

Washout toilet. A washout toilet is a kind of flush toilet predominantly used in Germany, Austria and France.
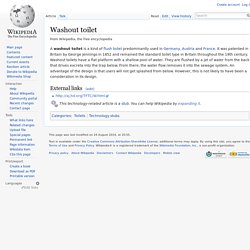
It was patented in Britain by George Jennings in 1852 and remained the standard toilet type in Britain throughout the 19th century. Washout toilets have a flat platform with a shallow pool of water. They are flushed by a jet of water from the back that drives excreta into the trap below. From there, the water flow removes it into the sewage system. An advantage of the design is that users will not get splashed from below. Toilet. Diseases, including cholera, which still affects some 3 million people each year, can be largely prevented when effective sanitation and water treatment prevents fecal matter from contaminating drinking water supplies.
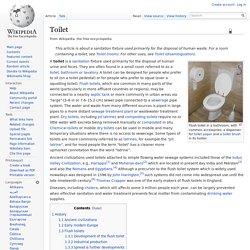
History Ancient civilizations According to Teresi et al. (2002):[7] The third millennium BC was the "Age of Cleanliness. " Pit latrine. Drawing of a simple pit latrine with a squatting pan and shelter.[1] A pit latrine or pit toilet is a type of toilet that collects human feces in a hole in the ground.
They use either no water or one to three liters per flush with pour-flush pit latrines.[2] When properly built and maintained they can decrease the spread of disease by reducing the amount of human feces in the environment from open defecation.[3][4] This decreases the transfer of pathogens between feces and food by flies.[3] These pathogens are major causes of infectious diarrhea and intestinal worm infections.[4] Infectious diarrhea resulted in about 0.7 million deaths in children under five years old in 2011 and 250 million lost school days.[4][5] Pit latrines are the lowest cost method of separating feces from people.[3]
Latrine. Privy midden. The privy midden (also midden closet) was a toilet system that consisted of a privy associated with a midden (or middenstead).
They were widely used in rapidly expanding industrial cities such as Manchester in England, but were difficult to empty and clean. A typical comment was that they were of "most objectionable construction" and "usually wet and very foul".[1] They were very often replaced eventually by pail closets and flush toilets. Toilet brush. Modern Toilet brush (2013) A toilet brush is a domestic implement designed for the cleaning of the lavatory pan.
The modern plastic version was invented in 1932 by William C. Schopp of Huntington Park, California, US and later patented in 1933 by The Addis Brush Company. [citation needed] In many cultures it is considered impolite to clean away biological debris without the use of chemical toilet cleaning products, as this can potentially leave residue on the bristles.
Flying toilet. Flying toilet and other waste in a slum in Cap-Haïtien, Haiti.
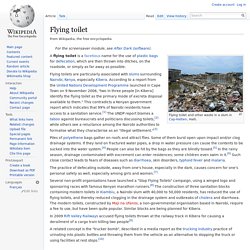
A flying toilet is a facetious name for the use of plastic bags for defecation, which are then thrown into ditches, on the roadside, or simply as far away as possible. Flying toilets are particularly associated with slums surrounding Nairobi, Kenya, especially Kibera. According to a report from the United Nations Development Programme launched in Cape Town on 9 November 2006, "two in three people [in Kibera] identify the flying toilet as the primary mode of excreta disposal available to them. " This contradicts a Kenyan government report which indicates that 99% of Nairobi residents have access to a sanitation service.[1] The UNDP report blames a taboo against bureaucrats and politicians discussing toilets,[2] while others see a reluctance among the Nairobi authorities to formalise what they characterise as an "illegal settlement.
Piles of polyethene bags gather on roofs and attract flies. Notes[edit] External links[edit] Dunny. Dunny or dunny can is Australian slang for toilet, either the room or the specific fixture, especially an outhouse or other outdoor toilets.
It is often used to specify a distinction between a flushing toilet and a non-flushing toilet (e.g., a longdrop or thunderbox). First used in print in 1952, the word is believed to be derived from the much older 'dunnakin' (also spelled 'dunnigin' and 'dunegan')[1] meaning privy. History[edit] Traditionally an outhouse could be found in unsewered areas and consisted of little more than a seat placed over a can or cesspit. The latter variation can be referred to more specifically as a longdrop. Norman Park, Queensland, like many areas of Brisbane was unsewered until the late 1960s, with each house having an outhouse or "dunny" in the back yard. By the middle of the twentieth century, outhouses had become much less common as modern plumbing diminished the need to keep toilets at a distance from the house.
See also[edit] Outhouse. Outhouse. Interior of an 1880s example near Stamford, South Dakota, showing seat with cover and a louvered vent to one side. 1940 WPA Community Sanitation Poster by John Buczak of Illinois promoting sanitary outhouse designs.
An outhouse, also commonly known as a privy, earth closet, or dunny in Australia, is a small structure, separate from a main building, which covers a pit toilet or a removable container. Outside North America, the term "outhouse" refers not to a toilet but to outbuildings in a general sense. Terminology[edit] The term outhouse is used in North American English for the structure over a pit toilet.[1] The structures are referred to by many other terms throughout the English-speaking world including dunny in Australia[A] and bog in the United Kingdom. Design and construction[edit] Outhouses vary in design and construction. Biological processes[edit] Main article: Pit latrine Soil percolation and groundwater pollution[edit] Bidet shower. A bidet shower, bidet spray, bidet sprayer or health faucet (sometimes colloquially, a "bum gun") is a hand-held triggered nozzle, similar to that on a sink sprayer, that delivers a spray of water to assist in cleansing the user's anus and genitals after defecation and urination.
