

What is Your Motivation Style? Printer-Friendly Version Motivation is the force that draws you to move toward something.
It can come from a desire or a curiosity within you or can be from an external force urging you on. In either case, you make the decision to seize or to skip a chance to learn. Motivation styles vary for different situations and topics but nonetheless, you draw on them all the time, especially when you try to learn something challenging. Personalize Learning. What is Mindset. Every so often a truly groundbreaking idea comes along.

This is one. Mindset explains: Why brains and talent don’t bring success How they can stand in the way of it Why praising brains and talent doesn’t foster self-esteem and accomplishment, but jeopardizes them How teaching a simple idea about the brain raises grades and productivity What all great CEOs, parents, teachers, athletes know Mindset is a simple idea discovered by world-renowned Stanford University psychologist Carol Dweck in decades of research on achievement and success—a simple idea that makes all the difference.
In a fixed mindset, people believe their basic qualities, like their intelligence or talent, are simply fixed traits. In a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—brains and talent are just the starting point. Teaching a growth mindset creates motivation and productivity in the worlds of business, education, and sports. What Is Your Learning Style? What Is Your Learning Style?
This quiz asks 24 questions and will take less than five minutes to complete. Try not to think too hard -- just go with your first thought when describing your daily activities and interests. By the end, you may have some new insights into your learning preferences. Editor's Note (2013): There is no scientific evidence, as of yet, that shows that people have specific, fixed learning styles or discrete intelligences, nor that students benefit when teachers target instruction to a specific learning style or intelligence. However, providing students with multiple ways to learn content has been shown to improve student learning (Hattie, 2011). Overview of learning styles. Many people recognize that each person prefers different learning styles and techniques.

Learning styles group common ways that people learn. Everyone has a mix of learning styles. Some people may find that they have a dominant style of learning, with far less use of the other styles. Others may find that they use different styles in different circumstances. There is no right mix. Using multiple learning styles and �multiple intelligences� for learning is a relatively new approach. By recognizing and understanding your own learning styles, you can use techniques better suited to you. The Seven Learning Styles Visual (spatial):You prefer using pictures, images, and spatial understanding. Why Learning Styles? Your learning styles have more influence than you may realize. Research shows us that each learning style uses different parts of the brain. For example: Visual: The occipital lobes at the back of the brain manage the visual sense.
Learner Profiles. Birmingham Grid for Learning - Multiple Intelligences (Secondary) David Peck: Innovation Self-Test: Are You a Change Maker or Change Breaker? - Innovation America. What is Universal Design for Learning. Universal Design for Learningis a set of principles for curriculum development that give all individuals equal opportunities to learn.
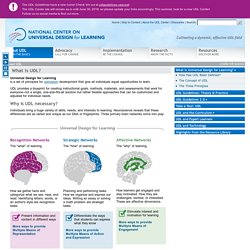
UDL provides a blueprint for creating instructional goals, methods, materials, and assessments that work for everyone--not a single, one-size-fits-all solution but rather flexible approaches that can be customized and adjusted for individual needs. Why is UDL necessary? Individuals bring a huge variety of skills, needs, and interests to learning. Neuroscience reveals that these differences are as varied and unique as our DNA or fingerprints. Three primary brain networks come into play: Recognition Networks The "what" of learning How we gather facts and categorize what we see, hear, and read. Strategic Networks The "how" of learning Planning and performing tasks.
Affective Networks The "why" of learning How learners get engaged and stay motivated. Source: CAST - What is UDL? Learn more about UDL: Index of Learning Styles Questionnaire.