

Structurer son enseignement avec des cartes conceptuelles et des objectifs pédagogiques. 22 novembre 2009 par Amaury Daele Dans une perspective de conception de l’enseignement axée sur l’apprentissage, nous abordons régulièrement avec mes collègues deux thématiques lors des formations-réflexions que nous proposons aux enseignant-e-s et aux assistant-e-s: la structuration des contenus au moyen de cartes conceptuelles et l’identification et la rédaction d’objectifs pédagogiques.

Ces deux thématiques sont fortement liées. La structuration des contenus est souvent la première question que se posent les enseignant-e-s universitaires quand ils/elles préparent un cours. L'idéateur en enseignement. Techniques pour l'apprentissage avec cartes conceptuelles. La carte conceptuelle : Un outil de développement de la métacognition. Introduction En tant que formateur chargé d’une part d’organiser l’enseignement et d’autre part de dispenser des cours, et face à la masse de connaissances qu’un étudiant se doit d’apprendre et de retenir lors de ses études, vous êtes-vous posé les questions suivantes : Comment fonctionne le cerveau ? Exemples de Cartes Conceptuelles. Faciliter l’apprentissage de nouveaux concepts par l’exercice des cartes conceptuelles. Dans le cadre du cours de chimie générale, les notions liées à la nomenclature et à l’écriture de formules chimiques sont présentées en début de session.
Ces notions, évaluées lors de chaque examen, occupent une place importante dans ce premier cours de chimie. Le nombre de catégories de composés chimiques ainsi que toutes les règles qui doivent être maîtrisées deviennent cependant vite un exercice très difficile pour un apprenant. Concept Mapping. « PreviousHomeNext » Social scientists have developed a number of methods and processes that might be useful in helping you to formulate a research project.

I would include among these at least the following -- brainstorming, brainwriting, nominal group techniques, focus groups, affinity mapping, Delphi techniques, facet theory, and qualitative text analysis. Here, I'll show you a method that I have developed, called concept mapping, which is especially useful for research problem formulation. How to use a Concept Map to organize and comprehend information.
Used as a learning and teaching technique, concept mapping visually illustrates the relationships between concepts and ideas.

Often represented in circles or boxes, concepts are linked by words and phrases that explain the connection between the ideas, helping students organize and structure their thoughts to further understand information and discover new relationships. Most concept maps represent a hierarchical structure, with the overall, broad concept first with connected sub-topics, more specific concepts, following. Basics of mind/concept mapping. Directing your thinking series Many of us have learned to outline information in our studies, as:

www.r-e-m.co.uk/logo/companion/twp/teaching_resources/Starting%20Concept%20Mapping.pdf. What is a Good Concept Map? - Degree Programme in Computer Science and Engineering. In constructing a concept map, the aim is to find essential concepts of a topic and their relationships.

The goal is to find clear concepts and relationships that can be described with one or at the most few words. Usually, the concept map cannot be finished on one session. Drawing a map is a learning process where concepts and relationships are added, deleted or changed. Especially, concidering the relationships can lead to changes of chosen concepts: noun is substituted with corresponding verb or adjective, general term to special term etc. Several terms can actually refer to one concept or different uses of a term can show up to be different concepts. 1. www.mlrg.org/memberpublications/CriteriaAndRationaleForGoodConceptMaps011204.pdf. How to make a concept map. "A good way to define the context for a concept map is to construct a Focus Question, that is a question that clearly specifies the problem or issue the concept map should help to resolve.
Every concept map responds to a focus question, and a good focus question can lead to a much richer concept map"[1] (Cañas and Novak) When you feel you have a focus question that gets to the heart of the subject you intend to map, you will add boxes containing the concepts related to the question. Where you can, add linking phrases showing how the concepts are related, but if you have not decided how they are linked, leave the linking phrase empty or the concepts unattached. Building a concept map - a concrete example Let us suppose that you have been asked to prepare a paper on the place of reason and emotion in management. Focus question First you develop the specific focus question that this map will attempt to answer: How are emotions and reason balanced in organizational management? Get started. Making Concept Maps (Novak) Novak's cmap home Excerpted, rearranged (and annotated) from an online manuscript by Joseph D.

Novak, Cornell University original manuscript was revised in 2008-> Concept maps are tools for organizing and representing knowledge. Building a Concept Map - What are the steps in building a concept map. The Theory Underlying Concept Maps and How to Construct and Use Them. Concept maps are graphical tools for organizing and representing knowledge.
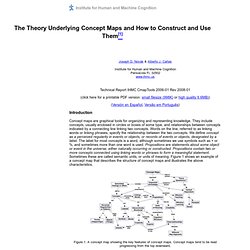
They include concepts, usually enclosed in circles or boxes of some type, and relationships between concepts indicated by a connecting line linking two concepts. Words on the line, referred to as linking words or linking phrases, specify the relationship between the two concepts. We define concept as a perceived regularity in events or objects, or records of events or objects, designated by a label. The label for most concepts is a word, although sometimes we use symbols such as + or %, and sometimes more than one word is used.
Propositions are statements about some object or event in the universe, either naturally occurring or constructed. Figure 1.