

Google Search Quality Rating General Guidelines July 27, 2017. How Google measures the authority of web pages. Official Google Webmaster Central Blog: Mobile-first Indexing. Today, most people are searching on Google using a mobile device.
However, our ranking systems still typically look at the desktop version of a page’s content to evaluate its relevance to the user. This can cause issues when the mobile page has less content than the desktop page because our algorithms are not evaluating the actual page that is seen by a mobile searcher. The Periodic Table Of SEO Success Factors. Ranking Factors 2015: Understand how the deck is stacked. The Myth of Google's 200 Ranking Factors. Did Google's Fred update hit low-value content sites that focus on revenue, not users?
HTTPS Required for Collecting Sensitive Information in Chrome as of January 2017 - Search Engine Journal. Google has cautioned site owners that, at the end of January 2017, Chrome will mark sites without HTTPS as non-secure if they collect sensitive information like passwords and credit cards.
“Enabling HTTPS on your whole site is important, but if your site collects passwords, payment info, or any other personal information, it’s critical to use HTTPS.” From the sounds of it, if a website collects sensitive information on any of its pages, the entire site will be marked as non-secure. Therefore, sitewide HTTPS is necessary for a site to be marked secure, even if only one page collects personal data. Without HTTPS, sensitive information can be stolen, which is why Google has been championing the use of HTTPS across the web with its #NoHacked campaign.
Newly-granted Google patent sheds light on how the search engine sees entities. June 2016 Google Webmaster Report: Mobile Friendly, Penguin, Search Console & More. Official Google Webmaster Central Blog: Penguin is now part of our core algorithm. Google's algorithms rely on more than 200 unique signals or "clues" that make it possible to surface what you might be looking for.
These signals include things like the specific words that appear on websites, the freshness of content, your region and PageRank. One specific signal of the algorithms is called Penguin, which was first launched in 2012 and today has an update. After a period of development and testing, we are now rolling out an update to the Penguin algorithm in all languages. Here are the key changes you'll see, which were also among webmasters' top requests to us:Penguin is now real-time. Everything you need to know about Google's 'Possum' algorithm update. Penguin 4.0 is finally here, Google confirms. After a couple of years waiting, and various algorithm fluctuations described as ‘normal turbulence’, Google has finally confirmed today that its Penguin algorithm update is rolling out in all languages.
The last update in 2014 – Penguin 3.0 – may have only affected less than 1% of US/UK searches, but that ultimately translated to 12 billion queries. Here we’ll detail all the changes you can expect from Penguin 4.0 according to Google’s blog post. But first a little refresher… What is Penguin? According to Adam Stetzer in his post on the delayed Penguin update, Google first launched the Penguin update in April 2012 to catch sites spamming the search results. FAQ: All About The New Google RankBrain Algorithm. The four pillars of the future of SEO. Google Penguin explained. Joost de Valk Joost de Valk is the founder and Chief Product Officer of Yoast.
He's a digital marketer, developer and an Open Source fanatic. One of the most painful Google updates that can hit a website is called Penguin. Google Penguin aims to remove sites from the search results that have been trying to game Google by buying or otherwise “unnaturally acquiring” links to their website. Search Engine Land's Guide to Google Hummingbird. SEO Basics: How Google Determines Search Engine Results. When it comes to SEO the question everybody wants an answer to is how does Google determine their search engine results?
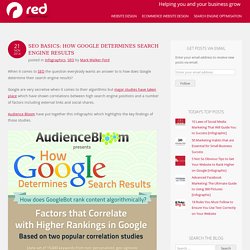
Google are very secretive when it comes to their algorithms but major studies have taken place which have shown correlations between high search engine positions and a number of factors including external links and social shares. Audience Bloom have put together this infographic which highlights the key findings of those studies. Share with your followers: Related. Google Toolbar PageRank Is Now Officially Dead. On Monday, March 7 2016, Google officially killed off Toolbar PageRank scores to the few browser tools and web site tools that use it.
The 0 to 10 PageRank score that was heavily used by SEOs and webmasters in the early 2000s will be completely unavailable to all within two weeks. Google told me it takes time for all the servers to completely remove the score. So technically, March 7th was the last Google Toolbar PageRank update, which essentially removed the data used by external tools. I covered this at Search Engine Land yesterday afternoon. If you are using tools now to check PageRank, which I doubt, they will stop working within a couple weeks.
10 Signs Google PageRank is Dead...to Non-Googlers. I keep seeing the same question posted over and over, “Is Google PageRank Dead?”
My thoughts are yes and no. Yes, it’s dead to those outside of Google. No, it’s not dead to Googlers (people who work at Google). In other words, I still think Google uses PageRank as a part of their organic ranking algorithm. Understanding Google Panda: Definitive Algo Guide for SEOs. Note: We have many brand new quotes about Panda from Google attributed to a “Google Spokesperson.”
These are all quotes given directly to the author and The SEM Post by Google. All other Google quotes are cited to their sources. Google Panda is one of Google’s ranking filters that seeks to downrank pages that are considered low quality, which results in sites with higher quality and valuable content to rise higher in the search results. But it is easily one of the most misunderstood algos. Google Panda Is Now Part Of Google's Core Ranking Signals. FAQ: All About The New Google "Hummingbird" Algorithm. How To Prep For The Pending Penguin Update & Ensure You're Penalty Free In 2016.