

Index of /soft. The Basics of C Programming". The previous discussion becomes a little clearer if you understand how memory addresses work in a computer's hardware.
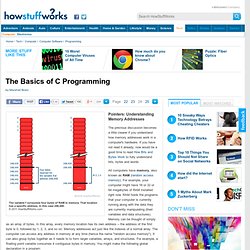
If you have not read it already, now would be a good time to read How Bits and Bytes Work to fully understand bits, bytes and words. All computers have memory, also known as RAM (random access memory). For example, your computer might have 16 or 32 or 64 megabytes of RAM installed right now. RAM holds the programs that your computer is currently running along with the data they are currently manipulating (their variables and data structures). Memory can be thought of simply as an array of bytes. jQuery: The Write Less, Do More, JavaScript Library. Javanotes 6.0. Introduction to Computer Science and Programming.
The C Library Reference Guide. UNIX Tutorial for Beginners.