

Principles of Biomedical Engineering - Sundararajan V. Madihally. DSM0707_021.pdf. The Implantable Insulin Pump. Can an 'artificial pancreas' normalize type 1 diabetes? - Discovery's Edge: Mayo Clinic's Online Research Magazine - Mayo Clinic Research. July 2011 Summary Mayo Clinic researchers have developed an "artificial pancreas" to monitor blood sugar and deliver the appropriate dose of insulin to people with type 1 diabetes.
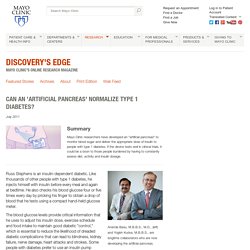
If the device tests well in clinical trials, it could be a boon to those people burdened by having to constantly assess diet, activity and insulin dosage. Ananda Basu, M.B.B.S., M.D., (left) and Yogish Kudva, M.B.B.S., are longtime collaborators who are now developing the artificial pancreas. Russ Stephens is an insulin-dependent diabetic. The blood glucose levels provide critical information that he uses to adjust his insulin dose, exercise schedule and food intake to maintain good diabetic "control," which is essential to reduce the likelihood of dreaded diabetic complications that can lead to blindness, kidney failure, nerve damage, heart attacks and strokes.
"They set the alarm and wake up to check. That burdensome routine might someday be medical history. How it works Assessing physical activity Dr. Drs. JDRF: Improving Lives. Curing Type 1 Diabetes. For more details on the JDRF Artificial Pancreas Project, click here.
Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems: Engineering the Algorithms. Introduction From the time of closed-loop hospital setting studies in the 1970s (1), the automation of blood glucose (BG) control has been a grand challenge for type 1 diabetes treatment, i.e., the artificial pancreas (AP).

The inconvenience of early intravenous BG sensing and insulin delivery motivated the development of subcutaneous (SC) continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and continuous SC insulin infusion (CSII) pumps, which remain the most widely used platforms for AP development. Initially, software algorithms utilizing CGM and CSII pumps operated with the goal of insulin suspension to prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia. Recent clinical trials have extended this approach with process control algorithms, often augmented with compensatory manual insulin boluses, to handle more complex challenges, such as meals and exercise. The application of advanced control algorithms has led to substantial improvements in BG control. Artificial Pancreas Project - JDRF Advocacy. The Artificial Pancreas Project The artificial pancreas will represent the most revolutionary development in diabetes care since the discovery of insulin.
Diabetes By The Numbers (Health Infographics) Diabetes By The Numbers - More than 8% of the US population has diabetes: 1) Total: 25.5 million people; 2) Diagnosed: 18.8 million people; 3) Undiagnosed: 7 million people; 4) Prediabetes: 79 million people; 5) New cases: In 2010, 1.9 million new cases of diabetes were diagnosed in people aged 20 years and older. - US Hispanics are 66% more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes compared to Non-Hispanic Whites. - More than 90% (9 in 10) of US Hispanics with diabetes or at risk, have not visited a podiatrist. - Nearly 12% of US Hispanics aged 20 or older have diabetes.

Insulin Regulation of Blood Sugar and Diabetes - The Important Roles of Insulin and Glucagon: Diabetes and Hypoglycemia. The human body wants blood glucose (blood sugar) maintained in a very narrow range.

The Importance of Controlling Blood Sugar. What happens if the blood glucose (sugar) goes too low or too high?
It is very important that blood sugar levels are kept as close to normal as possible. The Pancreas and Its Functions. National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering. Biomedical Engineering. The Biomedical Engineering Department at Boston University is among the largest of its kind in the United States and is home to award-winning faculty, exceptional students and numerous research centers and laboratories engaged in an array of interdisciplinary biomedical activities.
Biomedical engineering is advancing rapidly and producing important innovations that improve our quality of life. From understanding the human genome to pioneering surgical tools, Boston University biomedical engineers are committed to the advancement of research and education in biotechnology, biomolecular engineering, sensory systems, cardiopulmonary engineering, neuroscience, micro-and nano-systems, synthetic biology, systems biology and biomechanics and biomaterials. Bioengineering: The key to a better life or Frankenstein’s monster? The field of bioengineering is a convoluted and daunting subject for most.

