

CriticalThinking.pdf. Critical Thinking. VCE Literature. Poe: Philosophy of Composition. CHARLES DICKENS, in a note now lying before me, alluding to an examination I once made of the mechanism of "Barnaby Rudge," says- "By the way, are you aware that Godwin wrote his 'Caleb Williams' backwards?

He first involved his hero in a web of difficulties, forming the second volume, and then, for the first, cast about him for some mode of accounting for what had been done. " I cannot think this the precise mode of procedure on the part of Godwin- and indeed what he himself acknowledges, is not altogether in accordance with Mr. The Raven.
"The Raven" depicts a mysterious raven's midnight visit to a mourning narrator, as illustrated by John Tenniel (1858).
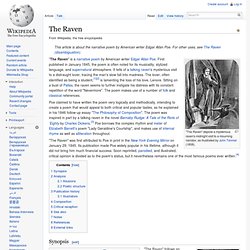
"The Raven" is a narrative poem by American writer Edgar Allan Poe. First published in January 1845, the poem is often noted for its musicality, stylized language, and supernatural atmosphere. It tells of a talking raven's mysterious visit to a distraught lover, tracing the man's slow fall into madness.
The lover, often identified as being a student,[1][2] is lamenting the loss of his love, Lenore. Sitting on a bust of Pallas, the raven seems to further instigate his distress with its constant repetition of the word "Nevermore". Edgar Allan Poe. Born in Boston, he was the second child of two actors.
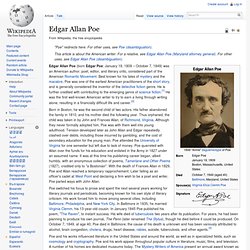
His father abandoned the family in 1810, and his mother died the following year. Thus orphaned, the child was taken in by John and Frances Allan, of Richmond, Virginia. The Count of Monte Cristo. The Count of Monte Cristo (French: Le Comte de Monte-Cristo) is an adventure novel by French author Alexandre Dumas (père) completed in 1844.
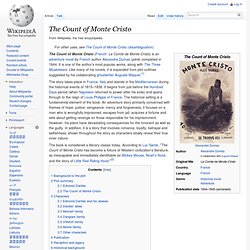
It is one of the author's most popular works, along with The Three Musketeers. Like many of his novels, it is expanded from plot outlines suggested by his collaborating ghostwriter Auguste Maquet.[1] Charles Baudelaire. Charles Pierre Baudelaire (French: [ʃaʁl bodlɛʁ]; April 9, 1821 – August 31, 1867) was a French poet who also produced notable work as an essayist, art critic, and pioneering translator of Edgar Allan Poe.
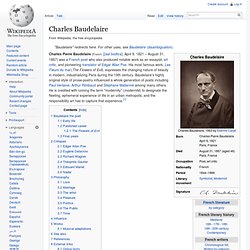
His most famous work, Les Fleurs du mal (The Flowers of Evil), expresses the changing nature of beauty in modern, industrializing Paris during the 19th century. Baudelaire's highly original style of prose-poetry influenced a whole generation of poets including Paul Verlaine, Arthur Rimbaud and Stéphane Mallarmé among many others. He is credited with coining the term "modernity" (modernité) to designate the fleeting, ephemeral experience of life in an urban metropolis, and the responsibility art has to capture that experience.[1] Baudelaire the poet[edit] The Adventures of Tom Sawyer. The Adventures of Tom Sawyer by Mark Twain is an 1876 novel about a young boy growing up along the Mississippi River.
The story is set in the fictional town of St. Petersburg, inspired by Hannibal, Missouri, where Twain lived.[2] Mark Twain. Samuel L.
Clemens stamp, 1940 Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910),[1] better known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American author and humorist. He wrote The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876) and its sequel, Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1885),[2] the latter often called "The Great American Novel". Twain grew up in Hannibal, Missouri, which provided the setting for Huckleberry Finn and Tom Sawyer. After an apprenticeship with a printer, he worked as a typesetter and contributed articles to the newspaper of his older brother, Orion Clemens. The Brothers Karamazov. The Brothers Karamazov (Russian: Бра́тья Карама́зовы, Brat'ya Karamazovy, pronounced [ˈbratʲjə kərɐˈmazəvɨ]), sometimes also translated as The Karamazov Brothers, is the final novel by the Russian author Fyodor Dostoyevsky.
Dostoyevsky spent nearly two years writing The Brothers Karamazov, which was published as a serial in The Russian Messenger and completed in November 1880. The author died less than four months after its publication. The Brothers Karamazov is a passionate philosophical novel set in 19th century Russia, that enters deeply into the ethical debates of God, free will, and morality. It is a spiritual drama of moral struggles concerning faith, doubt, and reason, set against a modernizing Russia, with a plot which revolves around the subject of patricide. Dostoyevsky composed much of the novel in Staraya Russa, which inspired the main setting.[1] Since its publication, it has been acclaimed as one of the supreme achievements in literature. Victor Hugo. Victor Marie Hugo (French pronunciation: [viktɔʁ maʁi yɡo]; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French poet, novelist, and dramatist of the Romantic movement.
He is considered one of the greatest and best known French writers. In France, Hugo's literary fame comes first from his poetry but also rests upon his novels and his dramatic achievements. Among many volumes of poetry, Les Contemplations and La Légende des siècles stand particularly high in critical esteem. Oscar Wilde. 19th-century Irish poet, playwright and aesthete Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 1854 – 30 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright.
After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. Thus Spoke Zarathustra. Thus Spoke Zarathustra: A Book for All and None (German: Also sprach Zarathustra: Ein Buch für Alle und Keinen, also translated as Thus Spake Zarathustra) is a philosophical novel by German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, composed in four parts between 1883 and 1885.
Much of the work deals with ideas such as the "eternal recurrence of the same", the parable on the "death of God", and the "prophecy" of the Übermensch, which were first introduced in The Gay Science.[1] Origins[edit] Thus Spoke Zarathustra was conceived while Nietzsche was writing The Gay Science; he made a small note, reading "6,000 feet beyond man and time," as evidence of this.[2] More specifically, this note related to the concept of the eternal recurrence, which is, by Nietzsche's admission, the central idea of Zarathustra; this idea occurred to him by a "pyramidal block of stone" on the shores of Lake Silvaplana in the Upper Engadine, a high alpine region whose valley floor is at 6,000 ft.
Synopsis[edit] Themes[edit] Friedrich Nietzsche. Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (/ˈniːtʃə/[1] or /ˈniːtʃi/;[2] German: [ˈfʁiːdʁɪç ˈvɪlhɛlm ˈniːt͡sʃə]; 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, cultural critic, poet, composer and Latin and Greek scholar. He wrote several critical texts on religion, morality, contemporary culture, philosophy and science, displaying a fondness for metaphor[3] and irony.
Nietzsche's key ideas include perspectivism, the will to power, the death of God, the Übermensch and eternal recurrence. One of the key tenets of his philosophy is "life-affirmation", which embraces the realities of the world in which we live over the idea of a world beyond. Nietzsche began his career as a classical philologist—a scholar of Greek and Roman textual criticism—before turning to philosophy.