

LOREM: Skills self-assessment for MOOC (pre) The Learning Online: Reflection, Engagement and Motivation (LOREM) self-assessment and resources have been developed to help you identify strategies you may need to put in place to get the most out of this MOOC.

Students who are aware of their strengths and weaknesses are more likely to stay engaged and motivated and more likely to complete the course. Once you enter the self-assessment tool, you will be asked to rate your confidence across the range of skills we have identified as being characteristic of successful online learners. You will receive automatic feedback and a list of resources for you to develop these skills both before and during the course. At the end of the MOOC you will have an opportunity to reflect on your skills development in a post-MOOC skills self-assessment. The self-assessment will take approximately ten minutes to complete. This self-assessment is in a secure Qualtrics account. DigiLit Leicester. Interested in finding out more about any of the Digital Literacy framework areas?
We’ve collected links to information and resources related to each strand to help you take your practice to the next level! Finding, Evaluating and Organising Creating and Sharing Assessment and Feedback Communication, Collaboration and Participation E-Safety and Online Identity Technology supported Professional Development Resources have also been created as part of a number of the BSF ICT Innovation projects that have run over the last two years: Innovation Project Resources.
Developing students' digital literacy. The issue Even today’s students need support with some areas of digital practice, particularly in an academic context, so it’s important to make sure that these needs are met.
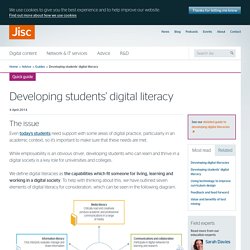
While employability is an obvious driver, developing students who can learn and thrive in a digital society is a key role for universities and colleges. We define digital literacies as the capabilities which fit someone for living, learning and working in a digital society. To help with thinking about this, we have outlined seven elements of digital literacy for consideration, which can be seen in the following diagram. What you can do Below, we've summarised some of the steps you can take to improve your students' digital literacy. Review your support for digital literacies An audit is a good way of finding out who’s already working in this area and starting productive conversations with staff. Link to other key priorities Create a buzz In any large organisation there will be all sorts of interesting digital practice.
Transforming the Way We Learn: Why Digital Literacy is So Important » K12 - Learning Liftoff - Free Parenting, Education, and Homeschooling Resources. Digital literacy is less about tools and more about thinking… When we talk about language literacy, we are discussing much more than the basic ability to recognize words on a page.
True literacy extends beyond the ability to read and encompasses the skills needed to gain meaning and knowledge from the written word, to think critically, and to write clearly. Likewise, digital literacy is more than simply knowing how to use digital tools. It is the ability to locate, organize, understand, evaluate, and analyze information using digital technology.
It’s also about knowing what to share and who to share it with. In other words, it is less about tools and more about thinking. The 5 Resources Model of Critical Digital Literacy. The 5 Resources Model provides a framework to articulate the scope and dimensions of digital literacies.

It is based on an established model of literacy which is underpinned by critical perspectives (the Four Resources Model of Critical Literacy, after Luke & Freebody). It has been adapted for the digital context. The model has been developed to encompass the varied perceptions and meanings attributed to digital literacy. On the one hand some stakeholders put a strong focus on ICT, i.e. the skills involved in using computers, software and digitally enabled devices; others emphasise the social and interpersonal, creative and communicative skills highlighted by social media and Web 2.0; there are also critical and intellectual approaches associated with the term digital scholarship.
Different stakeholders tend to emphasise different skillsets. What you will find on this site. Exploring Digital Literacies Workshop Pack - The 5 Resources Model of Critical Digital Literacy.