

Things they don't tell you about MongoDB. MongoDB is by far the most popular NoSQL database in Brazil (at least based on the amount of blog posts and articles writen about it here that I read).

It’s really an amazing solution but what really bothers me is the fact that very few people know about it’s limitations. So I see the same story repeating itself: people unhappy with it treating his limitations as if they were bugs. This post is about some of it’s limitations that really caught me by surprise, so that if you are thinking in adopting it at least you’ll be warned about them and so avoid these headaches. Hungry for bytes This was my first surprise: MongoDB consumes too much disk space. If storage space is a restriction to your project you MUST take this in consideration. Genghis, the single-file MongoDB admin app.
Apache CouchDB. MongoDB. Richardwilly98/elasticsearch-river-mongodb. Amazon EC2 and MongoDB configuration for great performance. Sometimes, we prefer using Amazon EC2 directly for our Rails stack.

No offense to Heroku but we need a more controlled environment; and no offense to EngineYard as they don’t support MongoDB on their environment as yet. We were faced with several problems that we wanted to solve Control our environment without MongoDB hogging all the memory.Choose the right instanceChoose the right fileSystem for the optimal performance. Choice of EC2 instance is always an interesting one – when you have to shell out the money from your pocket, you neither want to overspend nor underutilize the instance. We found that using an m1.medium instance (4 GB ram) gave us enough lee-way to manage our MongoDB instances.
Over the course of changing instances, tuning them up for performance, we realized these important pointers: Understanding MongoDB Storage - PolySpot Blog. Posted on July 4, 2012 by Arnaud BAILLY How MongoDB stores its Data This article tries to explain the intricacies of MongoDB storage and how it affects performances of the database.

It was sparked by questions which people who were more familiar with “traditional” databases asked, and more specifically questions regarding the memory consumption of mongod and its impact on other processes running in the same host. It is rather linux-centric. The following figure tries to present how the various components of a MongoDB node (Disks, File System, RAM) interact to provide access to the database. A Year with MongoDB - Engineering at Kiip. This week marks the one year anniversary of Kiip running MongoDB in production.

MongoDB strategies for the disk-averse. Feb 09th Behind the scenes at foursquare, we have a lot of data collection efforts that present interesting scaling puzzles.

One is the venue metrics system, which allows business owners to get information about checkins to their venue over time. It lets them see the effect of specials, understand their clientele’s demographics, and even identify their most loyal customers. An Articulate Introduction to MongoDB. NOSQL has become a very heated topic for large web-scale deployment where scalability and semi-structured data driven the DB requirement towards NOSQL.

There has been many NOSQL products evolving in over last couple years. In my past blogs, I have been covering the underlying distributed system theory of NOSQL, as well as some specific products such as CouchDB and Cassandra/HBase. Last Friday I was very lucky to meet with Jared Rosoff from 10gen in a technical conference and have a discussion about the technical architecture of MongoDb. I found the information is very useful and want to share with more people.
One thing I am very impressed by MongoDb is that it is extremely easy to use and the underlying architecture is also very easy to understand. Here are some simple admin steps to start/stop MongoDb server 02.mkdir /data/lib 05.... 08.... Major difference from RDBMSMongoDb differs from RDBMS in the following way. Trees in MongoDB. To model hierarchical or nested data relationships, you can use references to implement tree-like structures.
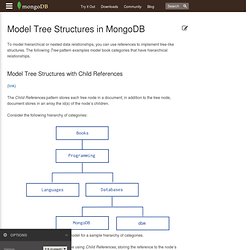
The following Tree pattern examples model book categories that have hierarchical relationships. Model Tree Structures with Child References (link) The Child References pattern stores each tree node in a document; in addition to the tree node, document stores in an array the id(s) of the node’s children. SimpleDB. Amazon SimpleDB is a highly available NoSQL data store that offloads the work of database administration.
Developers simply store and query data items via web services requests and Amazon SimpleDB does the rest. Unbound by the strict requirements of a relational database, Amazon SimpleDB is optimized to provide high availability and flexibility, with little or no administrative burden. Behind the scenes, Amazon SimpleDB creates and manages multiple geographically distributed replicas of your data automatically to enable high availability and data durability. The service charges you only for the resources actually consumed in storing your data and serving your requests.
You can change your data model on the fly, and data is automatically indexed for you. The service allows you to focus fully on value-added application development, rather than arduous and time-consuming database administration. Amazon SimpleDB passes on to you the financial benefits of Amazon’s scale. Document-Oriented NoSQL Database. RavenDB - 2nd generation document database.
Document-oriented database. This article is about the software type.
For usage/deployment instances, see Full text database. A document-oriented database is a computer program designed for storing, retrieving, and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data. Document-oriented databases are one of the main categories of NoSQL databases and the popularity of the term "document-oriented database" (or "document store") has grown[1] with the use of the term NoSQL itself. In contrast to relational databases and their notion of "Relation", i.e., a tuple (or row) of related strong-typed data items, these systems are designed around an abstract notion of a "document".