

NeurobiologyOfEmotion anUpdate(2017) Theory of drives and emotions - from Sigmund Freud to Jaak Panksepp. The article discusses the development of psychoanalytic theory in the direction of broadening the reflection on their own based on data derived from empirical studies other than clinical case study.

Particularly noteworthy is the convergence that followed between neuroscience and psychoanalysis and the rise of the so-called neuropsychoanalysis. Consequently, this led to eject empirical hypotheses and begin research on defense mechanisms, self, memory, dreams, empathy, dynamic unconscious and emotional-motivational processes (theory of drives). Currently neuropsychoanalysis constituted itself as a discipline contained in itself three separate areas: the psychodynamic neuroscience, clinical neuropsychoanalysis and theory building. The article introduces the theory of Jaak Panksepp emotional systems as an example of anintegrated neurobiology of affect, behavioral biology, evolutionary psychology and psychoanalysis.
Keywords: emotions; neuroscience; psychoanalysis. Psychiatria Polska - 1181Z. Psychiatr.
Pol. 2017; 51(6): 1181–1189 DOI: Cezary Żechowski FREE POLISH FULLTEXT: Teoria emocji i popędów – od Sigmunda Freuda do Jaaka Pankseppa FREE ENGLISH FULLTEXT: Theory of drives and emotions – from Sigmund Freud to Jaak Panksepp Summary The article discusses the development of psychoanalytic theory in the direction of broadening the reflection on their own based on data derived from empirical studies other than clinical case study. How emotions affect logical reasoning: evidence from experiments with mood-manipulated participants, spider phobics, and people with exam anxiety. IAMA brain surgery survivor and I no longer feel fear because my right amygdala was removed along with 10% of my brain. : IAmA. The Limbic System - Neuroscience - NCBI Bookshelf. The Limbic System Conception and Its Historical Evolution. The brain basis of emotion: A meta-analytic review. Scientists find brain center that 'profoundly' shuts down pain. A Duke University research team has found a small area of the brain in mice that can profoundly control the animals' sense of pain.
Somewhat unexpectedly, this brain center turns pain off, not on. It's also located in an area where few people would have thought to look for an anti-pain center, the amygdala, which is often considered the home of negative emotions and responses, like the fight or flight response and general anxiety. "People do believe there is a central place to relieve pain, that's why placebos work," said senior author Fan Wang, the Morris N. Broad Distinguished Professor of neurobiology in the School of Medicine. "The question is where in the brain is the center that can turn off pain. " "Most of the previous studies have focused on which regions are turned ON by pain," Wang said.
The work is a follow-up to earlier research in Wang's lab looking at neurons that are activated, rather than suppressed, by general anesthetics. "It's so drastic," Wang said. History of Emotions. The History of Emotions: An Introduction - Jan Plamper - Google Books. Right anterior cingulate emotional reactivity. + Author Affiliations Correspondence should be addressed to Virginia E.

Sturm, UCSF Department of Neurology, Memory and Aging Center, 350 Parnassus Avenue, Suite 905, Box 1207, San Francisco, California 94143-1207, USA. Tel: +(415)-476-8618. Fax: +(415)-476-4800. E-mail: virginia.sturm@ucsf.edu Received October 6, 2011. Self-conscious emotions such as embarrassment arise when one’s actions fail to meet salient social expectations and are accompanied by marked physiological and behavioral activation. Humor, Frontal Lobe.
From universities, journals, and other organizations Date: April 1, 1999 Source: University Of Toronto Summary: Study finds people with damage to the right frontal lobe of the brain have trouble getting punch lines and show a preference for slapstick humor -- first evidence that frontal lobe plays a pre-eminent role in our ability to appreciate humor and have a good belly laugh.

Emotionally Free: A Prescription for Healing Body, Soul and Spirit: Grant M.D. Mullen: 9780800793463: Amazon.com: Books. Limbic System. The limbic system, sometimes called “the emotional brain”, controls many of the complex emotional behaviors we think of as instinct.
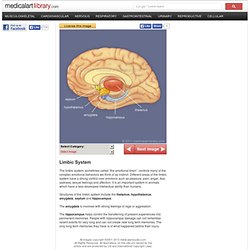
Different areas of the limbic system have a strong control over emotions such as pleasure, pain, anger, fear, sadness, sexual feelings and affection. It is an important system in animals which have a less developed intellectual ability than humans. Structures of the limbic system include the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, septum and hippocampus. The amygdala is involved with strong feelings of rage or aggression. The hippocampus helps control the transferring of present experiences into permanent memories.