

Pyramids. Giza Necropolis. The Giza Necropolis (Arabic: أهرامات الجيزة, IPA: [ʔɑhɾɑˈmɑːt elˈɡiːzæ], "pyramids of Giza") is an archaeological site on the Giza Plateau, on the outskirts of Cairo, Egypt.
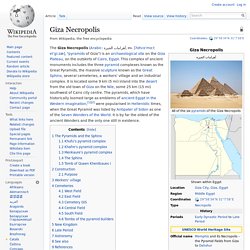
Pyramids of Güímar. The Pyramids of Güímar refer to six rectangular pyramid -shaped, terraced structures, built from lava stone without the use of mortar .
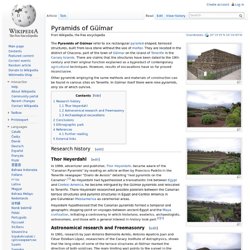
They are located in the district of Chacona, part of the town of Güímar on the island of Tenerife in the Canary Islands . There are claims that the structures have been dated to the 19th century and their original function explained as a byproduct of contemporary agricultural techniques. However, results of excavations have so far proved inconclusive. Other pyramids employing the same methods and materials of construction can be found in various sites on Tenerife.
In Güímar itself there were nine pyramids, only six of which survive. Research history [ edit ] Thor Heyerdahl [ edit ] Astronomical research and Freemasonry [ edit ] In 2005, a book was published in Spanish by Aparicio and Esteban titled The Pyramids of Güímar: Myth and Reality . Pyramid Hill of the Lake Baikal, Russia. Baikal is one of the biggest lakes in world on area of 31,722 km2 (12,248 sq miles) located in Eastern Siberia, Russia.

Baikal is famous for its depth in 1,642 m (5,387 ft) that makes Baikal is the deepest lake in the world with amazing clearest water. Wild nature and fresh Siberian air attracts people from all over the world even in extremely cold Siberian winter for visiting so pure lake Baikal. In 2007 an architect and scholar of the Irkutsk State Technical University Lubov Makogon visited with her student Port Baikal, a little fisher port town on western Baikal lakeshore where she noted an unusual hill with four visible sides oriented to the North. The hill in height of 80 meters with the width of the base in 170 meters located in the center of Baikal Port close to the lakeshore and had a perspective view from the lake and mouth of the Angara river. Great Pyramid of Giza. The Great Pyramid of Giza (also known as the Pyramid of Khufu or the Pyramid of Cheops) is the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in the Giza Necropolis bordering what is now El Giza, Egypt.
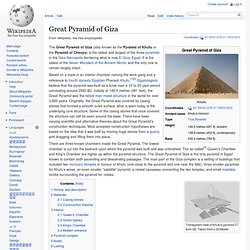
It is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one to remain largely intact. Based on a mark in an interior chamber naming the work gang and a reference to fourth dynasty Egyptian Pharaoh Khufu,[1][2] Egyptologists believe that the pyramid was built as a tomb over a 10 to 20-year period concluding around 2560 BC. Initially at 146.5 metres (481 feet), the Great Pyramid was the tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years. Originally, the Great Pyramid was covered by casing stones that formed a smooth outer surface; what is seen today is the underlying core structure. Pyramid of Khafre. The Pyramid of Khafre, also known as the Pyramid of Chephren,[1] is the second-tallest and second-largest of the ancient Egyptian Pyramids of Giza and the tomb of the fourth-dynasty pharaoh Khafre (Chefren), who ruled from c. 2558 to 2532 BC.[2] Size[edit] The pyramid has a base length of 215.5 m (706 ft) and rises to a height of 136.4 metres (448 ft) (originally 143.5 m or 471 ft).[1] The Pyramid is made of limestone blocks (weighing more than 2 tons each).
