

The Origin of the Solar System. The Origin of theSolar System The Nebular Hypothesis in its original form was proposed by Kant and Laplace in the 18th century.
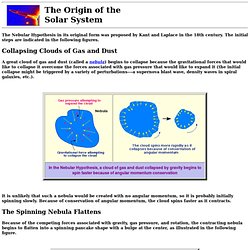
The initial steps are indicated in the following figures. Collapsing Clouds of Gas and Dust It is unlikely that such a nebula would be created with no angular momentum, so it is probably initially spinning slowly. Internet / websites - Harvard citation style - Guides at University of Western Australia. From Big Bang to Man (Cassiopeia Project)
Logarithmic timeline. A logarithmic timeline is a timeline laid out according to a logarithmic scale.
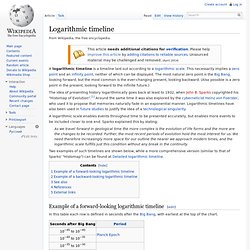
This necessarily implies a zero point and an infinity point, neither of which can be displayed. The most natural zero point is the Big Bang, looking forward, but the most common is the ever-changing present, looking backward. (Also possible is a zero point in the present, looking forward to the infinite future.) The idea of presenting history logarithmically goes back at least to 1932, when John B. Sparks copyrighted his "Histomap of Evolution".[1] Around the same time it was also explored by the cyberneticist Heinz von Foerster, who used it to propose that memories naturally fade in an exponential manner. A logarithmic scale enables events throughout time to be presented accurately, but enables more events to be included closer to one end. Fundamental Forces. Technological singularity. Hypothetical point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible The technological singularity—also, simply, the singularity[1]—is a hypothetical point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization.[2][3] According to the most popular version of the singularity hypothesis, called intelligence explosion, an upgradable intelligent agent will eventually enter a "runaway reaction" of self-improvement cycles, each new and more intelligent generation appearing more and more rapidly, causing an "explosion" in intelligence and resulting in a powerful superintelligence that qualitatively far surpasses all human intelligence.
I. J. Good's "intelligence explosion" model predicts that a future superintelligence will trigger a singularity.[7] Four polls of AI researchers, conducted in 2012 and 2013 by Nick Bostrom and Vincent C. Background[edit] Intelligence explosion[edit] I. ... Forecasting the Growth of Complexity and Change. Forecasting the Growth of Complexity and Change Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 69, No 4, 2002 In the spirit of punctuated equilibrium, complexity is quantified relatively in terms of the spacing between equally important evolutionary turning points (milestones).

Thirteen data sets of such milestones, obtained from a variety of scientific sources, provide data on the most important complexity jumps between the big bang and today. Forecasts for future complexity jumps are obtained via exponential and logistic fits on the data. The quality of the fits and common sense dictate that the forecast by the logistic function should be retained. 1. Change has always been an integral feature of life.
The accelerating amount of change in technology, medicine, information exchange, and other social aspects of our life, is familiar to everyone. What will happen if change continues at an accelerating rate? 2. Change is linked to complexity. Complexity § Complexity links to connectivity. 1. Cosmological Models.
Predictions. Astronomy. Evolution. Neuronal Connections and the Mind - The Connectome. In the age of computers and the Internet one of the most appealing theories of how mind is generated from the neurons of the brain is by the computation of large networks of connecting neurons.
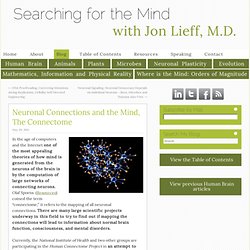
Olaf Sporns (Resources) coined the term “connectome;” it refers to the mapping of all neuronal connections. There are many large scientific projects underway in this field to try to find out if mapping the connections will lead to information about normal brain function, consciousness, and mental disorders. Currently, the National Institute of Health and two other groups are participating in the Human Connectome Project in an attempt to map all neuron connections in the human brain. One group consisting of UCLA and Harvard (MGH) has built the next generation MRI imaging device to visualize tracts of axons.
Source: This is actually an extremely difficult quest. Monumental Complexity In a human fetus, almost a trillion neurons are produced. Important Theoretical Issues Positive Connection Results. How many neurons make a human brain? Billions fewer than we thought. How many neurons are there in the human brain?
It was a question that scientists thought they had nailed – and the answer was 100bn (give or take). If you went looking you would find that figure repeated widely in the neuroscience literature and beyond. But when a researcher in Brazil called Dr Suzana Herculano-Houzel started digging, she discovered that no one in the field could actually remember where the 100bn figure had come from – let alone how it had been arrived at. So she set about discovering the true figure (HT to the excellent Nature neuroscience podcast NeuroPod). This involved a remarkable – and to some I suspect unsettling – piece of research.
"It took me a couple of months to make peace with this idea that I was going to take somebody's brain or an animal's brain and turn it into soup," she told Nature. She told me that so far, she has only looked at four brains, all of them from men.