

Mikhail Bulgakov. Mikhaíl Afanasyevich Bulgakov (Russian: Михаи́л Афана́сьевич Булга́ков, pronounced [mʲɪxɐˈiɫ ɐfɐˈnasʲjɪvʲɪt͡ɕ bʊɫˈɡakəf]; May 15 [O.S.
May 3] 1891 – March 10, 1940) was a Soviet writer and playwright active in the first half of the 20th century.[1] He is best known for his novel The Master and Margarita, which has been called one of the masterpieces of the 20th century.[3] Life and work[edit] Early life[edit] Mikhail Bulgakov was born on May 15, 1891, in Kiev, at that time in the Russian Empire. He was one of seven children (the oldest of three brothers) of Afanasiy Bulgakov, an assistant professor at the Kiev Theological Academy, and Varvara Mikhailovna, a former teacher. In 1901 Bulgakov joined the First Kiev Gymnasium, where he developed an interest in Russian and European literature (his favourite authors at the time being Gogol, Pushkin, Dostoyevsky, Saltykov-Shchedrin, and Dickens), theatre and opera.
In 1913, Bulgakov married Tatiana Lappa. Career[edit] Bulgakov, 1930 or earlier. Carlos Castaneda's don Juan's Teachings. Jyotiṣa. Jyotisha (or Jyotish from Sanskrit jyotiṣa, from jyótis- "light, heavenly body") is the traditional Hindu system of astronomy and astrology.
It is also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology, and more recently Vedic astrology. The term Hindu astrology has been in use as the English equivalent of Jyotiṣa since the early 19th century, whereasVedic astrology is a relatively recent term, entering common usage in the 1980s with self-help publications on Āyurveda or Yoga. Vedanga Jyotisha are one of the earliest writings about astrology and astronomy within Vedas.[1][2][3] Historical documentation suggests horoscopic astrology in the Indian subcontinent was a Hellenic influence post-dating the Vedic period.[4] It has been divided into three main branches:[5] Astrology has been debated in India.
History[edit] The foundation of Hindu astrology is the notion of bandhu of the Vedas, (scriptures), which is the connection between the microcosm and the macrocosm. Modern India[edit] Jainism. Jainism (/ˈdʒeɪnɪzəm/[1] or /ˈdʒaɪnɪzəm/[2]), traditionally known as Jin Sashana or Jain dharma (Sanskrit: जैन धर्म), is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of nonviolence (ahimsa) towards all living beings.
Practitioners believe that nonviolence and self-control are the means by which they can obtain liberation. The three main principles of Jainism are non-violence (ahimsa), non-absolutism (anekantavada) and non-possessiveness (aparigraha). Followers of Jainism take 5 major vows: non-violence, non-lying, non-stealing, chastity, and non-attachment. Asceticism is thus a major focus of the Jain faith. Jainism is derived from the word Jina (conqueror) referring to a human being who has conquered inner enemies like attachment, desire, anger, pride, greed, etc. and possesses infinite knowledge (Kevala Jnana). Doctrine[edit] Non-violence (ahimsa)[edit] The hand with a wheel on the palm symbolizes Ahimsa (nonviolence). Non-absolutism[edit] Main article: Anekantavada Non-possessiveness[edit] Writing system.
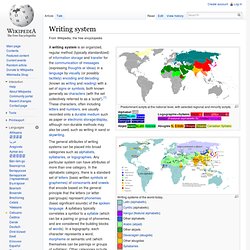
Writing systems of the world today.
Other alphabets Other abjads Other abugidas General properties[edit] Chinese characters (漢字) are morpho-syllabic. Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that a writing system is always associated with at least a spoken language. Every human community possesses language, which many regard as an innate and defining condition of mankind. All writing systems require: Basic terminology[edit] In the examination of individual scripts, the study of writing systems has developed along partially independent lines. A grapheme is a specific base unit of a writing system.
An individual grapheme may be represented in a wide variety of ways, where each variation is visually distinct in some regard, but all are interpreted as representing the "same" grapheme. Writing systems are conceptual systems, as are the languages to which they refer. History[edit] Functional classification[edit] Timeline of United States inventions - Wikipedia, the free encyc.