

What's happening in the Topic Maps world? Bloom's Taxonomy Blooms Digitally, Andrew Churches. 4/1/2008 By: Andrew Churches from Educators' eZine.

Mind Mapping and Bloom’s Taxonomy. Taxonomy Strangely, the first question I get when talking about Bloom’s taxonomy is: ‘What is a taxonomy?’ This is typical of Bloom’s studies. It was an academic exercise, done by academics in Higher Education. The words used are therefore not those used in everyday vocabulary. This article aims to make things a bit easier for you, as there is great benefit in knowing the different levels of human thinking so that you can incorporate it in your learning. SCAN » About. “… the abundance of information will be such that either you have reached such a level of maturity that you are able to be your own filter, or you will desperately need a filter… some professional filter.”

Umberto Eco, “A Conversation on Information” SCAN (Smart Content Aggregation and Navigation) is a personal semantic content manager for desktop users. It combines search, text analysis, tagging and metadata functions to provide new user experience of desktop navigation and personal document management. SCAN aims at problems of personal content organization and findability in information overload age. For that, SCAN solution provides an integrated set of tools and techniques: Aggregation • SCAN erases the boundaries put on information by different storage systems. Metadata • Unified metadata framework is provided to describe, classify and annotate the documents. Critical and Creative Thinking - Bloom's Taxonomy. What are critical thinking and creative thinking?

What's Bloom's taxonomy and how is it helpful in project planning? How are the domains of learning reflected in technology-rich projects? Benjamin Bloom (1956) developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior in learning. This taxonomy contained three overlapping domains: the cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. Within the cognitive domain, he identified six levels: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Critical Thinking. How To « The Taxonomy Blog. Recently, I ran into a neighbor who is a VP at a high-tech firm working on speech recognition, so I asked if she was using taxonomies.

“To me, Tom Brady is a topic and that’s enough. It’s too much work to build hierarchies.” But for me, there is way too much information about Tom Brady. I’d like to be able to find information based Tom Brady’s statistics, or how he is managed, or maybe, something about his social life. Taxonomies are not just about hierarchies or long lists of terms. A taxonomy term has to be categorized to have any meaning.
For example, in one project, I was handed a taxonomy that had 4,000 terms that we reduced to 9 top nodes. That’s why it’s important to integrate social networking with taxonomy tools. A well-managed taxonomy can be a strategic tool to like the “canary in the mine” to help identify emerging concepts. canary on a branch So take the planning or revisionof the taxonomy seriously. Here’s a five point plan. 1. 2. Bloom’s taxonomy « The Taxonomy Blog. During the 2001 recession, I decided to teach again.

After 15 years as a taxonomist and business systems analyst, I returned to an earlier career. I love teaching and learning about social studies and public policy. But my skills as a taxonomist infused my teaching. Semantic Technology Uses for Financial Services. BLOOM’S TAXONOMY, KNOWLEDGE AND KM REVISITED : SHOULD DIKW MODEL. Datasets. 1.

Background Wikipedia has grown into one of the central knowledge sources of mankind and is maintained by thousands of contributors. Wikipedia articles consist mostly of free text, but also contain different types of structured information, such as infobox templates, categorisation information, images, geo-coordinates, and links to external Web pages. The DBpedia project extracts various kinds of structured information from Wikipedia editions in 119 languages and combines this information into a huge, cross-domain knowledge base.
DBpedia uses the Resource Description Framework (RDF) as a flexible data model for representing extracted information and for publishing it on the Web. SPARQL query language to query this data. Developers Guide to Semantic Web Toolkits to find a development toolkit in your preferred programming language to process DBpedia data. 2. We provide localized versions of DBpedia in 119 languages. The table below contains links to some example “things” from the data set: Bloom's Taxonomy. Bloom's wheel, according to the Bloom's verbs and matching assessment types.
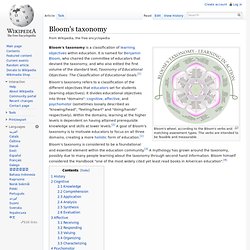
The verbs are intended to be feasible and measurable. Bloom's taxonomy is a classification of learning objectives within education. It is named for Benjamin Bloom, who chaired the committee of educators that devised the taxonomy, and who also edited the first volume of the standard text, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals.
Bloom's taxonomy refers to a classification of the different objectives that educators set for students (learning objectives). It divides educational objectives into three "domains": cognitive, affective, and psychomotor (sometimes loosely described as "knowing/head", "feeling/heart" and "doing/hands" respectively). Bloom's taxonomy is considered to be a foundational and essential element within the education community. History[edit] The first volume of the taxonomy, "Handbook I: Cognitive" (Bloom et al. 1956) was published in 1956. Cognitive[edit] Blooms Taxonomy Tutorial FLASH - CCCS Faculty Wiki.