

Top of the Web. Follow Springo on : Find top sites My top sites Top Sites News Music.

[Ancient] Rome. Roman Empire. [Ancient] Rome. Roman Empire. Anglo-Saxons. The Anglo-Saxons were a people who inhabited Great Britain from the 5th century.
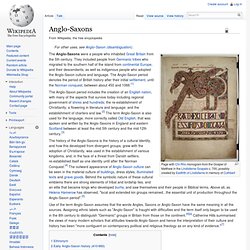
They included people from Germanic tribes who migrated to the southern half of the island from continental Europe, and their descendants; as well as indigenous people who adopted the Anglo-Saxon culture and language. The Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period of British history after their initial settlement, until the Norman conquest, between about 450 and 1066.[1] The history of the Anglo-Saxons is the history of a cultural identity, and how this developed from divergent groups, grew with the adoption of Christianity, was used in the establishment of various kingdoms, and, in the face of a threat from Danish settlers, re-established itself as one identity until after the Norman Conquest.[4] The outward appearance of Anglo-Saxon culture can be seen in the material culture of buildings, dress styles, illuminated texts and grave goods. Ethnonym. Aztecs. Culture. Medieval philosophy. Medieval philosophy is the philosophy in the era now known as medieval or the Middle Ages, the period roughly extending from the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century C.E. to the Renaissance in the 16th century.
Medieval philosophy, understood as a project of independent philosophical inquiry, began in Baghdad, in the middle of the 8th century, and in France, in the itinerant court of Charlemagne, in the last quarter of the 8th century.[1] It is defined partly by the process of rediscovering the ancient culture developed in Greece and Rome in the classical period, and partly by the need to address theological problems and to integrate sacred doctrine with secular learning.
The medieval era was disparagingly treated by the Renaissance humanists, who saw it as a barbaric 'middle' period between the classical age of Greek and Roman culture, and the 'rebirth' or renaissance of classical culture. Character of medieval philosophy[edit] History[edit] High Middle Ages[edit] Roman Empire.