of stars had massive planets attached to them, but the new results reported in the journal Nature suggest that there are at least twice as many planets as stars, and perhaps several times as many. Earthlike Planet Found Orbiting at Right Distance for Life. A possible Earth twin has been confirmed orbiting a sunlike star 600 light-years away—and the new planet may be in just the right spot for supporting life, NASA announced Monday. NASA Mars Rover Finds Mineral Vein Deposited by Water. NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity has found bright veins of a mineral, apparently gypsum, deposited by water.
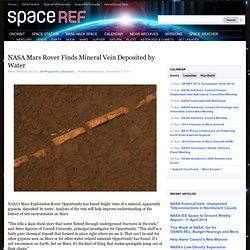
Analysis of the vein will help improve understanding of the history of wet environments on Mars. Nearby planet-forming disk holds water for thousands of oceans. NASA Telescope Confirms Alien Planet in Habitable Zone. This story was updated at 12:15 p.m.

ET. MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif. — NASA's planet-hunting Kepler spacecraft has confirmed the discovery of its first alien world in its host star's habitable zone — that just-right range of distances that could allow liquid water to exist — and found more than 1,000 new exoplanet candidates, researchers announced today (Dec. 5). The new finds bring the Kepler space telescope's total haul to 2,326 potential planets in its first 16 months of operation. These discoveries, if confirmed, would quadruple the current tally of worlds known to exist beyond our solar system, which recently topped 700. Puppis A. Puppis A is a supernova remnant (SNR) about 10 light-years in diameter.
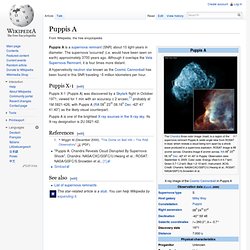
The supernova 'occurred' (i.e. would have been seen on earth) approximately 3700 years ago. Although it overlaps the Vela Supernova Remnant, it is four times more distant. Star Explosion Leaves Behind a Rose. About 3,700 years ago people on Earth would have seen a brand-new bright star in the sky.
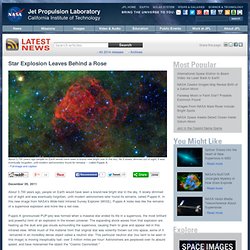
As it slowly dimmed out of sight, it was eventually forgotten, until modern astronomers found its remains -- called Puppis A. › Full image and caption December 09, 2011 About 3,700 years ago, people on Earth would have seen a brand-new bright star in the sky. Is the Universe Infinite? How Large is the Universe? "Vampire" Stars Found in Heart of Our Galaxy—A First. The stellar version of vampires—stars that drain life away from other stars—have been discovered for the first time in the heart of our Milky Way galaxy.

(See Milky Way pictures in National Geographic magazine.) Astronomers explain blue stragglers: How do mysterious stars stay so young? Mysterious "blue stragglers" are old stars that appear younger than they should be: they burn hot and blue.
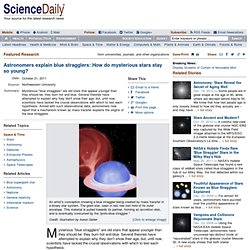
Several theories have attempted to explain why they don't show their age, but, until now, scientists have lacked the crucial observations with which to test each hypothesis. Armed with such observational data, two astronomers from Northwestern University and the University of Wisconsin-Madison report that a mechanism known as mass transfer explains the origins of the blue stragglers.
Essentially, a blue straggler eats up the mass, or outer envelope, of its giant-star companion. This extra fuel allows the straggler to continue to burn and live longer while the companion star is stripped bare, leaving only its white dwarf core. The scientists report their evidence in a study to be published Oct. 20 by the journal Nature.
Young stars take a turn in the spotlight. The European Southern Observatory's New Technology Telescope (NTT) has captured a striking image of the open cluster NGC 2100.
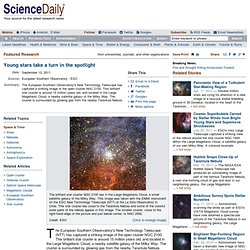
This brilliant star cluster is around 15 million years old, and located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. The cluster is surrounded by glowing gas from the nearby Tarantula Nebula. Ever wondered why Mars is red? One scientists thinks he knows. By Daily Mail Reporter Updated: 22:51 GMT, 2 April 2011 Mars has not always been red. At least that is the theory proposed by a scientist who has discovered a reason as to how the red planet got its rosy colour. According to Dr John Brandednberg, about 180 million years ago, a planet-shattering yet naturally occurring nuclear reaction may have wiped out everything on Mars, sending a shockwave that turned the planet into dry sand. Surface: Mars is covered with a thin layer of radioactive substances including uranium, thorium and radioactive potassium He told Fox News: 'The Martian surface is covered with a thin layer of radioactive substances including uranium, thorium and radioactive potassium - and this pattern radiates from a hot spot on Mars. 'A nuclear explosion could have sent debris all around the planet.
'Brown dwarf' has chance to shine after new telescope sees beyond brighter companion. By Julian Gavaghan Updated: 13:14 GMT, 25 March 2011. NASA's Swift finds most distant gamma-ray burst yet. Public release date: 27-May-2011 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Francis Reddyfrancis.j.reddy@nasa.gov 301-286-4453NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center On April 29, 2009, a five-second-long burst of gamma rays from the constellation Canes Venatici triggered the Burst Alert Telescope on NASA's Swift satellite. Giant star expels multiple dust shells, astronomers find.