

» The Constraints of Time, The Limits of Reason. Stanford prison experiment. The Stanford prison experiment (SPE) was a study of the psychological effects of becoming a prisoner or prison guard.
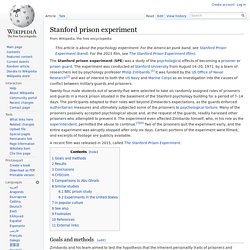
The experiment was conducted at Stanford University from August 14–20, 1971, by a team of researchers led by psychology professor Philip Zimbardo.[1] It was funded by the US Office of Naval Research[2] and was of interest to both the US Navy and Marine Corps as an investigation into the causes of conflict between military guards and prisoners. Goals and methods[edit] Milgram experiment. The experimenter (E) orders the teacher (T), the subject of the experiment, to give what the latter believes are painful electric shocks to a learner (L), who is actually an actor and confederate.
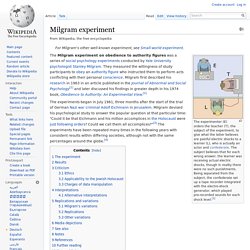
The subject believes that for each wrong answer, the learner was receiving actual electric shocks, though in reality there were no such punishments. Being separated from the subject, the confederate set up a tape recorder integrated with the electro-shock generator, which played pre-recorded sounds for each shock level.[1] Strip search prank call scam. The strip search phone call scam is a series of incidents that extended over a period of about ten years before an arrest was made in 2004.
The incidents involved a man calling a restaurant or grocery store, claiming to be a police officer and then convincing managers to conduct strip searches of female employees and to perform other bizarre acts on behalf of "the police". The calls were most often placed to fast-food restaurants in small towns located in rural areas of the United States. Over 70 such occurrences were reported in 30 U.S. states until an incident in 2004 in Mount Washington, Kentucky (population 9,117), finally led to the arrest of David R. The Confessions. Institute. The Singularity Institute is one of the leading research institutes on Singularity subjects.
Below are short answers to common questions we receive. (First published in 2011.) Basics. Judges orders millions paid in NYC firefighter bias case. The lack of minorities in U.S. fire departments has been the focus of many lawsuits.
Judge ordered New York to pay nearly $128 million to firefightersEntrance exam designed to keep blacks and Latinos off the force, says lawsuit"We believe the court's latest opinion is erroneous," says city's counsel (CNN) -- A U.S. district judge ordered New York City to pay $128 million in to firefighters who allege the city used an entrance exam that deliberately sought to keep African-Americans and Latino Americans off the force.
The judge also ordered the FDNY to hire 293 black and Latino applicants. "It has been in the city's power to prevent or remedy the need for damages proceedings for a decade, and it has not done so," U.S. District Judge Nicholas G. The federal government had sued the city (United States of America and Vulcan Society Inc. vs. Disparate impact. In United States employment law, the doctrine of disparate impact holds that employment practices may be considered discriminatory and illegal if they have a disproportionate "adverse impact" on persons along the lines of a protected trait.
Although the protected traits vary by statute, most federal civil rights laws include race, color, religion, national origin, and gender as protected traits, and some laws include disability status and other traits as well. Under the doctrine, a violation of Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act may be proven by showing that an employment practice or policy has a disproportionately adverse effect on members of the protected class as compared with non-members of the protected class.[1] Therefore, the disparate impact doctrine under Title VII prohibits employers "from using a facially neutral employment practice that has an unjustified adverse impact on members of a protected class. Disparate impact contrasts with disparate treatment. Intelligence and public policy. A large body of research indicates that intelligence measures such as Intelligence Quotient (IQ) varies between individuals and between certain groups, and that they correlate with socially important outcomes such as educational achievement, employment, crime, poverty and socioeconomic status.
In the United States, certain public policies and laws regarding employment, military service, education and crime incorporate IQ or similar measurements. Internationally, certain public policies, such as improving nutrition and prohibiting neurotoxic toxins, have as one of their goals raising or preventing a decline in intelligence. Use of cognitive tests in the United States legal system and public policy[edit] History[edit] In the early 20th century, eugenics legislation was passed in many US states which allowed, or encouraged, sterilization of "feeble-minded" individuals. Court OKs Barring High IQs for Cops. <br/><a href=" US News</a> | <a href=" Business News</a> Copy A man whose bid to become a police officer was rejected after he scored too high on an intelligence test has lost an appeal in his federal lawsuit against the city.
The 2nd U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in New York upheld a lower court’s decision that the city did not discriminate against Robert Jordan because the same standards were applied to everyone who took the test. Why Most Published Research Findings Are False. Summary There is increasing concern that most current published research findings are false.

The probability that a research claim is true may depend on study power and bias, the number of other studies on the same question, and, importantly, the ratio of true to no relationships among the relationships probed in each scientific field. Contradicted and Initially Stronger Effects in Highly Cited Clinical Research. How grant chasing corrupts science. The middle twentieth century saw a golden age in medical breakthroughs in a context where only modest numbers (and percentages) of people did 'medical research'.