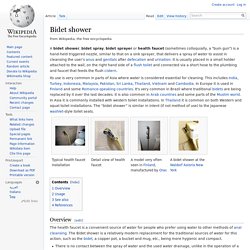
It is usually placed in a small holder attached to the wall, on the right hand side of a flush toilet and connected via a short hose to the plumbing and faucet that feeds the flush cistern. Its use is very common in parts of Asia where water is considered essential for cleaning. This includes India, Turkey, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam and Cambodia. Toilet-related injuries and deaths. A toilet with the potentially dangerous arrangement of the seat being up There are many toilet-related injuries and some toilet-related deaths throughout history and in urban legends.
Accidents[edit] In young boys, one of the most common causes of genital injury is when the toilet seat falls down while they are standing at the toilet.[1] Smaller children run the risk of drowning if they fall headfirst into the toilet. Injuries to adults include bruised buttocks, tail bones, and dislocated hips from unsuspectingly sitting on the toilet bowl rim because the seat is up or loose. Toilets in Japan. A cleansing jet of water designed to cleanse the anus of the user of this bidet-style toilet Control elements of a modern Japanese toilet Toilets in Japan are generally more sophisticated than toilets in other developed nations. There are two styles of toilets commonly found in Japan;[1][2] the oldest type is a simple squat toilet, which is still somewhat common in public conveniences. After World War II, modern Western-type flush toilets and urinals became common. The current state of the art for Western-style toilets is the bidet toilet, which, as of March 2010, is installed in 72% of Japanese households.[3][4][5][6] In Japan, these bidets are commonly called washlets, a brand name of Toto Ltd., and include many advanced features rarely seen outside of Asia.
History[edit] During the Jōmon period (14,000 B.C. to 300 B.C.) settlements were built in a horseshoe shape, with a central plaza in the middle and garbage heaps around the settlement. Terminology[edit] The word toire (トイレ?) Low-flush toilet. A low-flow toilet is a flush toilet that uses significantly less water than a full-flush toilet. Low-flow toilets use 6 liters (1.6 gallons) or less per flush as opposed to 13.2 liters (about 3.5 gallons) as was the norm in the 1980s and prior. They came into use in the United States in the 1990s, in response to water conservation concerns.[1] Low-flow toilets include single-flush models and dual-flush toilets, which typically use 1.6 gpf for the full flush and 1.1 gpf for a reduced flush. Although, technology have come along way since then and in saving the world and the fresh water supplies. Ultra low-flush toilets that the Swedish company Wostman Ecology have constructed since 1993 years of technology.
Is without any doubt the most ecological solution; Eco flush use only 0.6 liters (0.16 gallons) per average flush, Eco Dry and Eco vac(uum) go even lower than that, down to only 0.3 liters per average flush (0.08 gallons) Electronic bidet. Bog Standard Gallery. Bog Standard Gallery was previously a portable toilet cubicle and is believed to be one of the smallest "art galleries" in the world.[1][2][3] The gallery, complete with white walls and an oak floor, the piece of installation art mimicking a traditional gallery space, was created and curated by UK-based artist, Melanie Boda (née Warner) in 2007. Measuring just over one metre squared, the piece was created as part of Melanie Boda's degree course in Interactive Arts[4] at Manchester Metropolitan University gaining her first class honours.
Bog Standard Gallery was created to house photographs from Melanie Boda's 'Bog Standard Signs' series, a collection of photographs of toilet signs from around the world. [citation needed] The collection spans thousands of images of the symbols used to depict 'male' and 'female' on toilet doors from around the globe. References[edit] External links[edit] Dry toilet. Schematic of the Dry Toilet [1] A dry toilet is a toilet that operates without flushwater. The dry toilet may be a raised pedestal on which the user can sit, or a squat pan over which the user squats. In both cases, excreta (both urine and faeces) fall through a drop hole.[2] The excreta can either become mixed at the point of dropping (the more common scenario) or stay separated (the scenario in a toilet with urine diversion which is not as common).
Strictly speaking, a dry toilet refers only to the device that the user squats over or sits on. In practice, however, it is often used to denote a variety of technologies and in particular combinations of technologies, namely the user interface plus the storage or treatment unit below it. When speaking about a pit latrine with another person, one should therefore always clarify which type of toilet they actually mean. Pissoir. Šulak. Loo of the Year Awards. Clivus Multrum. Portable toilet. Toilet humour. Toilet humor, or scatological humor, is a type of off-color humor dealing with defecation, urination, and flatulence, and to a lesser extent vomiting and other body functions.
It sees substantial crossover with sexual humor, such as penis jokes. Public toilet. A public toilet (also called a bathroom, restroom, latrine, comfort room, powder room, toilet room, washroom, water closet, W.C., public lavatory, lav, convenience) is a room or small building containing one or more toilets and possibly also urinals which is available for use by the general public, or in a broader meaning of "public", by customers of other services. Public toilets are commonly separated by gender into male and female facilities, although some can be unisex, particularly the smaller or single occupancy types.
Increasingly, public toilets incorporate accessible toilets and features to cater for people with disabilities. Composting toilet. Public composting toilet facility on E6 highway in Sweden. Washlet.