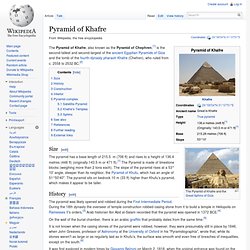
The slope of the pyramid rises at a 53° 10' angle, steeper than its neighbor, the Pyramid of Khufu, which has an angle of 51°50'40". The pyramid sits on bedrock 10 m (33 ft) higher than Khufu’s pyramid, which makes it appear to be taller. History[edit] La Danta pyramid - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. La Pirámide de La Danta es una pirámide construida por los antiguos mayas que se encuentra en El Mirador , Petén, Guatemala , cerca de la frontera con México .
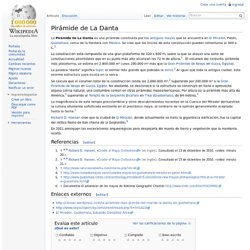
Se cree que los inicios de esta construcción pueden remontarse al 300 a. C. [ 1 ] La construcción está compuesta de una gran plataforma de 320 x 600 m, sobre la que se elevan una serie de construcciones piramidales que en su punto más alto alcanzan los 72 m de altura. [ 1 ] . El volumen del conjunto, pirámide más plataforma, se estima en 2.800.000 m³ (unos 200.000 m³ más que la Gran Pirámide de Keops en Guiza , Egipto ).
La palabra "danta" significa tapir : el animal más grande que poblaba la selva . [ 2 ] Al igual que toda la antigua ciudad, esta enorme estructura yace oculta en la selva. Great Pyramid of Cholula. Coordinates: The Great Pyramid of Cholula, also known as Tlachihualtepetl (Nahuatl for "artificial mountain"), is a huge complex located in Cholula, Puebla, Mexico.
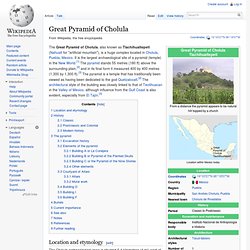
It is the largest archaeological site of a pyramid (temple) in the New World.[1] The pyramid stands 55 metres (180 ft) above the surrounding plain,[2] and in its final form it measured 400 by 400 metres (1,300 by 1,300 ft).[3] The pyramid is a temple that has traditionally been viewed as having been dedicated to the god Quetzalcoatl.[2] The architectural style of the building was closely linked to that of Teotihuacan in the Valley of Mexico, although influence from the Gulf Coast is also evident, especially from El Tajín.[3] Location and etymology[edit] The Cholula archaeological zone is situated 6.4 kilometres (4 mi) west of the city of Puebla,[4] in the city of Cholula.
The name cholula has its origin in the ancient Nahuatl word cholollan, which means "place of refuge".[4] Red Pyramid. The Red Pyramid was not always red.
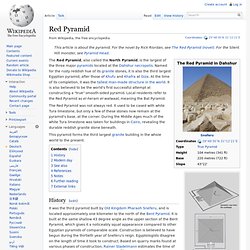
It used to be cased with white Tura limestone, but only a few of these stones now remain at the pyramid's base, at the corner. Bent Pyramid. The Bent Pyramid is an ancient Egyptian pyramid located at the royal necropolis of Dahshur , approximately 40 kilometres south of Cairo , built under the Old Kingdom Pharaoh Sneferu (c. 2600 BC).
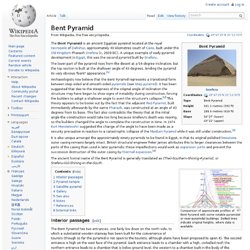
A unique example of early pyramid development in Egypt , this was the second pyramid built by Sneferu . The lower part of the pyramid rises from the desert at a 54-degree inclination, but the top section is built at the shallower angle of 43 degrees, lending the pyramid its very obvious "bent" appearance. [ 1 ] Pyramid of the Sun. Bosnian pyramids. Coordinates: The Bosnian pyramids are a pseudo-archaeological[1] claim promoted by author Semir Osmanagić, that a cluster of natural hills in central Bosnia and Herzegovina are the largest human-made ancient pyramids on Earth.