The word itself is hard to conceptualize. Many people can visualize the work of electrical engineers or even chemical engineers, but bioengineering seems to imply the application of engineering principles to life itself. However absurd this may sound, it is the correct definition. Bioengineering is a massive field that encompasses genetic testing, micromachines and robotics, prosthetics, tissue regeneration, and stem cell research. This field is incredibly useful and very hotly debated. One of the main arguments against bioengineering is that humans are not fit to play the role of god. Bionic Humans: Top 10 Technologies. Maggie Koerth-Baker | August 13, 2008 01:43pm ET <div class="countdown_data"><div><h2>Bionic Eyes</h2><p>When you're blind, being able to see even the basics of light, movement and shape can make a big difference.
Both the Argus II Retinal Prosthesis, currently in FDA trials, and a system being developed by Harvard Research Fellow Dr. John Pezaris record basic visual information via camera, process it into electronic signals and send it wirelessly to implanted electrodes. The Argus II uses electrodes implanted in the eye, which could help people who've lost some of their retinal function. Dr. Artificial Pancreas May Improve Type 1 Diabetes Treatment. An artificial pancreas may offer people with type 1 diabetes a better way to their keep glucose levels in check than the conventional diabetes treatment, which involves an insulin pump, according to a new study. The artificial pancreas is an automated system that helps people with diabetes control glucose levels through the automatic administration of one or two hormones. In the new study of 30 adults and teens with type 1 diabetes, researchers compared the conventional insulin-pump therapy to two types of artificial pancreas.
One type delivers two hormones, insulin and glucagon, while the other delivers only insulin. (Insulin triggers the cells in the body to take up glucose, so it lowers levels of sugar in the blood. Glucagon causes liver cells to release sugar into the blood, thereby raising blood sugar levels.) The patients stayed overnight in a research facility three times between February 2013 and May 2014, and the doctors monitored the participants' glucose levels. Why biomedicine is something bad religious context. Biomedicine Type 1 Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes EXPOSED - What Really Causes Diabetes. Insulin, Glucose and you. The Role and Anatomy of the Pancreas. New implanted form of artificial pancreas for diabetes set for human trials. Human trials of a new form of artificial pancreas that is implanted into the body to treat diabetes, has been scheduled to run in 2016.
Whilst a number of artificial pancreas systems are currently being developed, the majority of these are based around an insulin pump communicating and responding to readings provided by a continuous glucose monitor. The new device differs, however, in that it is an implantable device that contains a refillable reservoir of insulin. Cure Type 1 Diabetes - Cure Diabetes - Islet Sheet - Hanuman Medical Foundation - The Bioartificial Pancreas. “Development of a ‘bioartificial pancreas’ that housed islets, protected them from the immune system, and encouraged their growth would be a major step forward for transplantation.” —Kelly Close, in Targeting a Cure A bioartificial pancreas—a device that encapsulates and nurtures islets of Langerhans— replaces the islets and beta cells destroyed by type 1 diabetes.
Implanted in the peritoneal cavity or under the skin, it contains about a million islets. It responds to changing blood glucose levels by releasing hormones, chiefly insulin. Any bioartificial pancreas is fabricated from living and nonliving components. Several Approaches Medical technology firms, working with researchers, have tried various ways to create a bioartificial pancreas that performs as it should, using physical configurations such as coatings, capsules, hollow fibers and sheets. Pancreas Transplantation: American Diabetes Association® Some patients with type 1 diabetes have experienced positive results from pancreas transplants. Typically, part or all of a new pancreas is surgically implanted. The old pancreas is left alone; it still makes digestive enzymes, even though it doesn’t make insulin.
Most organs are obtained from someone who has died but has decided to be an organ donor. Artificial Pancreas. Can you build a human body?