

Copernicus and the Church: What the history books don't say. Legend has it that Nicolaus Copernicus and the church were at odds over his development of the heliocentric theory, a principle that disputed the widely held belief that Earth was the center of the universe.
Unlike Galileo and other controversial astronomers, however, Copernicus had a good relationship with the Catholic Church. It may come as a surprise, considering the Church banned Copernicus' "Des revolutionibus" for more than 200 years. Copernicus was actually respected as a canon and regarded as a renowned astronomer. Planetary Motion: The History of an Idea That Launched the Scientific Revolution : Feature Articles. By Holli Riebeek Design by Robert Simmon July 7, 2009 In the black dome of night, the stars seem fixed in their patterns.
They rotate through the sky over the seasons so unchangingly that most cultures have used the presence of one or another constellation to tell time. The planets, however, are different, puzzling. The Role of Religion in the Scientific Revolution - The Objective Standard. Scientific Revolution Video - Enlightenment. You're almost done!
You will soon receive an activation email. Once you click on the link, you will be added to our list. If you do not receive this email, please contact us. Khanacademy. The Scientific Revolution: Science & Society from the Renaissance to the Early Enlightenment: Lesson Plans. The Scientific Revolution resulted from a monumental series of discoveries, especially those in astronomy and related fields, in the 16th and 17th centuries.
The impact of these discoveries went far beyond the walls of the laboratory—it created a genuine revolution in the way Western people thought about the world. Participants in this institute will study how the revolution in science and technology was directly linked to revolutions in religion, politics, and society. See How The Gutenberg Press Worked: Demonstration Shows the Oldest Functioning Gutenberg Press in Action. People have spoken for decades, and with great certainty, of the impending death of print.

But even here into the 21st century, presses continue to run around the world, putting out books and periodicals of all different shapes, sizes, and print runs. The technology has endured so well in part because it has had so long to evolve. Everyone knows that printing began with something called the Gutenberg Press, and many know that Gutenberg himself (Johannes, a German blacksmith) unveiled his invention in 1440, introducing movable type to the world. Ten years later came the Gutenberg Bible, the first major book printed using it, still considered among the most beautiful books ever mass-produced. But how did the Gutenberg press actually work? Johannes Gutenberg's Information Revolution. Johann Gutenberg, the inventor of printing with moveable metal type, is a true benefactor of humankind.

His innovative application of printing technologies was not only a showcase example of market anarchism, but a greater source of benefit to mankind than state-sponsored technologies can ever hope to be. His is a story not only of innovation, but of immigration, opposition to politically connected interests, and freedom of information. Remember the Millennium? Nearly ten years ago – in time for the millennium celebrations – Johann Gutenberg (ca. 1400-1468) was singled out as the greatest inventor of the past 1,000 years by the British Broadcasting Company (BBC).
Life rated his printing of the Bible as the top event of that time period. Johannes Gutenberg. Johann Gutenberg and the Printing Press - An Introduction. A good cook can take leftovers and turn them into a delicious meal.
Like a good cook, Johann Gutenberg took what had already been discovered and created a small invention that had a large impact on history. About 1450, Gutenberg crafted the printing press, a machine that allowed him to move small blocks of letters in such a way that written material could be printed and mass-produced. Few people outside the clergy could read in Guttenberg’s time, but with the invention of the printing press, books became less expensive and therefore more available for people to read. Gutenberg Bible: the Basics. Or want to refresh your knowledge?

We have created this section to get you up to speed. Who was Gutenberg? The Gutenberg Bible. The Gutenberg Bible is the first substantial book printed in the West with moveable metal type.
Before its printing in 1454 or 1455, books were either copied by hand or printed from engraved wooden blocks—processes that could take months or years to complete. Johann Gutenberg invented a printing press that revolutionized the distribution of knowledge by making it possible to produce many copies of a work in a relatively short amount of time. Learn more about the Gutenberg Bible through the links below. Who was Johann Gutenberg? How was the Gutenberg Bible printed? Johannes Gutenberg - Inventor. German inventor Johannes Gutenberg developed a method of movable type and used it to create one of the Western world's first major printed books, the “Forty-Two-Line” Bible.
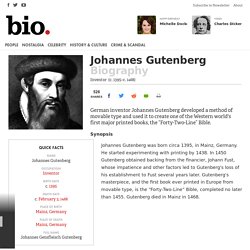
Synopsis Johannes Gutenberg was born circa 1395, in Mainz, Germany. He started experimenting with printing by 1438. In 1450 Gutenberg obtained backing from the financier, Johann Fust, whose impatience and other factors led to Gutenberg's loss of his establishment to Fust several years later. Gutenberg's masterpiece, and the first book ever printed in Europe from movable type, is the “Forty-Two-Line” Bible, completed no later than 1455. Leonardo Da Vinci - The Genius. Da Vinci's Inventions Leonardo's fascination with machines probably began during his boyhood. Some of his earliest sketches clearly show how various machine parts worked. Leonardo Da Vinci - The Genius. Da Vinci's Curiosities While greatly influenced by the writings of the ancient Greeks and Romans, Leonardo, unlike many of his contemporaries, saw the limitations of seeking the truth solely in those writings or the Bible.
Instead, he took the approach of actually observing nature and asking deceptively simple scientific questions like, "How do birds fly? " He then systematically recorded their solutions in his sketches. Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance . Renaissance . Brunelleschi. Few men have left a legacy as monumental as Filippo Brunelleschi.
He was the first modern engineer and a problem-solver with unorthodox methods. He solved one of the greatest architectural puzzles and invented his way to success. Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance . Renaissance . Galileo. Galileo Galilei was just five-years-old when he witnessed the power of Florence's first family with the coronation of Cosimo I. Galileo would become the greatest scientist in history, and the father of modern astronomy, but would end his life betrayed by his Medici patrons. The son of a court musician, Galileo grew up on the fringes of the Medici court, and was fascinated by the art of spectacle and display. A talented mathematician, his early scientific training required him to also study technical drawing at the Florentine Academy of Art and Design.
Galileo soon began lecturing in natural science at local universities. Nicolaus Copernicus - Facts & Summary. You're almost done! You will soon receive an activation email. Once you click on the link, you will be added to our list. If you do not receive this email, please contact us. To ensure delivery to your inbox, add us to your address book. Oops, there's a problem. History, Travel, Arts, Science, People, Places. Copernicus Unearthed. Copernican System. Beyond the Big Bang: Copernicus Video - Nicolaus Copernicus. Nicolaus Copernicus. Facts, Accomplishments, & Theory. Nicolaus Copernicus - Astronomer, Scientist, Mathematician.