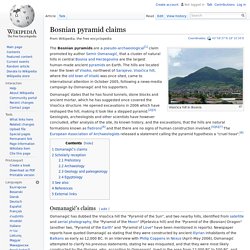
The hills are located near the town of Visoko, northwest of Sarajevo. Visočica hill, where the old town of Visoki was once sited, came to international attention in October 2005, following a news-media campaign by Osmanagić and his supporters. Osmanagić's claims[edit] According to Osmanagić, the excavation has produced evidence of building blocks as well as tunnels. Pyramid of the Moon. Obelisk. Caesarea obelisk. Cleopatra's Needle. Cleopatra's Needle, Central Park, New York Cleopatra's Needle is the popular name for each of three Ancient Egyptian obelisks re-erected in London , Paris , and New York City during the nineteenth century. The London and New York ones are a pair, while the Paris one comes from a different original site, Luxor , where its twin remains.
Although the needles are genuine Ancient Egyptian obelisks, they are somewhat misnamed as they have no particular connection with Queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt, and were already over a thousand years old in her lifetime. The London "needle" is one such example, as it was originally made during the reign of the 18th Dynasty Pharaoh Thutmose III but was falsely named "Cleopatra's needle". Heliopolis (ancient) The Al-Masalla obelisk , the largest surviving monument from Heliopolis Heliopolis ( / h i l i ˈ ɒ p ɵ l ʌ s / ; Ancient Greek : Ἡλιούπολις , "City of the Sun" or "City of Helios "; Egyptian : ỉwnw ; Arabic : عين شمس , Ain Shams , "Eye of the Sun") was one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt , the capital of the 13th Lower Egyptian nome that was located five miles (8 km) east of the Nile to the north of the apex of the Nile Delta .
Heliopolis has been occupied since the Predynastic Period , [ 1 ] with extensive building campaigns during the Old and Middle Kingdoms . Today it is mostly destroyed; its temples and other buildings were used for the construction of medieval Cairo . Most information about the ancient city comes from textual sources. Beneath a maze of busy narrow streets of a middle and lower-class district, lie vast hidden remains of ancient Heliopolis about fifteen to twenty metres down. Unfinished obelisk. Coordinates : The unfinished obelisk in its quarry at Aswan, 1990 The unfinished obelisk of Assuan The unfinished obelisk is the largest known ancient obelisk and is located in the northern region of the stone quarries of ancient Egypt in Aswan (Assuan), Egypt . Archaeologists claim the pharaoh known as Hatshepsut sanctioned its construction.
It is nearly one third larger than any ancient Egyptian obelisk ever erected. Luxor Temple. Statue at Temple Entrance To the rear of the temple are chapels built by Tuthmosis III, and Alexander. During the Roman era, the temple and its surroundings were a legionary fortress and the home of the Roman government in the area. Construction[edit] The original two obelisks, as seen in 1832. Luxor Obelisk. King Ezana's Stele. Saint Peter's Square.
Saint Peter's Square ( Italian : Piazza San Pietro , Latin : Forum Sancti Petri , pronounced [ˌpi̯aʦa san ˈpi̯ɛːtɾo] ) is a massive plaza located directly in front of St. Hippodrome. Obélisque d'Arles. The Obélisque d'Arles ("Arles Obelisk") is a 4th-century Roman obelisk , erected in the center of the Place de la République , in front of the town hall of Arles , France . Description [ edit ] The obelisk is made of red granite from Asia Minor . [ 2 ] It does not feature any inscription. Its height together with its pedestal is approximately 20 m. History [ edit ] Moai. Stone spheres of Costa Rica. “Imagen Cósmica”, a work on ancient mysticism, Costa Rican Art Museum, San José, Costa Rica, sculpture of Jorge Jiménez Deredia Pre-Columbian stone sphere, located at the University of Costa Rica as a symbol of tradition and ancient wisdom. The stone spheres (or stone balls) of Costa Rica are an assortment of over three hundred petrospheres in Costa Rica, located on the Diquís Delta and on Isla del Caño.
Locally, they are known as Las Bolas (literally The Balls). Rhind Mathematical Papyrus. Sphinx of Taharqo. Younger Memnon. Gilgamesh flood myth. Phobos monolith. Antikythera mechanism. Archimedes' screw. Rosetta Stone. Parthenon.