

Ford Model T - Wikipedia. The Ford Model T (colloquially known as the Tin Lizzie, T‑Model Ford, Model T, T, Leaping Lena, or flivver) is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927.[6][7] It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, the car that opened travel to the common middle-class American; some of this was because of Ford's efficient fabrication, including assembly line production instead of individual hand crafting.[8] Although automobiles had already existed for decades, they were still mostly scarce and expensive at the Model T's introduction in 1908.
Positioned as reliable, easily maintained mass market transportation, it was a runaway success. Untitled. Radio in the 1920s Emergence of Radio in the 1920s and its Cultural Significance Most radio historians asert that radio broadcasting began in 1920 with the historic broadcast of KDKA.

Few people actually heard the voices and music which were produced because of the dearth of radio receivers at that time. Charles Lindbergh. Charles Augustus Lindbergh (February 4, 1902 – August 26, 1974), nicknamed Slim,[1] Lucky Lindy, and The Lone Eagle, was an American aviator, author, inventor, explorer, and social activist.
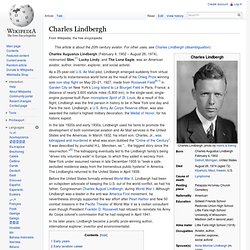
As a 25-year-old U.S. Air Mail pilot, Lindbergh emerged suddenly from virtual obscurity to instantaneous world fame as the result of his Orteig Prize-winning solo non-stop flight on May 20–21, 1927, made from Roosevelt Field[N 1] in Garden City on New York's Long Island to Le Bourget Field in Paris, France, a distance of nearly 3,600 statute miles (5,800 km), in the single-seat, single-engine purpose-built Ryan monoplane Spirit of St. Louis. As a result of this flight, Lindbergh was the first person in history to be in New York one day and Paris the next. Lindbergh, a U.S. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Lindbergh used his fame to promote the development of both commercial aviation and Air Mail services in the United States and the Americas. Empire State Building - Wikipedia. Office skyscraper in Manhattan, New York City Site The Empire State Building is located on the west side of Fifth Avenue in Manhattan, between 33rd Street to the south and 34th Street to the north.
Tenants enter the building through the Art Deco lobby located at 350 Fifth Avenue. Visitors to the observatories use an entrance at 20 West 34th Street; prior to August 2018, visitors entered through the Fifth Avenue lobby.[1] Although physically located in South Midtown,[15] a mixed residential and commercial area,[16] the building is so large that it was assigned its own ZIP Code, 10118;[17][18] as of 2012[update], it is one of 43 buildings in New York City that has its own ZIP code.[19][b] To the east of the Empire State Building is Murray Hill,[25] a neighborhood with a mix of residential, commercial, and entertainment activity.
History Site Planning process Early plans The land was then resold to Empire State Inc., a group of wealthy investors that included Louis G. Design changes Construction. Chrysler Building - Wikipedia. Office skyscraper in Manhattan, New York When the Chrysler Building opened, there were mixed reviews of the building's design, ranging from views of it as inane and unoriginal to the idea that it was modernist and iconic.
Perceptions of the building have slowly evolved into its now being seen as a paragon of the Art Deco architectural style; and in 2007, it was ranked ninth on the List of America's Favorite Architecture by the American Institute of Architects. The building was designated a New York City landmark in 1978, and was added to the National Register of Historic Places as a National Historic Landmark in 1976. Site[edit] The Grand Hyatt New York hotel and the Graybar Building are located across Lexington Avenue, while the Socony–Mobil Building is located across 42nd Street.
History[edit] Context[edit] Amelia Earhart - Wikipedia. During an attempt to make a circumnavigational flight of the globe in 1937 in a Purdue-funded Lockheed Model 10 Electra, Earhart disappeared over the central Pacific Ocean near Howland Island.
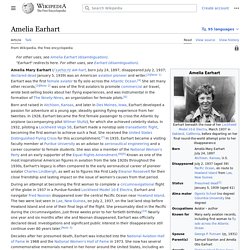
Fascination with her life, career and disappearance continues to this day. [N 3] Early life Childhood Amelia Earhart as a child Earhart was the daughter of Samuel "Edwin" Stanton Earhart (1867-1930) and Amelia "Amy" (nee Otis) (1869–1962).[10] She was born in Atchison, Kansas, in the home of her maternal grandfather, Alfred Gideon Otis (1827–1912), who was a former federal judge, the president of the Atchison Savings Bank and a leading citizen in the town. Early influence A spirit of adventure seemed to abide in the Earhart children, with the pair setting off daily to explore their neighborhood. Although there had been some missteps in his career up to that point, in 1907 Edwin Earhart's job as a claims officer for the Rock Island Railroad led to a transfer to Des Moines, Iowa.
Education.