

Geography. Ancient Egyptian History for Kids: Geography and the Nile River. History >> Ancient Egypt The Nile River played an important role in shaping the lives and society of Ancient Egypt.

The Nile provided the Ancient Egyptians with food, transportation, building materials, and more. Egypt Country Profile. Ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt.
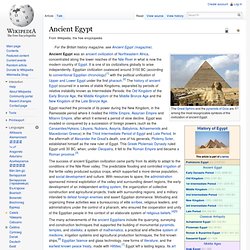
It is one of six civilizations globally to arise independently. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology)[1] with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh.[2] The history of ancient Egypt occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.
History Map of ancient Egypt, showing major cities and sites of the Dynastic period (c. 3150 BC to 30 BC) Predynastic period A typical Naqada II jar decorated with gazelles. In Predynastic and Early Dynastic times, the Egyptian climate was much less arid than it is today. Early Dynastic Period (c. 3050 –2686 BC) Ancient History/Egypt/Geography. The geography of ancient Egypt was dominated, as is today, by the combination of lack of rainfall and the Nile River.

The Greek historian Herodotus called Egypt the "gift of the Nile", since the kingdom owed its survival to the annual flooding of the Nile and the resulting depositing of fertile silt. The Nile River flows into the Mediterranean Sea, and there is a delta at the mouth. The Nile[edit] The green is the ancient Egyptian "Black Land", while everything else is the "Red Land" The Nile River was the only reason that civilization arose in ancient Egypt at all. The Nile's physical/chemical properties[edit] Since the headwaters of the Nile are deep in central east Africa (at Lake Victoria), the river flooded annually during the height of Egyptian civilization.
The Nile's annual Inundation thus established the pattern of Egyptian life very early. So constant was this pattern that its interruption may have caused the fall of several dynasties. Four Divisions[edit] Upper Egypt[edit] Geography. Ancient Egypt - Ancient History. Under Ahmose I, the first king of the 18th dynasty, Egypt was once again reunited.
During the 18th dynasty, Egypt restored its control over Nubia and began military campaigns in Palestine, clashing with other powers in the area such as the Mitannians and the Hittites. The country went on to establish the world’s first great empire, stretching from Nubia to the Euphrates River in Asia. In addition to powerful kings such as Amenhotep I (1546-1526 B.C.), Thutmose I (1525-1512 B.C.) and Amenhotep III (1417-1379 B.C.), the New Kingdom was notable for the role of royal women such as Queen Hatshepsut (1503-1482 B.C.), who began ruling as a regent for her young stepson (he later became Thutmose III, Egypt’s greatest military hero), but rose to wield all the powers of a pharaoh. All of the New Kingdom rulers (with the exception of Akhenaton) were laid to rest in deep, rock-cut tombs (not pyramids) in the Valley of the Kings, a burial site on the west bank of the Nile opposite Thebes.
Egypt Geography, Geography of Egypt, The River Nile. Geography of Egypt: Egypt is located in the northeastern fringes of Africa and shares international boundaries with Libya to the west (692 miles), Sudan to the south (791 miles), and Israel to the north-east (165 miles).

The Mediterranean Sea to the north of Egypt and the Red Sea, the Gulf of Suez, and the Gulf of Aqaba to the east endow the country with a coastline stretching over 1820 miles in all. Egypt covers an area of 386,660 sq mi and is the 30th largest country in the world. The highest elevations in Egypt are in the southern part of the country. The southern regions of the Sinai Peninsula are also mountainous.
Most of Egypt is an arid desert with little or no vegetation.