

Flat Panel Display Show 2010: The trend is transparent. Sharp’s Solar Powered Television. As part of G8 Summit in Hokkaido, Japan, Sharp will be showcasing some futuristic new technologies in the Zero Emission House.

Amongst the future-forward prototypes to be shown: a 26-inch solar-powered LCD television that can be powered by a thin-film photovoltaic panel! Sharp’s plan is to distribute the TV and solar module to areas that have no easy access to grid power. The triple-junction thin film solar cell module is the cost effective panel to date that is being mass produced by Sharp. The panel can be produced to be made semi-transparent, to be as windows, and is manufactured to not require rare or scarce metals.
The television itself is an ultra low-powered LCD screen that uses less than a third of the energy required by conventional LCDs. So, is a TV really the most practical use for a new solar panel? + Sharp to Exhibit at Hokkaido. MIT's Tiny Kinetic Generator Produces 100 Times More Power from Small Vibrations. The labs at MIT are shaking things up – literally – as they just unveiled a tiny device that harvests energy from everyday, low-frequency vibrations.
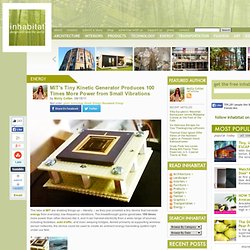
The breakthrough gizmo generates 100 times more power than other devices like it, and it can harvest electricity from a wide range of sources including footsteps, auto traffic, and even swaying bridges. Aimed primarily at supporting wireless sensor networks, the device could be used to create an ambient energy harvesting system right under our feet. Scientists have been using wireless sensor networks to measure and monitor the environmental conditions of just about everything these days. They can track pollution, measure bridge and building movement, monitor oil pipelines, and even help predict the temperature changes in forests before a mass fire. Though technological improvements have decreased the energy use of wireless sensor networks, their batteries still need to be changed periodically.
Usbcell - revolutionary rechargeable usb battery that can charge from any USB port. Next-Gen Electronics Charge Themselves With Energy-Harvesting LCD Screens. Engineers at UCLA have developed technology that allows energy gobbling gadgets like smartphones and laptops to convert sunlight, ambient light, and their own backlight into energy.
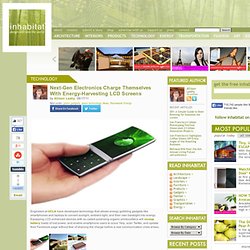
Equipping LCD-enhanced devices with so-called polarizing organic photovoltaics will recoup battery loads of lost power, and enable smartphone users to scour Yelp, scan Twitter, and update their Facebook page without fear of draining the charge before a real communication crisis arises. Liquid crystal displays make up the majority of the display screen market because they render bright and colorful images and are relatively easy to manufacture. As popular as they are, LCDs are by no means efficient — as much as 75% of energy is lost in the traditional polarization process and brightening the display drains the majority of the device’s stored electricity. Photovoltaic polarizers can capture and recycle light that would otherwise be lost in the transmission process. Via TG Daily. Meet the zero-energy transparent TV. A zero-energy TV you can see through?
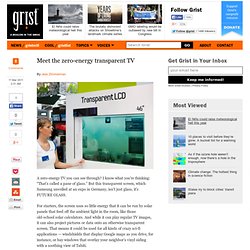
I know what you’re thinking: “That’s called a pane of glass.” But this transparent screen, which Samsung unveiled at an expo in Germany, isn’t just glass, it’s FUTURE GLASS. For starters, the screen uses so little energy that it can be run by solar panels that feed off the ambient light in the room, like those old-school solar calculators. And while it can play regular TV images, it can also project pictures or data onto an otherwise transparent screen. That means it could be used for all kinds of crazy sci-fi applications — windshields that display Google maps as you drive, for instance, or bay windows that overlay your neighbor’s vinyl siding with a soothing view of Tahiti. Read more: Bringing solar light bulbs to the world. Inventor Steve Katsaros believes selling his solar bulbs, instead of donating them, will help more people in developing countries.
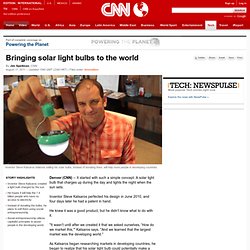
Inventor Steve Katsaros created a light bulb charged by the sun He hopes it will help the 1.4 billion people who have no access to electricity Instead of donating the bulbs, he plans to sell them using social entrepreneurship Social entrepreneurship utilizes capitalist principles to assist people in the developing world Denver (CNN) -- It started with such a simple concept: A solar light bulb that charges up during the day and lights the night when the sun sets. Inventor Steve Katsaros perfected his design in June 2010, and four days later he had a patent in hand. He knew it was a good product, but he didn't know what to do with it. "It wasn't until after we created it that we asked ourselves, 'How do we market this,'" Katsaros says. Many use fuel lamps that burn kerosene, which is costly, dirty and can also be unhealthy. Solar light from Nokero - The Worlds Only Solar Light Bulb.