

Flamenco. Flamenco (Spanish pronunciation: [flaˈmeŋko]) is a form of Spanish folk music and dance from the region of Andalusia in southern Spain.
It includes cante (singing), toque (guitar playing), baile (dance) and palmas (handclaps). First mentioned in literature in 1774, the genre grew out of Andalusian and Romani music and dance styles.[1][2][3] Flamenco is often associated with the Romani people of Spain (Gitanos) and a number of famous flamenco artists are of this ethnicity. Flamenco was first recorded in the late 18th century but the genre underwent a dramatic development in the late 19th century.[4] New Flamenco. Traditional flamenco had been displaced in Spain in the 1950s and 1960s by rock-and-roll.[4] Artists such as Camarón de la Isla worked with the music during that period, infusing it with new sound.
Jesse Cook. Life and career[edit] After his parents separated, Cook and his sister accompanied his mother to her birth country, Canada.
Recognizing the musical aptitude of her son, Cook's mother arranged for him to take lessons at Toronto’s Eli Kassner Guitar Academy. Rumba. Flamenco rumba, also called rumba flamenca, rumba gitana, gypsy rumba, Spanish rumba or, simply, rumba (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈrumba]), is a style of flamenco music from Spain.
It is known as one of the ida y vuelta (return songs), music which diverged in the new world, then returned to Spain in a new form.[1] In Cuba (before returning to Spain in the 1850s), the music was performed with percussion instruments.[1] The dance that it accompanied was improvised with prominent hip and shoulder movements, more overtly sexual than other styles of flamenco dances.[1] Gipsy Kings. The Gipsy Kings is a group of musicians from Arles and Montpellier in the south of France who perform in Spanish with an Andalusian accent.
Although group members were born in France, their parents were mostly gitanos, Spanish Romani people who fled Catalonia during the 1930s Spanish Civil War. Chico Bouchikhi is of Moroccan and Algerian descent. They are known for bringing rumba catalana, a pop-oriented music distantly derived from traditional flamenco music, to worldwide audiences. Jazz. The 1950s saw the emergence of free jazz, which explored playing without regular meter, beat and formal structures, and in the mid-1950s, hard bop, which introduced influences from rhythm and blues, gospel music, and blues, especially in the saxophone and piano playing.
Modal jazz developed in the late 1950s, using the mode, or musical scale, as the basis of musical structure and improvisation. Jazz-rock fusion appeared in the late 1960s and early 1970s, combining jazz improvisation with rock rhythms, electric instruments and the highly amplified stage sound of rock. In the early 1980s, a commercial form of jazz fusion called smooth jazz became successful, garnering significant radio airplay. Blues. Blues as a genre is based on the blues form but possesses other characteristics such as lyrics, bass lines, and instruments.
Blues sub-genres include country blues, such as Delta, Piedmont and Texas blues, and urban blues styles such as Chicago and West Coast blues. World War II marked the transition from acoustic to electric blues and the progressive opening of blues music to a wider audience, especially white listeners. Hugh Laurie. Soundtrack. 16 mm film showing a "variable area" sound track at right A soundtrack can be recorded music accompanying and synchronized to the images of a motion picture, book, television program or video game; a commercially released soundtrack album of music as featured in the soundtrack of a film or TV show; or the physical area of a film that contains the synchronized recorded sound.
Howard Shore. John Williams. Other notable works by Williams include theme music for four Olympic Games, NBC Sunday Night Football, the NBC Nightly News, the Statue of Liberty's rededication, the television series Lost in Space and Land of the Giants, and the original, not as well known calypso-based theme song to Gilligan's Island.
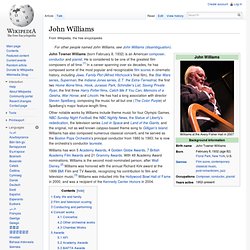
Williams has also composed numerous classical concerti, and he served as the Boston Pops Orchestra's principal conductor from 1980 to 1993; he is now the orchestra's conductor laureate. Williams has won 5 Academy Awards, 4 Golden Globe Awards, 7 British Academy Film Awards and 21 Grammy Awards. With 49 Academy Award nominations, Williams is the second most-nominated person, after Walt Disney.[2] Williams was honored with the annual Richard Kirk award at the 1999 BMI Film and TV Awards, recognizing his contribution to film and television music.[3] Williams was inducted into the Hollywood Bowl Hall of Fame in 2000, and was a recipient of the Kennedy Center Honors in 2004. Phil Collins.
Mychael Danna. Life and career[edit] He studied music composition at the University of Toronto, winning the Glenn Gould Composition Scholarship in 1985.
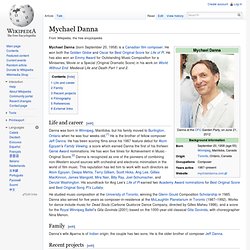
Danna also served for five years as composer-in-residence at the McLaughlin Planetarium in Toronto (1987–1992). Works for dance include music for Dead Souls (Carbone Quatorze Dance Company, directed by Gilles Maheu 1996), and a score for the Royal Winnipeg Ballet's Gita Govinda (2001) based on the 1000-year-old classical Gita Govinda, with choreographer Nina Menon. Family[edit] Danna's wife Aparna is of Indian origin; the couple has two sons. Kenji Kawai. Career[edit] Description of selected albums[edit] Ghost in the Shell (1995)[edit] Avalon[edit] Ghost in the Shell – Innocence[edit] Following on from Ghost in the Shell, the score again makes use of female vocals and percussion, though featuring a different melody.