Whether in the hope that this progress could be continued, or simply from self-interestedly using past breakthroughs as leverage for increasing future resource, medical research funding was vastly exanded from the nineteen sixties - doubling about every decade. Nowadays, 'medical research' - i.e. research justified by supposedly having medical relevance - is by far the biggest area of science. Scientists working in areas that were close to medicine began to re-orientate their research in order to justify applying for these sources of funding. Basic biologists working in cell chemistry, immunology, genetics - began to argue that their work may have potential medical relevance. Untitled. Efforts over the past decade to characterize the genetic alterations in human cancers have led to a better understanding of molecular drivers of this complex set of diseases.
Although we in the cancer field hoped that this would lead to more effective drugs, historically, our ability to translate cancer research to clinical success has been remarkably low1. Sadly, clinical trials in oncology have the highest failure rate compared with other therapeutic areas. Given the high unmet need in oncology, it is understandable that barriers to clinical development may be lower than for other disease areas, and a larger number of drugs with suboptimal preclinical validation will enter oncology trials. However, this low success rate is not sustainable or acceptable, and investigators must reassess their approach to translating discovery research into greater clinical success and impact. Confirming research findings. The Irrationality of Irrationality: The Paradox of Popular Psychology.
In 1996, Lyle Brenner, Derek Koehler and Amos Tversky conducted a study involving students from San Jose State University and Stanford University. The researchers were interested in how people jump to conclusions based on limited information. Previous work by Tversky, Daniel Kahneman and other psychologists found that people are “radically insensitive to both the quantity and quality of information that gives rise to impressions and intuitions,” so the researchers knew, of course, that we humans don’t do a particularly good job of weighing the pros and cons. But to what degree? Closing the achievement gap : the implementation of direct instruction in Whiteville City schools, UNCW Seahawk DOCKS (North Carolina Digital Online Collection of Knowledge and Scholarship) UNCW Author/Contributor (non-UNCW co-authors, if there are any, appear on document) Untitled. Has Physics Made Philosophy and Religion Obsolete? - Ross Andersen.
"I think at some point you need to provoke people. Science is meant to make people uncomfortable. " It is hard to know how our future descendants will regard the little sliver of history that we live in. It is hard to know what events will seem important to them, what the narrative of now will look like to the twenty-fifth century mind. Untitled. The Foreign-Language Effect. Thinking in a Foreign Tongue Reduces Decision Biases. Number of biracial babies soars over past decade. First Trailer for Documentary 'Samsara' Has Stunning 70mm Imagery.
Gay Couples More Likely To Be Interracial Or Inter-Ethnic, According To New 2010 Census Analysis. A new analysis of 2010 U.S. Census data has found that same-sex couples are more likely to be interracial or inter-ethnic compared to their heterosexual counterparts. 07%20NERA%202010_Winter%20GlobalEd2%20paper_Yukhymenko%20et%20al. JOSHUA KNOBE: The New Science of Morality. Feminist Speculative Fiction Anthology by Jef Smith.
This project will fund a speculative fiction (science fiction, fantasy, & horror) anthology devoted to feminist themes. Alfredo Quinones-Hinojosa. gQOre. The life of Samuel Johnson: including A journal of a tour to the Hebrides - James Boswell. Online disinhibition effect. The Righteous Mind: Why Good People Are Divided by Politics and Religion (9780307377906): Jonathan Haidt. Jonathan Haidt. Education and career[edit] Haidt was born in New York City and raised in Scarsdale, New York. PHILOSOPHY AND THE SCIENTIFIC IMAGE OF MAN. Benjamin Rosenbaum's Page. Catherynne M. Valente - Home. Paul Melko. Windupstories.com – fiction by paolo bacigalupi.
WKUK Insult Restaurant. Immigration Restrictions: A Solution in Search of a Problem. Michael Gazzaniga: "Who's in Charge: Free Will and the Science of the Brain. Book Review: Who's in Charge? Eng_o_ml-sefer-kabbalah-science-and-the-meaning-of-life. What the Bleep Do We Know!? Quantum Consciousness. Entitlement issues... Work Is Never Over: On Publishing and Its Many Faces. Let Me Tell You About the Birds and the Bees: Gender and the Fallout Over Christopher Priest.
The Last Magic Show: A Blind Brain Theory of the Appearance of Consciousness « Three Pound Brain. Cooperation and the evolution of intelligence. ALL THE THINGS - semester almost over reread all the bakker books. Saturday Morning Breakfast Cereal. Doc.renlearn.com/KMNet/R004101202GH426A.pdf. American High School Students Are Reading Books At 5th-Grade-Appropriate Levels: Report.
Researchers may have discovered how memories are encoded in the brain. Becoming Ourselves - memetics. Why People Are Irrational about Politics. GoFlow - World's First tDCS Kit. Incognitumhactenus-vol2. Brainport Vision Device helps a blind man "see" 3D-nanoprinting speed record set by Vienna University. R. Scott Bakker on A Game of Thrones and deconstructing the epic fantasy genre. Can a pill 'cure racism' Should we use LSD to treat alcoholism. Better Living Through Electrochemistry. Modular Prosthetic Limb. Understanding Comics - Scott McCloud. Left Brain – Right brain and the Spinning Girl. Theory of Everything: What is Matter? Brian Cox - Everything is Connected to Everything. An Alien God. Rejectamentalist manifesto. Online papers on consciousness. Three Roses, Bk. 1: The House of Yesteryear (by Roger E. Eichorn) « Three Pound Brain. Economics Under My Skin: Introducing Physiological Observations in the Sciences of Decision-Making by Clement Levallois.
The Republican Brain: Why Even Educated Conservatives Deny Science. Duty Calls. Mark Charan Newton » Things I got wrong. Mark Charan Newton » Efforts to avoid Racefail. Can We Add Carmen and Gang Signs to the “Formerly Repugnant” List? Review: The Wayward Mind by Guy Claxton. August 28th, 2009. Why I Didn’t Delete Tiger Beatdown. Safe space. Amazon. Untitled. Derailing for Dummies. How Companies Learn Your Secrets. The Anti-Male Shaming Tactics Catalog. Bing. Liars and Outliers: Table of Contents. Dr. Neal Goldsmith - Home Page. NYU Psilocybin Cancer Anxiety Study.