World ancestry. Why Do Human Children Stay So Small For So Long? Why does it take so long for human children to grow up?
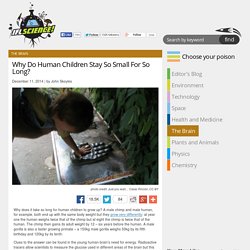
A male chimp and male human, for example, both end up with the same body weight but they grow very differently: at year one the human weighs twice that of the chimp but at eight the chimp is twice that of the human. The chimp then gains its adult weight by 12 – six years before the human. A male gorilla is also a faster growing primate – a 150kg male gorilla weighs 50kg by its fifth birthday and 120kg by its tenth. Clues to the answer can be found in the young human brain’s need for energy. Radioactive tracers allow scientists to measure the glucose used in different areas of the brain but this procedure is only used rarely when it is justified by investigating neurological problems. From about the age of four to puberty, the young brain guzzles glucose – the cerebral cortex, its largest part, uses nearly (or more than) double that used earlier or later in life. Brain energy use and body size It’s the connections that count. 19 Pieces Of Non-Human DNA Found In Human Genome.
Eight percent of your DNA is alien, in that it’s made up of non-human, viral fragments. In fact, viral fragments are often hiding within the genome of anything on Earth that has a jaw and a spinal cord, which is a remarkable reminder of how they’ve shaped evolution for hundreds of millions of years. A new study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, reveals that we are even less “human” than previously thought: Nineteen new pieces of ancient viral DNA have been uncovered within our own genome. Perhaps most strikingly, the full genetic “recipe” for an entire virus was found within 2 percent of the people examined. This Population Map Will Tell You If You Have Ancient Denisovan Or Neanderthal DNA In Your Genome. Rich sexual past between modern humans and Neandertals revealed. Only a bit of the DNA coiled inside the cells of Europeans and Asians comes from Neandertals, but those snippets have sparked a flurry of research.
In the past few years, researchers have traced them to one or two ancient encounters with our extinct cousins. Now, a report published online in Science this week details a far richer sexual past for modern humans and their archaic cousins, one that played out at multiple times and places over the past 60,000 years. By developing powerful new statistical methods, an international team has identified how often and on which continents modern humans, Neandertals, and a second kind of archaic human called Denisovans met and mated.
The researchers conclude that if you’re an East Asian, you have three Neandertals in your family tree; Europeans and South Asians have two, and Melanesians only one. Brain food: Clever eating. Jon Foster/National Geographic Creative/Bridgeman Images Early humans who hunted animals for meat developed bigger brains than plant eaters.
Around 6 million years ago, primates started moving from tropical forests into the savannahs. Unlike today, these prehistoric expanses were humid and probably provided a year-round supply of fruit and vegetables. But then, some 3 million years ago, the climate changed and the savannahs — along with their plentiful food supply — dried up. Many mammals, including some primates, went extinct, but others adapted. Only two types of primate survived the climate catastrophe, says Domínguez-Rodrigo.
The meat-eating machine became us. Homo Naledi, New Human Species, Is Found in South African Cave. Continue reading the main story Video Acting on a tip from spelunkers two years ago, scientists in South Africa discovered what the cavers had only dimly glimpsed through a crack in a limestone wall deep in the Rising Star Cave: lots and lots of old bones.

The remains covered the earthen floor beyond the narrow opening. This was, the scientists concluded, a large, dark chamber for the dead of a previously unidentified species of the early human lineage — Homo naledi. The new hominin species was announced on Thursday by an international team of more than 60 scientists led by Lee R. New Species Of Human Discovered In South Africa. Brace yourself: this discovery is huge.
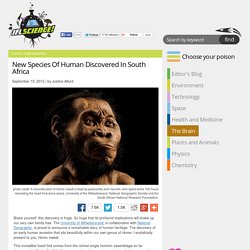
So huge that its profound implications will shake up our very own family tree. The University of Witwatersrand, in collaboration with National Geographic, is proud to announce a remarkable story of human heritage. The discovery of an early human ancestor that sits beautifully within our own genus of Homo. I ecstatically present to you, Homo naledi. This incredible fossil find comes from the richest single hominin assemblage so far discovered in Africa.
A textbook-worthy accident, H. naledi was first stumbled upon two years ago by amateur cavers during an exploration of a cave system known as Rising Star, located within South Africa’s famous Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site. That something different turned out to be not several, but 15 individuals from a single hominin species, represented by more than 1,500 fossil elements found within a single chamber in total darkness some 90 meters (295 feet) from the entrance. Photo Gallery. New human species discovered. From the moment in 2013 when paleoanthropologist Lee Berger posted a plea on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn for “tiny and small, specialised cavers and spelunkers with excellent archaeological, palaeontological and excavation skills,” some experts began grumbling that the excavation of a mysterious hominin in the Rising Star Cave in South Africa was more of a media circus than a serious scientific expedition.