Vampire Princess Miyu – TV OST[edit] This CD includes 34 tracks. Hans Zimmer. Danny Elfman. Early life and career[edit] Danny Elfman was born in Los Angeles, California, the son of Blossom Elfman (née Bernstein), a writer and teacher, and Milton Elfman, a teacher who was in the Air Force.[5] Elfman grew up in a Jewish family.[6] He was raised in a racially mixed community in the Baldwin Hills area of Los Angeles.[7] He spent much of his time in the local movie theatre, adoring the music of such film composers as Bernard Herrmann and Franz Waxman. Stating that he hung out with the "band geeks" in high school, he started a ska band. After dropping out of high school, he followed his brother Richard to France,[8] where he performed with Le Grand Magic Circus, an avant-garde musical theater group. Violin in tow, Elfman next journeyed to Africa where he traveled through Ghana, Mali, and Upper Volta, absorbing new musical styles, including the Ghanaian highlife genre which would eventually influence his own music.
[citation needed] Rock. Rock music is a genre of popular music that originated as "rock and roll" in the United States in the 1950s, and developed into a range of different styles in the 1960s and later, particularly in the United Kingdom and the United States.[1][2] It has its roots in 1940s' and 1950s' rock and roll, itself heavily influenced by rhythm and blues and country music. Rock music also drew strongly on a number of other genres such as blues and folk, and incorporated influences from jazz, classical and other musical sources.
By the late 1960s, referred to as the "golden age"[3] or "classic rock"[1] period, a number of distinct rock music sub-genres had emerged, including hybrids like blues rock, folk rock, country rock, and jazz-rock fusion, many of which contributed to the development of psychedelic rock, which was influenced by the countercultural psychedelic scene. Characteristics[edit] A simple 4/4 drum pattern common in rock music Play. Soda Stereo. Soda Stereo were an Argentine rock band formed in Uruguay in 1982, considered by critics to be the most important and influential Iberoamerican band of all time.[2][3][4][5][6][7] This power trio made up of Gustavo Cerati (lead vocals, guitars) Héctor "Zeta" Bosio (bass, backing vocals), and Charly Alberti (drums, percussion) achieved international success throughout the 1980s and 1990s. Soda Stereo were the first Latin rock group to achieve success throughout South and Central America.
They helped popularize Rock en Español, Ibero-American Rock, and Latin Rock genres to a mainstream audience. The band established what would become the template for many other popular Spanish-speaking rock music groups. History[edit] Formation and early years: From "Los Estereotipos" to Soda Stereo (1982-1984)[edit] In the summer of 1982 Gustavo Cerati at 22 years of age and Hector Zeta Bosio at 23 years of age collided at Punta del Este, Uruguay. The Beatles. The Beatles were an English rock band that formed in Liverpool, in 1960. With John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr, they became widely regarded as the greatest and most influential act of the rock era.[1] Rooted in skiffle, beat and 1950s rock and roll, the Beatles later experimented with several genres, ranging from pop ballads to psychedelic and hard rock, often incorporating classical elements in innovative ways.
In the early 1960s, their enormous popularity first emerged as "Beatlemania", but as their songwriting grew in sophistication they came to be perceived as an embodiment of the ideals shared by the era's sociocultural revolutions. History. Queen. Héroes del Silencio. Vocal. Vocal music is a genre of music performed by one or more singers, with or without instrumental accompaniment, in which singing (i.e. vocal performance) provides the main focus of the piece.[1] Music which employs singing but does not feature it prominently is generally considered instrumental music (e.g. the wordless women's choir in the final movement of Holst's The Planets) as is music without singing.
Music without any non-vocal instrumental accompaniment is referred to as a cappella.[2] Christopher Tin. Christopher Tin (Chinese: 田志仁) is an American composer whose work is primarily classical with a world music influence. He is a composer for films, video games, and commercials and has won two Grammy Awards for his classical crossover album, Calling All Dawns. Tin is best known for his composition "Baba Yetu", featured in the 2005 computer game Civilization IV. Reggae. Reggae is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. Bobby McFerrin. Robert Keith "Bobby" McFerrin, Jr. (born March 11, 1950) is an American vocalist and conductor.
He is best known for his 1988 hit song "Don't Worry, Be Happy". He is a ten-time Grammy Award winner. Folk. Folk music includes both traditional music and the genre that evolved from it during the 20th century folk revival. The term originated in the 19th century but is often applied to music that is older than that. Hawaiian. Israel Kamakawiwoʻole. Israel "Iz" Kaʻanoʻi Kamakawiwoʻole (Hawaiian pronunciation: [kəˌmɐkəˌvivoˈʔole]) translation: "The Fearless Eyed"; May 20, 1959 – June 26, 1997), also called Bruddah Iz (Brother Iz), was a Hawaiian musician.
Pop. Tracy Chapman. Early life Chapman was born in Cleveland, Ohio. Alberto Plaza. Shakira. Michael Jackson. Amaia Montero. Ana Torroja. Miguel Bosé. La Oreja de Van Gogh. Mecano. Sting. Phil Collins. Electronic. Jean Michel Jarre. Daft Punk. Instrumental. Vangelis. Enya. Loreena McKennitt. Adiemus.